Abstract
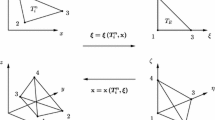
In this paper we present a new and efficient quadrature-free formulation for the family of cell-centered high order accurate direct arbitrary-Lagrangian–Eulerian one-step ADER-WENO finite volume schemes on unstructured triangular and tetrahedral meshes that has been developed by the authors in a recent series of papers (Boscheri et al. in J Comput Phys 267:112–138, 2014; Boscheri and Dumbser in Commun Comput Phys 14:1174–1206, 2013; Boscheri and Dumbser in J Comput Phys 275:484–523, 2014; Dumbser and Boscheri in Comput Fluids 86:405–432, 2013). High order of accuracy in time is obtained by using a local space–time Galerkin predictor on moving curved meshes, while a high order accurate nonlinear WENO method is adopted to produce high order essentially non-oscillatory reconstruction polynomials in space. The mesh is moved at each time step according to the solution of a node solver algorithm that assigns a unique velocity vector to each node of the mesh. A rezoning procedure can also be applied when mesh distortions and deformations become too severe. The space–time mesh is then constructed by straight edges connecting the vertex positions at the old time level \(t^n\) with the new ones at the next time level \(t^{n+1}\), yielding closed space–time control volumes, on the boundary of which the numerical flux must be integrated. This is done here with a new and efficient quadrature-free approach: the space–time boundaries are split into simplex sub-elements, i.e. either triangles in 2D or tetrahedra in 3D. This leads to space–time normal vectors as well as Jacobian matrices that are constant within each sub-element. Within the space–time Galerkin predictor stage that solves the Cauchy problem inside each element in the small, the discrete solution and the flux tensor are approximated using a nodal space–time basis. Since these space–time basis functions are defined on a reference element and do not change, their integrals over the simplex sub-surfaces of the space–time reference control volume can be integrated once and for all analytically during a preprocessing step. The resulting integrals are then used together with the space–time degrees of freedom of the predictor in order to compute the numerical flux that is needed in the finite volume scheme. We apply the high order algorithm presented in this paper to the equations of hydrodynamics obtaining convergence rates up to fourth order of accuracy in space and time. A set of classical Lagrangian test problems has been solved and the results have been compared with the ones given by the original formulation of the algorithm (Boscheri and Dumbser 2013, 2014). The efficiency has been monitored and measured for each test case and the new quadrature-free schemes were up to 3.7 times faster than the ones based on Gaussian quadrature.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balsara, D.S.: Multidimensional HLLE Riemann solver: application to Euler and magnetohydrodynamic flows. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 1970–1993 (2010)
Balsara, D.S.: A two-dimensional HLLC Riemann solver for conservation laws: application to Euler and magnetohydrodynamic flows. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 7476–7503 (2012)
Balsara, D.S.: Self-adjusting, positivity preserving high order schemes for hydrodynamics and magnetohydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 7504–7517 (2012)
Benson, D.J.: Computational methods in Lagrangian and Eulerian hydrocodes. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 99, 235–394 (1992)
Berndt, M., Breil, J., Galera, S., Kucharik, M., Maire, P.H., Shashkov, M.: Two-step hybrid conservative remapping for multimaterial arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian methods. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 6664–6687 (2011)
Berndt, M., Kucharik, M., Shashkov, M.J.: Using the feasible set method for rezoning in ALE. Procedia Comput. Sci. 1, 1879–1886 (2010)
