Abstract
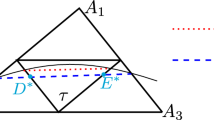
It is known that the convergence rate of the traditional iteration methods like the conjugate gradient method depends on the condition number of the stiffness matrix. Moreover the construction of fast solvers like multigrid and domain decomposition methods also need to estimate the condition number of the stiffness matrix. The main purpose of this paper is to give a rigorous condition number estimate of the stiffness matrix resulting from the linear and bilinear immersed finite element approximations of the high-contrast interface problem. It is shown that the condition number is \(C\rho h^{-2}\), where \(\rho \) is the jump of the discontinuous coefficients, h is the mesh size, and the constant C is independent of \(\rho \) and the location of the interface on the triangulation. Numerical results are also given to verify our theoretical findings.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burman, E.: Ghost penalty. C. R. Math. 348(21), 1217–1220 (2010)
Chen, Z., Zou, J.: Finite element methods and their convergence for elliptic and parabolic interface problems. Numer. Math. 79(2), 175–202 (1998)
Chou, S.-H., Kwak, D.Y., Wee, K.T.: Optimal convergence analysis of an immersed interface finite element method. Adv. Comput. Math. 33(2), 149–168 (2010)
Chu, C.-C., Graham, I., Hou, T.-Y.: A new multiscale finite element method for high-contrast elliptic interface problems. Math. Comput. 79(272), 1915–1955 (2010)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam (1978)
Guo, R., Lin, T.: A group of immersed finite-element spaces for elliptic interface problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 39(1), 482–511 (2017)
Guo, R., Lin, T., Zhang, X.: Nonconforming immersed finite element spaces for elliptic interface problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 75(6), 2002–2016 (2018)
Guzmán, J., Sánchez, M.A., Sarkis, M.: A finite element method for high-contrast interface problems with error estimates independent of contrast. J. Sci. Comput. 73(1), 330–365 (2017)
He, X., Lin, T., Lin, Y.: Approximation capability of a bilinear immersed finite element space. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 24(5), 1265–1300 (2008)
He, X., Lin, T., Lin, Y.: Immersed finite element methods for elliptic interface problems with non-homogeneous jump conditions. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 8(2), 284–301 (2011)
He, X., Lin, T., Lin, Y.: The convergence of the bilinear and linear immersed finite element solutions to interface problems. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 28(1), 312–330 (2012)
Huang, P., Wu, H., Xiao, Y.: An unfitted interface penalty finite element method for elliptic interface problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 323, 439–460 (2017)
Ji, H., Chen, J., Li, Z.: A symmetric and consistent immersed finite element method for interface problems. J. Sci. Comput. 61(3), 533–557 (2014)
Johansson, A., Larson, M.G.: A high order discontinuous Galerkin Nitsche method for elliptic problems with fictitious boundary. Numer. Math. 123(4), 607–628 (2013)
Li, Z., Lin, T., Lin, Y., Rogers, R.C.: An immersed finite element space and its approximation capability. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 20(3), 338–367 (2004)
Li, Z., Lin, T., Wu, X.: New Cartesian grid methods for interface problems using the finite element formulation. Numer. Math. 96(1), 61–98 (2003)
Lin, T., Lin, Y., Zhang, X.: Partially penalized immersed finite element methods for elliptic interface problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 53(2), 1121–1144 (2015)
Zhang, X.: Nonconforming immersed finite element methods for interface problems. Ph.D. thesis, Virginia Tech (2013)
Zunino, P., Cattaneo, L., Colciago, C.M.: An unfitted interface penalty method for the numerical approximation of contrast problems. Appl. Numer. Math. 61(10), 1059–1076 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The work of Saihua Wang and Xuejun Xu was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11671302, 11871272). Feng Wang was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11871281, 11871272). The author would like to thank the editor and the anonymous referees, who meticulously read through the paper and made valuable suggestions and comments which improve this paper greatly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Wang, F. & Xu, X. A Rigorous Condition Number Estimate of an Immersed Finite Element Method. J Sci Comput 83, 29 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-020-01212-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-020-01212-1