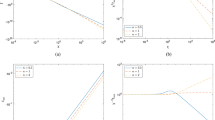
Abstract
A high-order explicit level-set method based on the total variation diminishing Runge–Kutta method, a high-order scheme for distance computation and a smoothing scheme has been developed for simulating curvature driven flows and surface diffusion motion. This method overcomes the high-order CFL time restriction. The enhanced stability is achieved by utilizing several techniques, resulting in an accurate and smooth velocity field. In particular, the scheme for distance computation is used to reinitialize the level-set function and to extend the velocity from the zero level-set to the rest of the domain. As such, it greatly reduces the accumulated errors typically observed in the traditional PDE-based methods. The smoothing technique is used to remove the high-frequency oscillations produced by the high-order derivatives of the level-set function and is the key to the stability enhancement. A local treatment scheme was also developed which is crucial in the simulation of merging events. Results on several benchmark problems have demonstrated. Compared with some semi-implicit methods, the developed method is more accurate and has the same, if not better, stability.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Osher, S., Sethian, J.A.: Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton–Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 79(1), 12–49 (1988)
Mulder, W., Osher, S., Sethian, J.A.: Computing interface motion in compressible gas dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 100(2), 209–228 (1992)
Sussman, M., Smereka, P., Osher, S.: A level set approach for computing solutions to incompressible two-phase flow. J. Comput. Phys. 114(1), 146–159 (1994)
English, R.E., Qiu, L., Yu, Y., Fedkiw, R.: Chimera grids for water simulation. In: Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation 2013, pp. 85–94. ACM (2013)
Caselles, V., Morel, J.-M., Sapiro, G., Tannenbaum, A.R.: Introduction to the special issue on partial differential equations and geometry-driven diffusion in image processing and analysis. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 7(3), 269–274 (1998)
Li, C., Xu, C., Gui, C., Fox, M.D.: Distance regularized level set evolution and its application to image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(12), 3243–3254 (2010)
Xie, X., Wang, C., Zhang, A., Meng, X.: Active contours model exploiting hybrid image information: an improved formulation and level set method. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 9(20), 8371–8379 (2013)
Li, Z., Zhao, H., Gao, H.: A numerical study of electro-migration voiding by evolving level set functions on a fixed Cartesian grid. J. Comput. Phys. 152(1), 281–304 (1999)
Chopp, D.L., Sethian, J.A.: Motion by intrinsic Laplacian of curvature. Interfaces Free Bound. 1(1), 107–123 (1999)
Smereka, P.: Semi-implicit level set methods for curvature and surface diffusion motion. J. Sci. Comput. 19(1), 439–456 (2003)
Kolahdouz, E.M., Salac, D.: A semi-implicit gradient augmented level set method. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 35(1), A231–A254 (2013)
Bruchon, J., Drapier, S., Valdivieso, F.: 3D finite element simulation of the matter flow by surface diffusion using a level set method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 86(7), 845–861 (2011)
Ascher, U.M., Ruuth, S.J., Spiteri, R.J.: Implicit-explicit Runge–Kutta methods for time-dependent partial differential equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 25(2), 151–167 (1997)
Boscarino, S., Filbet, F., Russo, G.: High order semi-implicit schemes for time dependent partial differential equations. preprint (2014)
Chopp, D.L.: Computing minimal surfaces via level set curvature flow. J. Comput. Phys. 106(1), 77–91 (1993)
Peng, D., Merriman, B., Osher, S., Zhao, H., Kang, M.: A PDE-based fast local level set method. J. Comput. Phys. 155(2), 410–438 (1999)
Sethian, J.A.: Fast marching methods. SIAM Rev. 41(2), 199–235 (1999)
Salac, D.: The augmented fast marching method for level set reinitialization. Bull. Am. Phys. Soc. 56 (2011)
Anumolu, L., Trujillo, M.F.: Gradient augmented reinitialization scheme for the level set method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 73(12), 1011–1041 (2013)
Sethian, J.A.: Curvature and the evolution of fronts. Commun. Math. Phys. 101(4), 487–499 (1985)
Osher, S., Ronald, F.: Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces, 2003 edition. Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol. 153. Springer, New York, 31 Oct (2002)
Elsey, M., Esedoglu, S.: Fast and accurate redistancing by directional optimization. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 36(1), A219–A231 (2014)
Saye, R.: High-order methods for computing distances to implicitly defined surfaces. Commun. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 9(1), 107–141 (2014)
Macklin, P., Lowengrub, J.: Evolving interfaces via gradients of geometry-dependent interior Poisson problems: application to tumor growth. J. Comput. Phys. 203(1), 191–220 (2005)
Ruuth, S.J.: Efficient algorithms for diffusion-generated motion by mean curvature. J. Comput. Phys. 144(2), 603–625 (1998). doi:10.1006/jcph.1998.6025
Ruuth, S.J.: A diffusion-generated approach to multiphase motion. J. Comput. Phys. 145(1), 166–192 (1998). doi:10.1006/jcph.1998.6028
Zhang, K.H., Zhang, L., Song, H.H., Zhang, D.: Reinitialization-free level set evolution via reaction diffusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(1), 258–271 (2013). doi:10.1109/tip.2012.2214046
Strang, G.: The discrete cosine transform. SIAM Rev. 41(1), 135–147 (1999)
Weinert, H.L.: Efficient computation for Whittaker–Henderson smoothing. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 52(2), 959–974 (2007)
Garcia, D.: Robust smoothing of gridded data in one and higher dimensions with missing values. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 54(4), 1167–1178 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.csda.2009.09.020
Pan, J., Cocks, A., Kucherenko, S.: Finite element formulation of coupled grain-boundary and surface diffusion with grain-boundary migration. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 453(1965), 2161–2184 (1997)
Barrett, J.W., Garcke, H., Nürnberg, R.: A parametric finite element method for fourth order geometric evolution equations. J. Comput. Phys. 222(1), 441–467 (2007)
Chopp, D.L.: Some improvements of the fast marching method. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 23(1), 230–244 (2001)
Buckley, M.J.: Fast computation of a discretized thin-plate smoothing spline for image data. Biometrika 81(2), 247–258 (1994). doi:10.1093/biomet/81.2.247
Shu, C.-W., Osher, S.: Efficient implementation of essentially non-oscillatory shock-capturing schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 77(2), 439–471 (1988)
Salac, D., Lu, W.: A local semi-implicit level-set method for interface motion. J. Sci. Comput. 35(2–3), 330–349 (2008). doi:10.1007/s10915-008-9188-6
Lervåg, K.Y.: Calculation of interface curvature with the level-set method. In: Sixth National Conference on Computational Mechanics MekIT’ 11, Trondherim (2011)
Macklin, P., Lowengrub, J.: An improved geometry-aware curvature discretization for level set methods: application to tumor growth. J. Comput. Phys. 215(2), 392–401 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2005.11.016
Ervik, Å., Lervåg, K.Y., Munkejord, S.T.: A robust method for calculating interface curvature and normal vectors using an extracted local level set. J. Comput. Phys. 257, 259–277 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2013.09.053
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
The algorithm for our new approach is summarized as follows:

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Ye, W. A High-Order Level-Set Method with Enhanced Stability for Curvature Driven Flows and Surface Diffusion Motion. J Sci Comput 69, 1316–1345 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0236-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0236-3