Bochev, P., Ridzal, D., Shashkov, M.J.: Fast optimization-based conservative remap of scalar fields through aggregate mass transfer. J. Comput. Phys. 246, 37–57 (2013)
Boscheri, W., Balsara, D.S., Dumbser, M.: Lagrangian ADER-WENO finite volume schemes on unstructured triangular meshes based on genuinely multidimensional HLL Riemann solvers. J. Comput. Phys. 267, 112–138 (2014)
Boscheri, W., Dumbser, M.: Arbitrary-Lagrangian–Eulerian one-step WENO finite volume schemes on unstructured triangular meshes. Commun. Comput. Phys. 14, 1174–1206 (2013)
Boscheri, W., Dumbser, M.: A direct arbitrary-Lagrangian–Eulerian ADER-WENO finite volume scheme on unstructured tetrahedral meshes for conservative and nonconservative hyperbolic systems in 3D. J. Comput. Phys. 275, 484–523 (2014)
Boscheri, W., Dumbser, M., Balsara, D.S.: High order Lagrangian ADER-WENO schemes on unstructured meshes—application of several node solvers to hydrodynamics and magnetohydrodynamics. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 76, 737–778 (2014)
Boscheri, W., Dumbser, M., Zanotti, O.: High order cell-centered Lagrangian-type finite volume schemes with time-accurate local time stepping on unstructured triangular meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 291, 120–150 (2015)
Boscheri, W., Loubère, R., Dumbser, M.: Direct Arbitrary-Lagrangian-Eulerian ADER-MOOD Finite Volume Schemes for Multidimensional Hyperbolic Conservation Laws. J. Comput. Phys. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2015.03.015
Breil, J., Harribey, T., Maire, P.H., Shashkov, M.J.: A multi-material ReALE method with MOF interface reconstruction. Comput. Fluids 83, 115–125 (2013)
Caramana, E.J., Burton, D.E., Shashkov, M.J., Whalen, P.P.: The construction of compatible hydrodynamics algorithms utilizing conservation of total energy. J. Comput. Phys. 146, 227–262 (1998)
Carré, G., Del Pino, S., Després, B., Labourasse, E.: A cell-centered Lagrangian hydrodynamics scheme on general unstructured meshes in arbitrary dimension. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 5160–5183 (2009)
Cesenek, J., Feistauer, M., Horacek, J., Kucera, V., Prokopova, J.: Simulation of compressible viscous flow in time-dependent domains. Appl. Math. Comput. 219, 7139–7150 (2013)
Cheng, J., Shu, C.W.: A high order ENO conservative Lagrangian type scheme for the compressible Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 1567–1596 (2007)
Cheng, J., Toro, E.F.: A 1D conservative Lagrangian ADER scheme. Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 30, 501–508 (2013)
Clain, S., Diot, S., Loubère, R.: A high-order finite volume method for systems of conservation laws—multi-dimensional optimal order detection (MOOD). J. Comput. Phys. 230, 4028–4050 (2011)
Claisse, A., Després, B., Labourasse, E., Ledoux, F.: A new exceptional points method with application to cell-centered Lagrangian schemes and curved meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 4324–4354 (2012)
Cockburn, B., Karniadakis, G.E., Shu, C.W.: Discontinuous Galerkin Methods. Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Després, B., Mazeran, C.: Symmetrization of Lagrangian gas dynamic in dimension two and multimdimensional solvers. C. R. Mecanique 331, 475–480 (2003)
Després, B., Mazeran, C.: Lagrangian gas dynamics in two-dimensions and Lagrangian systems. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 178, 327–372 (2005)
Diot, S., Clain, S., Loubère, R.: Improved detection criteria for the multi-dimensional optimal order detection (mood) on unstructured meshes with very high-order polynomials. Comput. Fluids 64, 43–63 (2012)
Diot, S., Loubère, R., Clain, S.: The MOOD method in the three-dimensional case: very-high-order finite volume method for hyperbolic systems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 73, 362–392 (2013)
Dobrev, V.A., Ellis, T.E., Kolev, T.V., Rieben, R.N.: Curvilinear finite elements for Lagrangian hydrodynamics. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 65, 1295–1310 (2011)
