Abstract
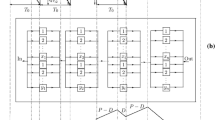
In remanufacturing industries, inventory is significant because remanufacturing industries includes the stock of recycled products, stock of components (parts) after disassembly and refurbishing operation, stock of new parts purchased from manufacturers and stock of remanufactured products. Therefore, current research presents an approach to search an appropriate inventory policy for single product with multi-components for a third party remanufacturing company cooperated with the original equipment manufacturer (OEM). The third party for remanufacturing working in close cooperation with the OEM (such as dealer) can acquire the regional protection rules and can gain the technical support from the OEM. A general mathematical model is developed to describe the multiple components and multi-level inventory. Moreover, a case company problem is solved to validate the proposed model. Base on considered problem, the proposed model provided an efficient inventory management method to solve the situation in which remanufacturing company only recycled products but not components (parts). Furthermore, the presented model is significant to help the case company to set the best resource allocation by analyzing the impact on inventory policy from different replenishment quantities in remanufacturing process (recycling, disassembling and refurbishing). At last the proposed model is proved by a numerical experiment which used genetic algorithm (GA) to solve the inventory policy, and the result discusses the sensitivity analysis for model parameters in different replenishment quantities scenarios.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alinovi, A., Bottani, E., & Montanari, R. (2012). Reverse logistics: A stochastic EOQ-based inventory control model for mixed manufacturing/remanufacturing systems with return policies. International Journal of Production Research, 50(5), 1243–1264. doi:10.1080/00207543.2011.571921.
Bulmus, S. C., Zhu, S. X., & Teunter, R. (2014). Competition for cores in remanufacturing. European Journal of Operational Research, 233(1), 105–113. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2013.08.025.
Chen, J.-M., & Chang, C.-I. (2012). The co-opetitive strategy of a closed-loop supply chain with remanufacturing. Transportation Research Part E-Logistics and Transportation Review, 48(2), 387–400. doi:10.1016/j.tre.2011.10.001.
Corum, A., Vayvay, O., & Bayraktar, E. (2014). The impact of remanufacturing on total inventory cost and order variance. Journal of Cleaner Production, 85, 442–452. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.06.024.
Fathi, M., Zandi, F., & Jouini, O. (2015). Modeling the merging capacity for two streams of product returns in remanufacturing systems. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 37, 265–276. doi:10.1016/j.jmsy.2014.08.006.
Fleischmann, M., BloemhofRuwaard, J. M., Dekker, R., vanderLaan, E., vanNunen, J., & VanWassenhove, L. N. (1997). Quantitative models for reverse logistics: A review. European Journal of Operational Research, 103(1), 1–17. doi:10.1016/s0377-2217(97)00230-0.
Guide, V. D. R, Jr. (2000). Production planning and control for remanufacturing: Industry practice and research needs. Journal of Operations Management, 18(4), 467–483. doi:10.1016/S0272-6963(00)00034-6.
Guide, V. D. R, Jr., Jayaraman, V., & Srivastava, R. (1999). Production planning and control for remanufacturing: A state-of-the-art survey. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 15(3), 221–230. doi:10.1016/S0736-5845(99)00020-4.
Guo, J., & Ya, G. (2015). Optimal strategies for manufacturing/remanufacturing system with the consideration of recycled products. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 89, 226–234. doi:10.1016/j.cie.2014.11.020.
Hsu, V. N., Lee, C. Y., & So, K. C. (2006). Optimal component stocking policy for assemble-to-order systems with lead-time-dependent component and product pricing. Management Science, 52(3), 337–351. doi:10.1287/mnsc.1050.0438.
Jin, X. N., Hu, S. J., Ni, J., & Xiao, G. X. (2013). Assembly strategies for remanufacturing systems with variable quality returns. Ieee Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 10(1), 76–85. doi:10.1109/tase.2012.2217741.
Karaarslan, A. G., Kiesmueller, G. P., & de Kok, A. G. (2013). Analysis of an assemble-to-order system with different review periods. International Journal of Production Economics, 143(2), 335–341. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2011.11.030.
