Abstract
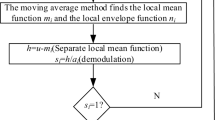
Because images contain rich characteristic information, adaptive image decomposition algorithms are necessary to achieve multi-scale extraction of image information in multi-scale image decomposition processing. For this reason, based on local mean decomposition (LMD), which has good self-adaptive characteristics, this paper proposes a new adaptive image processing algorithm, bi-dimensional local mean decomposition (BLMD). BLMD can decompose the original image into multiple bi-dimensional product functions (BPFs). Aiming at the decomposition of BLMD, this paper proposes targeted solutions and designs for the extraction of extremum points, screening process interpolation methods, and decomposition and stop conditions involved in BLMD. After fully recognizing the self-adaptive and multi-scale characteristics of BLMD, this paper proposes a variable neighborhood window method to obtain the extreme points in the decomposition process and uses fractal theory to interpolate the image and obtain the corresponding mean surface and other information. Then, the number of non-coincident extreme points on the zero-valued plane projection between adjacent surfaces in the screening process is counted and analyzed, and a stop condition that matches the characteristics of the image is given to ensure the BPF component obtained by decomposition accurately reflects certain feature information of an image. Finally, the BLMD proposed in this paper is formed. Empirical analysis shows this method can quickly decompose and maintain the characteristics of data-drivenness, adaptability and scale consistency of LMD; it can also avoid the disadvantages of other adaptive processing algorithms, such as the bi-dimensional intrinsic mode function obtained by the decomposition of bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition and the residual failing to completely contain the feature information of the original image.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gonzalez, R.C.: Digital Image Processing. Pearson Education India, Delhi (2009)
Scarano, F., Riethmuller, M.L.: Advances in iterative multigrid PIV image processing. Exp. Fluids 29(1), S051–S060 (2000)
Daneshvar, S., Ghassemian, H.: MRI and PET image fusion by combining IHS and retina-inspired models. Inf. Fusion 11(2), 114–123 (2010)
Semmlow, J.L., Griffel, B.: Biosignal and Medical Image Processing. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL (2014)
Schindelin, J., Arganda-Carreras, I., Frise, E., et al.: Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 9(7), 676–682 (2012)
Gupta, D., Choubey, S.: Discrete wavelet transform for image processing. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 4(3), 598–602 (2015)
Singh, A., Dutta, M.K., ParthaSarathi, M., et al.: Image processing based automatic diagnosis of glaucoma using wavelet features of segmented optic disc from fundus image. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 124, 108–120 (2016)
Lai, Z., Qu, X., Liu, Y., et al.: Image reconstruction of compressed sensing MRI using graph-based redundant wavelet transform. Med. Image Anal. 27, 93–104 (2016)
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S.R., et al.: The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for non-linear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 454(12), 903–995 (1998)
Liu, Z., Jin, Y., Zuo, M.J., et al.: Time–frequency representation based on robust local mean decomposition for multicomponent AM-FM signal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 95, 468–487 (2017)
Nunes, J.C., Bouaouue, Y., Delechelle, E., et al.: Image analysis by bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition. Image Vis. Comput. 21(3), 1019–1026 (2003)
Nunes, J.C., Guyot, S., Delechelle, E.: Texture analysis based on local analysis of the bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition. Mach. Vis. Appl. 16(5), 177–188 (2005)
Bhuiyan, S.M.A., Adhami, R.R., Khan, J.F.: Fast and adaptive bidimensional empirical mode decomposition using order-statistics filter based envelope estimation. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2008(1), 1–18 (2008)
Trusiak, M., Wielgus, M., Patorski, K.: Advanced processing of optical fringe patterns by automated selective reconstruction and enhanced fast empirical mode decomposition. Opt. Lasers Eng. 52, 230–240 (2014)
Cai, B., Xiang, J.: Digital image compression based on BEMD and PCA. Comput. Eng. Appl. 47(23), 185–187 (2011)
Zhi, He, Qiang, Wang, Yi, Shen, et al.: Multivariate gray model-based BEMD for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 62(5), 889–904 (2013)
An, F.P., Lin, D.C., Zhou, X.W., et al.: Enhancing image denoising performance of bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition by improving the edge effect. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2015, 1–12 (2015)
