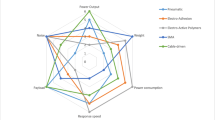
Abstract
Variable stiffness actuators (VSAs) are a new generation of robotic drives that are developed to enhance the robot’s ability to safely interact with unknown and dynamic environments. Furthermore, stiffness adjsutability can enhance energy efficiency in some particular applications, e.g. periodic motions with different frequencies. To adjust the stiffness, different mechanisms have been implemented in VSAs, each to fulfill the requirements of different applications with certain determinants. This paper explains these determinants and presents a comprehensive framework to systematically analyse performances of different stiffness adjustment mechanisms. First, a classification of different stiffness adjustment mechanisms is presented. Then, characteristics of each class regarding different determinants are evaluated and compared through numerical analysis. This will give additional insights into intrinsic pros and cons of different classes of stiffness adjustment mechanisms that enable a systematic future development of variable stiffness actuators and their applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaimo, S., Pollini, L., Bresciani, J.-P., Bülthoff, H.: Evaluation of direct and indirect haptic aiding in an obstacle avoidance task for tele-operated systems. In: Bittanti, S., A.C.S.Z. (eds.) Proceedings of the IARP/IEEE-RAS/EURON Workshop on Technical Challenges for Dependable Robots in Human Environments, pp 6472–6477. Max-Planck Gesellschaft, Curran, Red Hook (2011)
Albu-Schaffer, A., Bicchi, A., Boccadamo, G., Chatila, R., De Luca, A., De Santis, A., Giralt, G., Hirzinger, G., Lippiello, V., Mattone, R., et al.: Physical human–robot interaction in anthropic domains: safety and dependability. In: Proceedings of the 4th IARP/IEEE-RAS/EURON Workshop on Technical Challenges for Dependable Robots in Human Environments, T17-06, Nagoya (2005)
Albu-Schäffer, A., Haddadin, S., Ott, C., Stemmer, A., Wimböck, T., Hirzinger, G.: The dlr lightweight robot: design and control concepts for robots in human environments. Industrial Robot: An International Journal 34(5), 376–385 (2007)
Anderson, W., Eshghinejad, A., Azadegan, R., Cooper, C., Elahinia, M.: A variable stiffness transverse mode shape memory alloy actuator as a minimally invasive organ positioner. The European Physical Journal Special Topics 222(7), 1503–1518 (2013)
Berselli, G., Vertechy, R., Babic, M., Parenti Castelli, V.: Implementation of a variable stiffness actuato based on dielectric elastomers. In: 2012 ASME Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Inteligent Systems, pp. 19–21 (2012)
Beyl, P., Cherelle, P., Knaepen, K., Lefeber, D.: A proof-of-concept exoskeleton for robot-assisted rehabilitation of gait. In: Sloten, J., Verdonck, P., Nyssen, M., Haueisen, J. (eds.): IFMBE Proceedings of the 4th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering, vol. 22, pp. 1825–1829. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (2009)
Bicchi, A., Tonietti, G.: Fast and soft arm tactics: Dealing with the safety-performance trade-off in robot arms design and control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 11(2), 22–33 (2004)
Bureau, M., Keller, T., Perry, J., Velik, R., Veneman, J.: Variable stiffness structure for limb attachment. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), pp. 1–4 (2011)
Carloni, R., Visser, L., Stramigioli, S.: Variable stiffness actuators: A port-based power-flow analysis. IEEE Trans. Robot. 28(1), 1–11 (2012)
Carpi, F., DeRossi, D., Kornbluh, R., Pelrine, R., Sommer-Larsen, P.: Dielectric elastomers as electromechanical transducers. Fundamentals, materials, devices, models and applications of an emerging electroactive polymer technology. Elsevier Press, New York (2008)
Carpino, G., Dino, A., Sergi, F., Tagliamonte, N., Guglielmelli, E.: A novel compact torsional spring for series elastic actuators for assistive wearable robots. J. Mech. Des., 134(12) (2012)
Catalano, M., Grioli, G., Bonomo, F., Schiavi, R., Bicchi, A.: Vsa-hd: From the enumeration analysis to the prototypical implementation. In: 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 3676–3681 (2010)