Dobrev, V.A., Ellis, T.E., Kolev, T.V., Rieben, R.N.: High order curvilinear finite elements for Lagrangian hydrodynamics. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 34, 606–641 (2012)
Dobrev, V.A., Ellis, T.E., Kolev, T.V., Rieben, R.N.: High order curvilinear finite elements for axisymmetric Lagrangian hydrodynamics. Comput. Fluids 83, 58–69 (2013)
Balsara, D.S., Dumbser, M., Abgrall, R.: Multidimensional HLLC Riemann solver for unstructured meshes—with application to Euler and MHD flows. J. Comput. Phys. 261, 172–208 (2014)
Dubcova, L., Feistauer, M., Horacek, J., Svacek, P.: Numerical simulation of interaction between turbulent flow and a vibrating airfoil. Comput. Vis. Sci. 12, 207–225 (2009)
Dubiner, M.: Spectral methods on triangles and other domains. J. Sci. Comput. 6, 345–390 (1991)
Dumbser, M.: Arbitrary-Lagrangian–Eulerian ADER-WENO finite volume schemes with time-accurate local time stepping for hyperbolic conservation laws. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 280, 57–83 (2014)
Dumbser, M., Balsara, D.S., Toro, E.F., Munz, C.-D.: A unified framework for the construction of one-step finite volume and discontinuous Galerkin schemes on unstructured meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 8209–8253 (2008)
Dumbser, M., Boscheri, W.: High-order unstructured Lagrangian one-step WENO finite volume schemes for non-conservative hyperbolic systems: applications to compressible multi-phase flows. Comput. Fluids 86, 405–432 (2013)
Dumbser, M., Enaux, C., Toro, E.F.: Finite volume schemes of very high order of accuracy for stiff hyperbolic balance laws. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 3971–4001 (2008)
Dumbser, M., Hidalgo, A., Castro, M., Parés, C., Toro, E.F.: FORCE schemes on unstructured meshes II: non-conservative hyperbolic systems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199, 625–647 (2010)
Dumbser, M., Käser, M.: Arbitrary high order non-oscillatory finite volume schemes on unstructured meshes for linear hyperbolic systems. J. Comput. Phys. 221, 693–723 (2007)
Dumbser, M., Käser, M., Titarev, V.A., Toro, E.F.: Quadrature-free non-oscillatory finite volume schemes on unstructured meshes for nonlinear hyperbolic systems. J. Comput. Phys. 226, 204–243 (2007)
Dumbser, M., Toro, E.F.: On universal Osher-type schemes for general nonlinear hyperbolic conservation laws. Commun. Comput. Phys. 10, 635–671 (2011)
Dumbser, M., Uuriintsetseg, A., Zanotti, O.: On arbitrary-Lagrangian–Eulerian one-step WENO schemes for stiff hyperbolic balance laws. Commun. Comput. Phys. 14, 301–327 (2013)
Dumbser, M., Zanotti, O., Loubère, R., Diot, S.: A posteriori subcell limiting of the discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 278, 47–75 (2014)
Feistauer, M., Horacek, J., Ruzicka, M., Svacek, P.: Numerical analysis of flow-induced nonlinear vibrations of an airfoil with three degrees of freedom. Comput. Fluids 49, 110–127 (2011)
Feistauer, M., Kucera, V., Prokopova, J., Horacek, J.: The ALE discontinuous Galerkin method for the simulation of air flow through pulsating human vocal folds. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1281, pp. 83–86 (2010)
Francois, M.M., Shashkov, M.J., Masser, T.O., Dendy, E.D.: A comparative study of multimaterial Lagrangian and Eulerian methods with pressure relaxation. Comput. Fluids 83, 126–136 (2013)
Galera, S., Maire, P.H., Breil, J.: A two-dimensional unstructured cell-centered multi-material ALE scheme using VOF interface reconstruction. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 5755–5787 (2010)
Hidalgo, A., Dumbser, M.: ADER schemes for nonlinear systems of stiff advection–diffusion–reaction equations. J. Sci. Comput. 48, 173–189 (2011)
Hirt, C., Amsden, A., Cook, J.: An arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian computing method for all flow speeds. J. Comput. Phys. 14, 227253 (1974)