LiHong, Qiao, KaiFu, Niu, Ning, Wang, et al.: Perfect reconstruction image modulation based on BEMD and quaternionic analytic signals. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 54(12), 2602–2614 (2011)
Hu, J., Wang, X., Qin, H.: Improved, feature-centric EMD for 3D surface modeling and processing. Graph. Models 76(5), 340–354 (2014)
Ye, Q., Xiang, M., Cui, Z.: Fingerprint image enhancement algorithm based on two dimension emd and gabor filter. Procedia Eng. 29, 1840–1844 (2012)
Van Tung, T., Yang, B.-S., Gu, F., et al.: Thermal image enhancement using bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition in combination with relevance vector machine for rotating machinery fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 38(2), 601–614 (2013)
Lahmiri, S.: Image characterization by fractal descriptors in variational mode decomposition domain: application to brain magnetic resonance. Physica A 456, 235–243 (2016)
Lahmiri, S., Shmuel, A.: Variational mode decomposition based approach for accurate classification of color fundus images with hemorrhages. Opt. Laser Technol. 96, 243–248 (2017)
Guryanov, F., Krylov, A.: Fast medical image registration using bidirectional empirical mode decomposition. Signal Process. Image Commun. 59, 12–17 (2017)
Yang, B.S., Gu, F., Ball, A.: Thermal image enhancement using bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition in combination with relevance vector machine for rotating machinery fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 38(2), 601–614 (2013)
Qin, X., Zheng, J., Hu, G., et al.: Multi-focus image fusion based on window empirical mode decomposition. Infrared Phys. Technol. 85, 251–260 (2017)
Lu, Y., Lu, R.: Fast bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition as an image enhancement technique for fruit defect detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 152, 314–323 (2018)
Qin, Y., Qiao, L., Wang, Q., et al.: Bidimensional empirical mode decomposition method for image processing in sensing system. Comput. Electr. Eng. 68, 215–224 (2018)
Damerval, Christophe: A fast algorithm for bi-dimensional EMD. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 12(10), 701–704 (2005)
Liu, Z., Peng, S.: Boundary processing of bi-dimensional EMD using texture synthesis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 12(1), 33–36 (2005)
Guang-tao, Ge, En-fang, Sang, Zhuo-fu, Liu, et al.: Novel BEMD criterion for stopping sifting process. J. Data Acquis. Process. 25(2), 195–200 (2010)
Wu, Z., Huang, N.E., Chen, X.: The multi-dimenstional ensemble empirical mode decomposition method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 1(5), 339–372 (2009)
Rilling, G., Flandrin, P., Gancalves, P.: On empirical mode decomposition and its algorithms. In: Proceedings of IEEE-EURASIP Workshop on Nonlinear Signal and Image Processing, vol. 3, pp. 8–11 (2003)
Yang, Z.H., Qi, D.X., Yang, L.H.: Signal period analysis based on Hilbert–Huang transform and its application to texture analysis. In: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Image and Graphics, pp. 430–433. IEEE (2004)
Xiong, C.Z., Xu, J.Y., Zou, J.C., et al.: Texture classification based on EMD and FFT. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Sci. A) 7(9), 1516–1521 (2006)
Cuiyun, L., Pan, H., Hongbing, J.: A novel surface interpolation approach for bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition. In: International Conference on Network Computing and Information Security (NCIS), pp. 335–338 (2011)
Nan, D., Bi, D., Xu, Y., et al.: Retinex color image enhancement based on adaptive bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition. J. Comput. Appl. 31(6), 1552–1559 (2011)
Kim, D., Park, M., Oh, H.S.: Bi-dimensional statistical empirical mode de-composition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19(4), 191–194 (2012)
Smith, J.S.: The local mean decomposition and its application to EEG perception data. J. R. Soc. Interface 2(5), 443–454 (2005)
Mandelbrot, B.B.: The variation of certain speculative prices. In: Mandelbrot, B.B. (ed.) Fractals and Scaling in Finance. Springer, New York (1997)
Dekking, M., Lévy-Véhel, J., Lutton, E., Tricot, C. (eds.): Fractals: Theory and Applications in Engineering. Theory and Applications in Engineering. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Torres, I.C., Rubio, J.M.A., Ipsen, R.: Using fractal image analysis to characterize microstructure of low-fat stirred yoghurt manufactured with microparticulated whey protein. J. Food Eng. 109(4), 721–729 (2012)
Brodatz, P.: Textures: A Photographic Album for Artists and Designers. Dover Publications, New York (1966)
Acknowledgements
This paper is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61701188).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, FP., Liu, ZW. Image Processing Algorithm Based on Bi-dimensional Local Mean Decomposition. J Math Imaging Vis 61, 1243–1257 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-019-00899-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-019-00899-8