Abstract
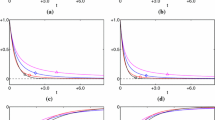
In this paper, we develop a fast algorithm for solving an unconstrained optimization model for uniform noise removal which is an important task in inverse problems. The optimization model consists of an \(\ell _\infty \) data fitting term and a total variation regularization term. By utilizing the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) for such optimization model, we demonstrate that one of the ADMM subproblems can be formulated by involving a projection onto \(\ell _1\) ball which can be solved efficiently by iterations. The convergence of the ADMM method can be established under some mild conditions. In practice, the balance between the \(\ell _\infty \) data fitting term and the total variation regularization term is controlled by a regularization parameter. We present numerical experiments by using the L-curve method of the logarithms of data fitting term and total variation regularization term to select regularization parameters for uniform noise removal. Numerical results for image denoising and deblurring, inverse source, inverse heat conduction problems and second derivative problems have shown the effectiveness of the proposed model.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alliney, S.: A property of the minimum vectors of a regularizing functional defined by means of the absolute norm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45(4), 913–917 (1997)
Aubert, G., Aujol, J.-F.: A variational approach to removing multiplicative noise. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 68(4), 925–946 (2008)
Bai, M., Zhang, X., Shao, Q.: Adaptive correction procedure for TVL1 image deblurring under impulse noise. Inverse Probl. 32(8), 085004 (2016)
Bertero, M., Boccacci, P.: Introduction to Inverse Problems in Imaging. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1998)
Bovik, A.: Handbook of Image and Video Processing. Academic Press, New York (2000)
Boyd, S., Parikh, N., Chu, E., Peleato, B., Eckstein, J.: Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 3(1), 1–122 (2011)
Castellanos, J.L., Gómez, S., Guerra, V.: The triangle method for finding the corner of the L-curve. Appl. Numer. Math. 43(4), 359–373 (2002)
Chan, T.F., Esedoglu, S.: Aspects of total variation regularized \({L}^1\) function approximation. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 65(5), 1817–1837 (2005)
Clason, C.: \({L}^{\infty }\) fitting for inverse problems with uniform noise. Inverse Probl. 28(10), 104007 (2012)
Clason, C., Jin, B., Kunisch, K.: A semismooth Newton method for \(\text{ L }^1\) data fitting with automatic choice of regularization parameters and noise calibration. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 3(2), 199–231 (2010)
Colton, D., Coyle, J., Monk, P.: Recent developments in inverse acoustic scattering theory. SIAM Rev. 42(3), 369–414 (2000)
Condat, L.: Fast projection onto the simplex and the \(l_1\) ball. Math. Program. 158(1–2), 575–585 (2016)
Dong, Y., Zeng, T.: A convex variational model for restoring blurred images with multiplicative noise. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 6(3), 1598–1625 (2013)
Duchi, J., Shalev-Shwartz, S., Singer, Y., Chandra, T.: Efficient projections onto the \(\ell _1\)-ball for learning in high dimensions. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 272–279. ACM (2008)
Durand, S., Nikolova, M.: Denoising of frame coefficients using \(\ell ^1\) data-fidelity term and edge-preserving regularization. Multiscale Model. Simul. 6(2), 547–576 (2007)
Fazel, M., Pong, T.K., Sun, D., Tseng, P.: Hankel matrix rank minimization with applications to system identification and realization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 34(3), 946–977 (2013)
Gabay, D., Mercier, B.: A dual algorithm for the solution of nonlinear variational problems via finite element approximation. Comput. Math. Appl. 2(1), 17–40 (1976)
Glowinski, R., Marrocco, A.: Sur l’approximation par éléments finis d’ordre un, et la résolution, par pénalisation-dualité, d’une classe de problèmes de Dirichlet non linéaires. Revue Française d’Autom. Informat. Rech. Opér. Anal. Numér 9(R2), 41–76 (1975)
Gonzalez, R.C., Woods, R.E.: Digital Image Processing, 3rd edn. Pearson, London (2008)
Hansen, P.C.: Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of the L-curve. SIAM Rev. 34(4), 561–580 (1992)
Hansen, P.C.: Rank-Deficient and Discrete Ill-Posed Problems: Numerical Aspects of Linear Inversion. SIAM, Philadephia (1998)
Hansen, P.C.: Regularization tools version 4.0 for Matlab 7.3. Numer. Algorithms 46(2), 189–194 (2007)
Hansen, P.C., O’Leary, D.P.: The use of the L-curve in the regularization of discrete ill-posed problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 14(6), 1487–1503 (1993)
Held, M., Wolfe, P., Crowder, H.P.: Validation of subgradient optimization. Math. Program. 6(1), 62–88 (1974)
Huang, Y.-M., Lu, D.-Y., Zeng, T.: Two-step approach for the restoration of images corrupted by multiplicative noise. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 35(6), A2856–A2873 (2013)