Catalano, M., Grioli, G., Garabini, M., Bonomo, F., Mancinit, M., Tsagarakis, N., Bicchi, A.: Vsa-cubebot: A modular variable stiffness platform for multiple degrees of freedom robots. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 5090–5095 (2011)
Cherelle, P., Matthys, A., Grosu, V., Brackx, B., Van Damme, M., Vanderborght, B., Lefeber, D.: Design of the amp-foot 2.0: An active trans-tibial prosthesis that mimicks able-bodied ankle behavior. In: The 2nd Joint International Conference on Multibody System Dynamics (2012)
Choi, J., Hong, S., Lee, W., Kang, S., Kim, M.: A robot joint with variable stiffness using leaf springs. IEEE Trans. Robot. 27(2), 229–238 (2011)
Darden, F.: Conception and Realization of Pleated Pneumatic Artificial Muscles and their Use as Compliant Actuation Elements. PhD thesis, Vrije Universiteit Brussel (1999)
Dastoor, S., Cutkosky, M.: Variable impedance due to elecrromechanical coupling in electroactive polymer actuators. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Inteligent Robotics and Systems (IROS), pp. 774–779 (2011)
De Santis, A., Siciliano, B., De Luca, A., Bicchi, A.: An atlas of physical human?robot interaction. Mech. Mach. Theory 43(3), 253–270 (2008)
Eiberger, O., Haddadin, S., Weis, M., Albu-Schaeffer, A., Hirzinger, G.: On joint design with intrinsic variable compliance: derivation of the DLR QA-joint. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1687–1694 (2010)
Enoch, A., Sutas, A., Nakaoka, S., Vijayakumar, S.: BLUE: A Bipedal Robot with Variable Stiffness and Damping. In: Proc. 12th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Osaka, Japan (2012) (2012)
Fumagalli, M., Barrett, E., Stramigioli, S., Carloni, R.: The mvsa-ut: A miniaturized differential mechanism for a continuous rotational variable stiffness actuator. In: 2012 4th IEEE RAS EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), pp. 1943–1948 (2012)
Galloway, K.C.: Variable stiffness legs for robust, efficient, and stable dynamic running. Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics 5(1), 011009 (2013)
Garabini, M., Passaglia, A., Belo, F., Salaris, P., Bicchi, A.: Optimality principles in stiffness control: The vsa kick. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3341–3346. IEEE (2012)
Grebenstein, M., Chalon, M., Hirzinger, G., Siegwart, R.: Antagonistically driven finger design for the anthropomorphic dlr hand arm system. In: 2010 10th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), pp. 609–616. IEEE (2010)
Groothuis, S.S., Rusticelli, G., Zucchelli, A., Stramigioli, S., Carloni, R.: The vsaut-ii: A novel rotational variable stiffness actuator. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3355–3360 (2012)
Haddadin, S., Huber, F., Albu-Schaffer, A.: Optimal control for exploiting the natural dynamics of variable stiffness robots. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3347–3354. IEEE (2012)
Ham, R., Sugar, T., Vanderborght, B., Hollander, K., Lefeber, D.: Compliant actuator designs. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 16(3), 81–94 (2009)
Hogan, N.: Adaptive control of mechanical impedance by coactivation of antagonist muscles. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 29(8), 681–690 (1984)
Hollander, K., Sugar, T.: Concepts for compliant actuation in wearable robotic systems. In: Proceeding of US-Korea Conference on Science, Technology and Entrepreneurship (UKC04), vol. 128, pp. 644–650 (2004)
Hollander, K., Sugar, T., Herring, D.: Adjustable robotic tendon using a ‘jack spring’ trade. In: 9th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, 2005 (ICORR), pp. 113–118 (2005)
Hurst, J., Rizzi, A.: Series compliance for an efficient running gait. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 15(3), 42–51 (2008)
Hurst, J.W.: The Role and Implementation of Compliance in Legged Locomotion. PhD thesis, Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA (2008)
Hurst, J.W., Chestnutt, J.E., Rizzi, A.A.: The actuator with mechanically adjustable series compliance. IEEE Trans. Robot. 26(4), 597–606 (2010)