Kenne, J. P., Dejax, P., & Gharbi, A. (2012). Production planning of a hybrid manufacturing–remanufacturing system under uncertainty within a closed-loop supply chain. International Journal of Production Economics, 135(1), 81–93. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2010.10.026.
Li, M., & Liu, G. (2008). Return policy for used products in remanufacturing system. In: Proceedings of the 38th international conference on computers and industrial engineering (Vol. 1–3).
Lund, R. T. (1983). Remanufacturing: United States experience and implications for developing nations. Center for Policy Alternatives, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Lund, R. T. (1996). The Remanufacturing industry-hidden giant. Research Report, Manufacturing Engineering Department, Boston University.
Macedo, P. B., Alem, D., Santos, M., Junior, M. L., & Moreno, A. (2016). Hybrid manufacturing and remanufacturing lot-sizing problem with stochastic demand, return, and setup costs. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 82(5–8), 1241–1257. doi:10.1007/s00170-015-7445-z.
Mitra, S., & Webster, S. (2008). Competition in remanufacturing and the effects of government subsidies. International Journal of Production Economics, 111(2), 287–298. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2007.02.042.
Naeem, M. A., Dias, D. J., Tibrewal, R., Chang, P. C., & Tiwari, M. K. (2013). Production planning optimization for manufacturing and remanufacturing system in stochastic environment. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 24(4), 717–728. doi:10.1007/s10845-011-0619-0.
Shi, L., Sheng, Z., & Xu, F. (2015). The dynamics of competition in remanufacturing: A stability analysis. Economic Modelling, 50, 245–253. doi:10.1016/j.econmod.2015.07.002.
Takahashi, K., Doi, Y., Hirotani, D., & Morikawa, K. (2014). An adaptive pull strategy for remanufacturing systems. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 25(4), 629–645. doi:10.1007/s10845-012-0710-1.
Teunter, R. H., van der Laan, E., & Inderfurth, K. (2000). How to set the holding cost rates in average cost inventory models with reverse logistics? Omega-International Journal of Management Science, 28(4), 409–415. doi:10.1016/s0305-0483(99)00070-5.
van der Laan, E., Salomon, M., & Dekker, R. (1999). An investigation of lead-time effects in manufacturing/remanufacturing systems under simple PUSH and PULL control strategies. European Journal of Operational Research, 115(1), 195–214. doi:10.1016/s0377-2217(98)00108-8.
van der Laan, E. A., & Teunter, R. H. (2006). Simple heuristics for push and pull remanufacturing policies. European Journal of Operational Research, 175(2), 1084–1102. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2005.06.030.
Xiao, Y., Chen, J., & Lee, C.-Y. (2010). Optimal decisions for assemble-to-order systems with uncertain assembly capacity. International Journal of Production Economics, 123(1), 155–165. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2009.07.012.
Xu, X. L., Li, Y. J., & Cai, X. Q. (2012). Optimal policies in hybrid manufacturing/remanufacturing systems with random price-sensitive product returns. International Journal of Production Research, 50(23), 6978–6998. doi:10.1080/00207543.2011.640956.
Yazdian, S. A., Shahanaghi, K., & Makui, A. (2016). Joint optimisation of price, warranty and recovery planning in remanufacturing of used products under linear and non-linear demand, return and cost functions. International Journal of Systems Science, 47(5), 1155–1175. doi:10.1080/00207721.2014.915355.
Zied, H., Sofiene, D., & Nidhal, R. (2014). Joint optimisation of maintenance and production policies with subcontracting and product returns. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 25(3), 589–602. doi:10.1007/s10845-012-0707-9.
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by MOST (the Ministry of Science and Technology of China) under the Grants Nos. 2013AA040206, 2012BAF12B20, and 2012BAH08F04, and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants Nos. 51035001, 51121002 and 71131004), and National High Technology Research and Development Program of the P.R. China under Grant Nos. 2013AA040206
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Guan, Z., Zhang, L. et al. Inventory management for a remanufacture-to-order production with multi-components (parts). J Intell Manuf 30, 59–78 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-016-1232-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-016-1232-z