Hu, C., Shu, C.W.: Weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes on triangular meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 150, 97–127 (1999)
Kamm, J.R., Timmes, F.X.: On efficient generation of numerically robust Sedov solutions. Technical Report LA-UR-07-2849, LANL (2007)
Karniadakis, G.E., Sherwin, S.J.: Spectral/hp Element Methods in CFD. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1999)
Kidder, R.E.: Laser-driven compression of hollow shells: power requirements and stability limitations. Nucl. Fusion 1, 3–14 (1976)
Knupp, P.M.: Achieving finite element mesh quality via optimization of the Jacobian matrix norm and associated quantities. Part II—a framework for volume mesh optimization and the condition number of the Jacobian matrix. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 48, 1165–1185 (2000)
Kucharik, M., Breil, J., Galera, S., Maire, P.H., Berndt, M., Shashkov, M.J.: Hybrid remap for multi-material ALE. Comput. Fluids 46, 293–297 (2011)
Kucharik, M., Shashkov, M.J.: One-step hybrid remapping algorithm for multi-material arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian methods. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 2851–2864 (2012)
Li, Z., Yu, X., Jia, Z.: The cell-centered discontinuous Galerkin method for Lagrangian compressible Euler equations in two dimensions. Comput. Fluids 96, 152–164 (2014)
Liska, R., Shashkov, M.J., Váchal, P., Wendroff, B.: Synchronized flux corrected remapping for ALE methods. Comput. Fluids 46, 312–317 (2011)
Liu, W., Cheng, J., Shu, C.W.: High order conservative Lagrangian schemes with Lax–Wendroff type time discretization for the compressible Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 8872–8891 (2009)
Loubère, R., Dumbser, M., Diot, S.: A new family of high order unstructured mood and ader finite volume schemes for multidimensional systems of hyperbolic conservation laws. Commun. Comput. Phys. 16, 718–763 (2014)
Loubère, R., Maire, P.H., Váchal, P.: A second-order compatible staggered Lagrangian hydrodynamics scheme using a cell-centered multidimensional approximate Riemann solver. Procedia Comput. Sci. 1, 1931–1939 (2010)
Loubère, R., Maire, P.H., Váchal, P.: 3D staggered Lagrangian hydrodynamics scheme with cell-centered Riemann solver-based artificial viscosity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 72, 22–42 (2013)
Maire, P.H.: A high-order cell-centered Lagrangian scheme for two-dimensional compressible fluid flows on unstructured meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 2391–2425 (2009)
Maire, P.H.: A high-order one-step sub-cell force-based discretization for cell-centered Lagrangian hydrodynamics on polygonal grids. Comput. Fluids 46(1), 341–347 (2011)
Maire, P.H.: A unified sub-cell force-based discretization for cell-centered Lagrangian hydrodynamics on polygonal grids. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 65, 1281–1294 (2011)
Maire, P.H., Abgrall, R., Breil, J., Ovadia, J.: A cell-centered Lagrangian scheme for two-dimensional compressible flow problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 29, 1781–1824 (2007)
Maire, P.H., Breil, J.: A second-order cell-centered Lagrangian scheme for two-dimensional compressible flow problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 56, 1417–1423 (2007)
Maire, P.H., Nkonga, B.: Multi-scale Godunov-type method for cell-centered discrete Lagrangian hydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 799–821 (2009)
Munz, C.D.: On Godunov-type schemes for Lagrangian gas dynamics. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 31, 17–42 (1994)
Noh, W.F.: Errors for calculations of strong shocks using artificial viscosity and an artificial heat flux. J. Comput. Phys. 72, 78–120 (1987)
Ortega, A.L., Scovazzi, G.: A geometrically-conservative, synchronized, flux-corrected remap for arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian computations with nodal finite elements. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 6709–6741 (2011)
