Abstract
This paper investigates an information security game between two competitive firms in a market consisting of loyal customers and switchers. The switchers are classified into unaggressive switchers and aggressive switchers based on whether they always transact with the more secure firm. We find that the switcher type plays a significant role in affecting firms’ information security decisions. Firms can achieve pure strategy Nash equilibrium in the unaggressive case while no pure strategy Nash equilibrium exists in the aggressive case. Instead, a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium in the aggressive case is obtained. Our analyses show that firms will acquire more profits in the unaggressive case compared to that in the aggressive case when they determine their information security levels individually. Whereas, when they make their information security decisions jointly, the profits in the unaggressive case will be smaller than that in the aggressive case. Furthermore, we find that the loyal customer rate has different impacts on firms’ profits in Nash equilibrium and optimal solution for both the unaggressive case and the aggressive case. At last, two contracts are proposed to help firms coordinate their information security strategies when they make individual decisions.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
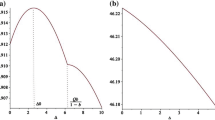
It should be noted that \( h_{1} \left( 1 \right) \), \( h_{2} \left( 1 \right) \), and \( h_{3} \left( 1 \right) \) may be negative. However, it is not our concern that \( h_{1} \left( 1 \right) \), \( h_{2} \left( 1 \right) \), and \( h_{3} \left( 1 \right) \) are negative or positive. Figure 2 just shows that \( h_{1} \left( 1 \right) \), \( h_{2} \left( 1 \right) \), and \( h_{3} \left( 1 \right) \) are positive.
References
Bandyopadhyay T, Jacob V, Raghunathan S (2010) Information security in networked supply chains: impact of network vulnerability and supply chain integration on incentives to invest. Inf Technol Manag 11(1):7–23
Gal-Or E, Ghose A (2005) The economic incentives for sharing security information. Inf Syst Res 16(2):186–208
Gao X, Zhong W (2015) Information security investment for competitive firms with hacker behavior and security requirements. Ann Oper Res 235(1):277–300
Gao X, Zhong W (2016) Economic incentives in security information sharing: the effects of market structures. Inf Technol Manag 17(4):361–377
Gao X, Zhong W, Mei S (2013) A differential game approach to information security investment under hackers’ knowledge dissemination. Oper Res Lett 41:421–425
Gao X, Zhong W, Mei S (2014) A game-theoretic analysis of information sharing and security investment for complementary firms. J Oper Res Soc 65(11):1682–1691
Gao X, Zhong W, Mei S (2015) Security investment and information sharing under an alternative security breach probability function. Inf Syst Front 17(2):423–438
Gordon LA, Loeb MP (2002) The economics of information security investment. ACM Trans Inf Syst Secur 5(4):438–457
Hausken K (2006) Returns to information security investment: the effect of alternative information security breach functions on optimal investment and sensitivity to vulnerability. Inf Syst Front 8(5):338–349
Hausken K (2007) Information sharing among firms and cyber attacks. J Account Public Policy 26(6):639–688
Huang CD, Behara RS (2013) Economics of information security investment in the case of concurrent heterogeneous attacks with budget constraints. Int J Prod Econ 141(1):255–268
Huang CD, Hu Q, Behara RS (2008) An economic analysis of the optimal information security investment in the case of a risk-averse firm. Int J Prod Econ 114(2):793–804
Hyken S (2015) Six types of loyal customers by Shep Hyken. https://hyken.com/customer-experience-2/six-types-of-loyal-customers/. Accessed 12 Jan 2019
Jiang W (2018) Huazhu Hotels Group investigates alleged info leak. https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201808/29/WS5b86473da310add14f38871b.html. Accessed 12 Jan 2019
Jing B, Wen Z (2008) Finitely loyal customers, switchers, and equilibrium price promotion. J Econ Manag Strategy 17(3):683–707
Keylor B (2018) Under Armour data breach impacts 150 million MyFitnessPal accounts. https://www.identityforce.com/blog/under-armour-data-breach-myfitnesspal. Accessed 12 Jan 2019
Liu D, Ji Y, Mookerjee V (2011) Knowledge sharing and investment decisions in information security. Decis Support Syst 52(1):95–107
Liu X, Qian X, Pei J, Pardalos PM (2018) Security investment and information sharing in the market of complementary firms: impact of complementarity degree and industry size. J Glob Optim 70(2):413–436
Lye KW, Wing JM (2005) Game strategies in network security. Int J Inf Secur 4(1–2):71–86
Marte J (2014) Are data breaches creating smarter consumers? https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/get-there/wp/2014/10/20/are-data-breaches-creating-better-consumers/. Accessed 12 Jan 2019
Qian X, Liu X, Pei J, Pardalos PM, Liu L (2017) A game-theoretic analysis of information security investment for multiple firms in a network. J Oper Res Soc 68(10):1290–1305
Qian X, Liu X, Pei J, Pardalos PM (2018) A new game of information sharing and security investment between two allied firms. Int J Prod Res 56(12):4069–4086
Srinidhi B, Yan J, Tayi GK (2015) Allocation of resources to cyber-security: the effect of misalignment of interest between managers and investors. Decis Support Syst 75:49–62
Wu Y, Feng G, Wang N, Liang H (2015) Game of information security investment: impact of attack types and network vulnerability. Expert Syst Appl 42(15–16):6132–6146
Wu Y, Fung RY, Feng G, Wang N (2017) Decisions making in information security outsourcing: impact of complementary and substitutable firms. Comput Ind Eng 110:1–12
Wu Y, Feng G, Fung RY (2018) Comparison of information security decisions under different security and business environments. J Oper Res Soc 69(5):747–761
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 71801071), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JZ2018HGBZ0113, JZ2018HGTA0222), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71922009, 71801035, 71231004, 71601065, 71690235, 71690230, 71501058), Innovative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71521001), and the Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province (No. 2017C31069). Panos M. Pardalos is partially supported by the project of “Distinguished International Professor by the Chinese Ministry of Education” (MS2014HFGY026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, X., Pei, J., Liu, X. et al. Information security decisions for two firms in a market with different types of customers. J Comb Optim 38, 1263–1285 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-019-00446-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-019-00446-6