Hyun, D., Yang, H.S., Park, J., Shim, Y.: Variable stiffness mechanism for human-friendly robots. Mech. Mach. Theory 45(6), 880–897 (2010)
Jafari, A., Tsagarakis, N., Sardellitti, I., Caldwell, D.: How design can affect the energy required to regulate the stiffness in variable stiffness actuators. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2792–2797 (2012a)
Jafari, A., Tsagarakis, N., Vanderborght, B., Caldwell, D.: A novel actuator with adjustable stiffness (awas). In: 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 4201–4206 (2010)
Jafari, A., Tsagarakis, N.G., Sardellitti, I., Caldwell, D.G.: A new actuator with adjustable stiffness based on a variable ratio lever mechanism. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. PP(99), 1–9 (2012b)
Khatib, O.: Mobile manipulation: The robotic assistant. Robot. Auton. Syst. 26(2), 175–183 (1999)
Kim, B.-S., Song, J.-B.: Hybrid dual actuator unit: A design of a variable stiffness actuator based on an adjustable moment arm mechanism. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1655–1660 (2010)
Kim, B.-S., Song, J.-B.: Design and control of a variable stiffness actuator based on adjustable moment arm. IEEE Trans. Robot. 28(5), 1145–1151 (2012)
Leach, D., Gunther, F., Maheshwari, N., Iida, F.: Linear multi-modal actuation through discrete coupling. In: 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 2437–2442 (2012)
Li, Z., Tsagarakis, N., Caldwell, D.G.: A passivity based admittance control for stabilizing the compliant humanoid COMAN. In: IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Osaka, Japan, pp. 44–49 (2012)
Migliore, S., Brown, A., Deweerth, S.: Novel nonlinear actuators for passively controlling robotic joint compliance. J. Mech. Des. 129(4), 406–412 (2007)
Migliore, S., Brown, E., DeWeerth, S.: Biologically inspired joint stiffness control. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA 2005, pp. 4508–4513 (2005)
Morita, T., Sugano, S.: Development and evaluation of seven dof mia arm. In: Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, vol. 1, pp. 462–467 (1997)
Nakanishi, J.: Exploiting Passive Dynamics with Variable Stiffness Actuation in Robot Brachiation. In: IEEE Transaction on Mechatronics (2012)
Nam, K., Kim, B., Song, J.: Compliant actuation of parallel-type variable stiffness actuator based on antagonistic actuation. Journal of Mechanical Sceince and Technology 24(11), 2315–2321 (2010)
Pali, G., Berselli, C., Melchiori, C., Vasssura, G.: Desing of variable stiffness actuator based on flexures. Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics 3(3), 034501–034505 (2011)
Park, J.-J., Kim, H.-S., Song, J.-B.: Safe robot arm with safe joint mechanism using nonlinear spring system for collision safety. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA 2009, pp. 3371–3376 (2009)
Park, J.-J., Song, J.-B.: Safe joint mechanism using inclined link with springs for collision safety and positioning accuracy of a robot arm. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 813–818 (2010)
Park, J.-J., Song, J.-B., Kim, H.-S.: Safe joint mechanism based on passive compliance for collision safety. In: Lee, S., Suh, I., Kim, M. (eds.): Recent Progress in Robotics: Viable Robotic Service to Human, volume 370 of Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences, pp. 49–61. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (2008)
Petit, F., Chalon, M., Friedl, W., Grebenstein, M., Albu-Schaeffer, A., Hirzinger, G.: Bidirectional antagonistic variable stiffness actuation: Analysis, design amp; implementation. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4189–4196 (2010)
Pfeifer, R., Lungarella, M., Iida, F.: The challenges ahead for bio-inspired ‘soft’ robotics. ACM Commun. 55(11), 76–87 (2012)
Rodriguez, A.G., Chacon, J., Donoso, A., Rodriguez, A.G.: Design of an adjustable-stiffness spring: Mathematical modeling and simulation, fabrication and experimental validation. Mech. Mach. Theory 46 (12), 1970–1979 (2011)
