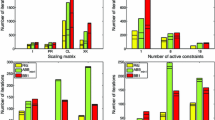
Abstract
The ability of the modern graphics processors to operate on large matrices in parallel can be exploited for solving constrained image deblurring problems in a short time. In particular, in this paper we propose the parallel implementation of two iterative regularization methods: the well known expectation maximization algorithm and a recent scaled gradient projection method. The main differences between the considered approaches and their impact on the parallel implementations are discussed. The effectiveness of the parallel schemes and the speedups over standard CPU implementations are evaluated on test problems arising from astronomical images.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barzilai J., Borwein J.M.: Two point step size gradient methods. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 8, 141–148 (1988)
Bertero M., Boccacci P.: Introduction to Inverse Problems in Imaging. Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol (1998)
Bonettini S., Zanella R., Zanni L.: A scaled gradient projection method for constrained image deblurring. Inverse Probl. 25, 015002 (2009)
Csiszär I.: Why least squares and maximum entropy? An axiomatic approach to inference for linear inverse problems. Ann. Stat. 19, 2032–2066 (1991)
Dai Y.H., Fletcher R.: On the asymptotic behaviour of some new gradient methods. Math. Program. 103(3), 541–559 (2005)
Dai Y.H., Hager W.W., Schittkowski K., Zhang H.: The cyclic barzilai-borwein method for unconstrained optimization. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 26, 604–627 (2006)
Davis P.J.: Circulant Matrices. Wiley, New York (1979)
Frassoldati G., Zanghirati G., Zanni L.: New adaptive stepsize selections in gradient methods. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 4(2), 299–312 (2008)
Friedlander A., Martínez J.M., Molina B., Raydan M.: Gradient method with retards and generalizations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 36, 275–289 (1999)
Galligani E., Ruggiero V., Zanni L.: Parallel solution of large-scale quadratic programs. In: De Leone, R., Murli, A., Pardalos, P.M., Toraldo, G. (eds) High Performance Algorithms and Software in Nonlinear Optimization, Applied Optimization 24, pp. 189–205. Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht (1998)
Gergel V.P., Sergeyev Y.D., Strongin R.G.: A parallel global optimization method and its implementation on a transputer system. Optimization 26, 261–275 (1992)
Hansen P.C.: Rank-deficient and Discrete Ill-posed Problems. SIAM, Philadelphia (1998)
Harris, M.: Optimizing parallel reduction in CUDA. NVidia Technical Report (2007). Available: http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/1_1/Website/projects/reduction/doc/reduction.pdf
Iusem A.N.: Convergence analysis for a multiplicatively relaxed EM algorithm. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 14, 573–593 (1991)
Iusem A.N.: A short convergence proof of the EM algorithm for a specific Poisson model. REBRAPE 6, 57–67 (1992)
Lange K., Carson R.: EM reconstruction algorithms for emission and transmission tomography. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 8, 306–316 (1984)
Lee, S., Wright, S.J.: Implementing algorithms for signal and image reconstruction on graphical processing units. Submitted (2008). Available: http://www.optimization-online.org/DB_HTML/2008/11/2131.html
Lucy L.B.: An iterative technique for the rectification of observed distributions. Astronom. J. 79, 745–754 (1974)
Migdalas A., Toraldo G., Kumar V.: Parallel computing in numerical optimization. Parallel Comput. 24(4), 373–551 (2003)
Mülthei H.N., Schorr B.: On properties of the iterative maximum likelihood reconstruction method. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 11, 331–342 (1989)
NVIDIA: NVIDIA CUDA Compute Unified Device Architecture, Programming guide. Version 2.0 (2008). Available at: http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/2_0/docs/NVIDIA_CUDA_Programming_Guide_2.0.pdf
Resmerita E., Engl H.W., Iusem A.N.: The expectation-maximization algorithm for ill-posed integral equations: a convergence analysis. Inverse Probl. 23, 2575–2588 (2007)
Richardson W.H.: Bayesian-based iterative method of image restoration. J. Opt. Soc. Amer. A 62, 55–59 (1972)
Rudin L.I., Osher S., Fatemi E.: Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D 60, 259–268 (1992)
Serafini T., Zanghirati G., Zanni L.: Gradient projection methods for quadratic programs and applications in training support vector machines. Optim. Meth. Soft. 20(2–3), 353–378 (2005)
Shepp L.A., Vardi Y.: Maximum likelihood reconstruction for emission tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1, 113–122 (1982)
Strongin R.G., Sergeyev Y.D.: Global multidimensional optimization on parallel computer. Parallel Comput. 18, 1259–1273 (1992)
Strongin R.G., Sergeyev Ya.D.: Global Optimization with Non-convex Constraints and Parallel Algorithms. Kluwer Academic Publ., Dordrecht (2000)
Vardi Y., Shepp L.A., Kaufman L.: A statistical model for positron emission tomography. J. Amer. Statist. Soc. 80(389), 8–37 (1985)
Zanella R., Boccacci P., Zanni L., Bertero M.: Efficient gradient projection methods for edge-preserving removal of Poisson noise. Inverse Probl. 25, 045010 (2009)
Zanni L.: An improved gradient projection-based decomposition technique for support vector machines. Comput. Manag. Sci. 3, 131–145 (2006)
Zanni L., Serafini T., Zanghirati G.: Parallel software for training large scale support vector machines on multiprocessor systems. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 7, 1467–1492 (2006)
Zhou B., Gao L., Dai Y.H.: Gradient methods with adaptive step-sizes. Comput. Optim. Appl. 35(1), 69–86 (2006)
Zhu, M., Chan, T.F.: An efficient primal-dual hybrid gradient algorithm for total variation image restoration. CAM Report 08-34, Mathematics Department, UCLA (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research is supported by the PRIN2006 project of the Italian Ministry of University and Research Inverse Problems in Medicine and Astronomy, grant 2006018748.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruggiero, V., Serafini, T., Zanella, R. et al. Iterative regularization algorithms for constrained image deblurring on graphics processors. J Glob Optim 48, 145–157 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-009-9516-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-009-9516-x