Peery, J.S., Carroll, D.E.: Multi-material ALE methods in unstructured grids. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 187, 591–619 (2000)
Sambasivan, S.K., Shashkov, M.J., Burton, D.E.: A finite volume cell-centered Lagrangian hydrodynamics approach for solids in general unstructured grids. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 72, 770–810 (2013)
Sambasivan, S.K., Shashkov, M.J., Burton, D.E.: Exploration of new limiter schemes for stress tensors in Lagrangian and ALE hydrocodes. Comput. Fluids 83, 98–114 (2013)
Scovazzi, G.: Lagrangian shock hydrodynamics on tetrahedral meshes: a stable and accurate variational multiscale approach. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 8029–8069 (2012)
Smith, R.W.: AUSM(ALE): a geometrically conservative arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian flux splitting scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 150, 268286 (1999)
Stroud, A.H.: Approximate Calculation of Multiple Integrals. Prentice-Hall Inc., Englewood Cliffs (1971)
Titarev, V.A., Toro, E.F.: ADER: arbitrary high order Godunov approach. J. Sci. Comput. 17(1–4), 609–618 (2002)
Titarev, V.A., Toro, E.F.: ADER schemes for three-dimensional nonlinear hyperbolic systems. J. Comput. Phys. 204, 715–736 (2005)
Titarev, V.A., Tsoutsanis, P., Drikakis, D.: WENO schemes for mixed-element unstructured meshes. Commun. Comput. Phys. 8, 585–609 (2010)
Toro, E.F., Titarev, V.A.: Derivative Riemann solvers for systems of conservation laws and ADER methods. J. Comput. Phys. 212(1), 150–165 (2006)
Toro, E.F.: Anomalies of conservative methods: analysis, numerical evidence and possible cures. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 11, 128–143 (2002)
Toro, E.F.: Riemann Solvers and Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics: A Practical Introduction. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Tsoutsanis, P., Titarev, V.A., Drikakis, D.: WENO schemes on arbitrary mixed-element unstructured meshes in three space dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 1585–1601 (2011)
Vilar, F.: Cell-centered discontinuous Galerkin discretization for two-dimensional Lagrangian hydrodynamics. Comput. Fluids 64, 64–73 (2012)
Vilar, F., Maire, P.H., Abgrall, R.: Cell-centered discontinuous Galerkin discretizations for two-dimensional scalar conservation laws on unstructured grids and for one-dimensional Lagrangian hydrodynamics. Comput. Fluids 46(1), 498–604 (2010)
Vilar, F., Maire, P.H., Abgrall, R.: A discontinuous Galerkin discretization for solving the two-dimensional gas dynamics equations written under total Lagrangian formulation on general unstructured grids. J. Comput. Phys. 276, 188–234 (2014)
von Neumann, J., Richtmyer, R.D.: A method for the calculation of hydrodynamics shocks. J. Appl. Phys. 21, 232–237 (1950)
Yanilkin, Y.V., Goncharov, E.A., Kolobyanin, V.Y., Sadchikov, V.V., Kamm, J.R., Shashkov, M.J., Rider, W.J.: Multi-material pressure relaxation methods for Lagrangian hydrodynamics. Comput. Fluids 83, 137–143 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The presented research has been financed by the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013) with the research project STiMulUs, ERC Grant Agreement No. 278267. The authors acknowledge PRACE for awarding us access to the SuperMUC supercomputer of the Leibniz Rechenzentrum (LRZ) in Munich, Germany.
The authors would like to thank the two anonymous referees for their constructive comments and suggestions, which definetely helped to improve the quality of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boscheri, W., Dumbser, M. An Efficient Quadrature-Free Formulation for High Order Arbitrary-Lagrangian–Eulerian ADER-WENO Finite Volume Schemes on Unstructured Meshes. J Sci Comput 66, 240–274 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-015-0019-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-015-0019-2