Sardellitti, I., Palli, G., Tsagarakis, N., Caldwell, D.: Antagonistically actuated compliant joint; torque and stiffness control. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Inteligent Robotics and Systems (IROS), pp. 18–22 (2011)
Sardellitti, I., Medrano-Cerda, G., Tsagarakis, N., Jafari, A., Caldwell, D.: A position and stiffness control strategy for variable stiffness actuators. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2785–2791 (2012)
Schiavi, R., Grioli, G., Sen, S., Bicchi, A.: Vsa-ii: a novel prototype of variable stiffness actuator for safe and performing robots interacting with humans. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA 2008, pp. 2171–2176 (2008)
Stramigioli, S., van Oort, G., Dertien, E.: A concept for a new energy efficient actuator. In: IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, AIM 2008, pp. 671–675 (2008)
Tagliamonte, N.L., Sergi, F., Accoto, D., Carpino, G., Guglielmelli, E.: Double actuation architectures for rendering variable impedance in compliant robots: A review. Mechatronics 22 (8), 1187–1203 (2012)
Tonietti, G., Schiavi, R., Bicchi, A.: Design and control of a variable stiffness actuator for safe and fast physical human/robot interaction. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA 2005, pp. 526–531 (2005)
Tsagarakis, N., Sardellitti, I., Caldwell, D.: A new variable stiffness actuator (compact-vsa): Design and modelling. In: 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 378–383 (2011)
Van Ham, R., Vanderborght, B., Van Damme, M., Verrelst, B., Lefeber, D.: Mechanically adjustable and controllable compliance, equilibrium position actuator (maccepa). In: Proceeding of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2195–2200 (2006)
Vanderborght, B., Albu-Schaeffer, A., Bicchi, A., Burdet, E., Caldwell, D., Carloni, R., Catalano, M., Eiberger, O., Friedl, W., Ganesh, G., Garabini, M., Grebenstein, M., Grioli, G., Haddadin, S., Hoppner, H., Jafari, A., Laffranchi, M., Lefeber, D., Petit, F., Stramigioli, S., Tsagarakis, N., Damme, M.V., Ham, R.V., Visser, L., Wolf, S.: Variable impedance actuators: A review . Robot. Auton. Syst. 61(12), 1601–1614 (2013)
Vanderborght, B., Tsagarakis, N.G., Ham, R., Thorson, I., Caldwell, D.G.: MACCEPA 2.0: compliant actuator used for energy efficient hopping robot Chobino1D. Auton. Robot. 31(1), 55–65 (2011)
Vanderborght, B., Verrelst, B., Ham, R., Damme, M., Beyl, P., Lefeber, D.: Development of a compliance controller to reduce energy consumption for bipedal robots. Auton. Robot. 24(4), 419–434 (2008)
Vanderborght, B., Van Ham, R., Lefeber, D., Sugar, T., Hollander, K.: Comparison of mechanical design and energy consumption of adaptable, passive-compliant actuators. Int. J. Robot. Res. 28, 90–113 (2009)
Visser, L., Carloni, R., Stramigioli, S.: Energy-efficient variable stiffness actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 27(5), 865–875 (2011)
Vu, H., Aryananda, L., Sheikh, F., Casanova, F., Pfeifer, R.: A novel mechanism for varying stiffness via changing transmission angle. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 5076 –5081 (2011)
Wolf, S., Eiberger, O., Hirzinger, G.: The DLR FSJ: Energy based design of a variable stiffness joint. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 5082–5089 (2011)
Wolf, S., Hirzinger, G.: A new variable stiffness design: Matching requirements of the next robot generation. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA 2008, pp. 1741–1746 (2008)
Yang, C., Ganesh, G., Haddadin, S., Parusel, S., Albu-Schaeffer, A., Burdet, E.: Human-like adaptation of force and impedance in stable and unstable interactions. IEEE Trans. Robot. 27(5), 918–930 (2011)
Zinn, M., Khatib, O., Roth, B., Salisbury, J.K.: Playing it safe [human-friendly robots]. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 11(2), 12–21 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafari, A., Vu, H.Q. & Iida, F. Determinants for Stiffness Adjustment Mechanisms. J Intell Robot Syst 82, 435–454 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-015-0253-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-015-0253-8