Huang, Y.-M., Moisan, L., Ng, M.K., Zeng, T.: Multiplicative noise removal via a learned dictionary. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(11), 4534–4543 (2012)
Huang, Y.-M., Ng, M.K., Wen, Y.-W.: A fast total variation minimization method for image restoration. Multiscale Model. Simul. 7(2), 774–795 (2008)
Kay, S.M.: Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing: Estimation Theory. Prentice-Hall PTR, Englewood Cliffs (1993)
Le, T., Chartrand, R., Asaki, T.J.: A variational approach to reconstructing images corrupted by Poisson noise. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 27(3), 257–263 (2007)
Ng, M.K.: Iterative Methods for Toeplitz Systems. Oxford University Press, London (2004)
Ng, M.K., Chan, R.H., Tang, W.-C.: A fast algorithm for deblurring models with Neumann boundary conditions. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 21(3), 851–866 (1999)
Nikolova, M.: Minimizers of cost-functions involving non-smooth data-fidelity terms. Application to the processing of outliers. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40(3), 965–994 (2002)
Nikolova, M.: A variational approach to remove outliers and impulse noise. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 20(1–2), 99–120 (2004)
Nikolova, M.: Weakly constrained minimization: application to the estimation of images and signals involving constant regions. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 21(2), 155–175 (2004)
Parikh, N., Boyd, S.: Proximal algorithms. Found. Trends Optim. 1(3), 127–239 (2014)
Rockafellar, R.T.: Convex Analysis. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1970)
Rockafellar, R.T., Wets, R.J.-B.: Variational Analysis, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Rudin, L.I., Osher, S.: Total variation based image restoration with free local constraints. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, volume 1, pp. 31–35. Austin, TX (1994)
Rudin, L.I., Osher, S., Fatemi, E.: Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D 60(1–4), 259–268 (1992)
Sciacchitano, F., Dong, Y., Zeng, T.: Variational approach for restoring blurred images with Cauchy noise. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 8(3), 1894–1922 (2015)
Setzer, S., Steild, G., Teuber, T.: Deblurring Poissonian images by split Bregman techniques. J. Vis. Commun. Image Rep. 21(3), 193–199 (2010)
Steidl, G., Teuber, T.: Removing multiplicative noise by Douglas–Rachford splitting methods. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 36(2), 168–184 (2010)
Tikhonov, A.N., Arsenin, V.Y.: Solutions of Ill-Posed Problems. Winston, Washington, DC (1977)
van den Berg, E., Friedlander, M.P.: Probing the pareto frontier for basis pursuit solutions. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31(2), 890–912 (2008)
Wan, T., Canagarajah, N., Achim, A.: Segmentation of noisy colour images using Cauchy distribution in the complex wavelet domain. IET Image Process. 5(2), 159–170 (2011)
Wang, F., Zhao, X.-L., Ng, M.K.: Multiplicative noise and blur removal by framelet decomposition and \(\ell _1\)-based L-curve method. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(9), 4222–4232 (2016)
Weiss, P., Aubert, G., Blanc-Féraud, L.: Some Applications of \(\ell ^{\infty }\)-Constraints in Image Processing. INRIA Resarch Report 6115 (2006)
Wen, Y.-W., Chan, R.H., Zeng, T.: Primal-dual algorithms for total variation based image restoration under Poisson noise. Sci. China Math. 59(1), 141–160 (2016)
Wen, Y.-W., Ching, W.-K., Ng, M.K.: A semi-smooth Newton method for inverse problem with uniform noise. J. Sci. Comput. 75(2), 713–732 (2018)
Yang, J., Zhang, Y., Yin, W.: An efficient TVL1 algorithm for deblurring multichannel images corrupted by impulsive noise. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31(4), 2842–2865 (2009)
Zhang, X., Bai, M., Ng, M.K.: Nonconvex-TV based image restoration with impulse noise removal. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 10(3), 1627–1667 (2017)
Zhang, X., Ng, M.K., Bai, M.: A fast algorithm for deconvolution and Poisson noise removal. J. Sci. Comput. 75(3), 1535–1554 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous referees for their constructive comments and suggestions that have helped improve the presentation of the paper greatly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiongjun Zhang: Research supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 11801206, 11571098, 11871026, Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 2018CFB105, and Self-Determined Research Funds of CCNU from the Colleges’ Basic Research and Operation of MOE under Grant CCNU17XJ031. Michael K. Ng: Research supported in part by the HKRGC GRF 1202715, 12306616, 12200317 and HKBU RC-ICRS/16-17/03.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Ng, M.K. A Fast Algorithm for Solving Linear Inverse Problems with Uniform Noise Removal. J Sci Comput 79, 1214–1240 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-018-0888-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-018-0888-2
Keywords
- Uniform noise
- Linear inverse problems
- Total variation
- \(\ell _\infty \)-Norm
- Alternating direction method of multipliers