Abstract
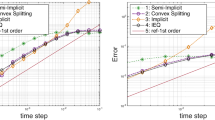
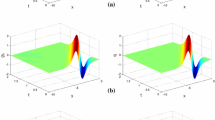
In this paper, we develop a fully discrete scheme to solve the well-known Allen–Cahn equation, where space is discretized by the hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method, and the time discretization is based on the newly developed Invariant Energy Quadratization approach. At each time step, the scheme results in a linear and uniquely solvable algebraic system. The scheme is shown to be unconditionally energy stable, and the optimal error estimates are rigorously established. Some numerical examples are presented to illustrate the temporal and spatial order of accuracy.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Allen, S.M., Cahn, J.W.: A microscopic theory for antiphase boundary motion and its application to antiphase domain coarsening. Acta Metallurgica 27(6), 1085–1095 (1979)
Chen, C., Yang, X.: Efficient numerical scheme for a dendritic solidification phase field model with melt convection. J. Comput. Phys. 388, 41–62 (2019)
Chen, C., Yang, X.: Fast, provably unconditionally energy stable, and second-order accurate algorithms for the anisotropic cahn-hilliard model. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 351, 35–59 (2019)
Cheng, Q., Shen, J.: Multiple scalar auxiliary variable (msav) approach and its application to the phase-field vesicle membrane model. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 40(6), A3982–A4006 (2018)
Choi, J.-W., Lee, H.G., Jeong, D., Kim, J.: An unconditionally gradient stable numerical method for solving the Allencahn equation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 388(9), 1791–1803 (2009)
Cockburn, B., Dong, B., Guzmán, J.: A hybridizable and superconvergent discontinuous galerkin method for biharmonic problems. J. Sci. Comput. 40(1–3), 141–187 (2009)
Cockburn, B., Gopalakrishnan, J., Lazarov, R.: Unified hybridization of discontinuous galerkin, mixed, and continuous galerkin methods for second order elliptic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47(2), 1319–1365 (2009)
Cockburn, B., Gopalakrishnan, J., Sayas, F.: A projection-based error analysis of hdg methods. Math. Comput. 79(271), 1351–1367 (2010)
Cockburn, B., Singler, J., Zhang, Y.: Interpolatory hdg method for parabolic semilinear pdes. J. Sci. Comput. 79(3), 1777–1800 (2019)
Dobrosotskaya, J., Bertozzi, A.: A wavelet-laplace variational technique for image deconvolution and inpainting. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 17(5), 657–663 (2008)
Dong, H., Wang, B., Xie, Z., Wang, L.-L.: An unfitted hybridizable discontinuous galerkin method for the poisson interface problem and its error analysis. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 37(1), 444–476 (2017)
Feng, X., Li, Y.: Analysis of symmetric interior penalty discontinuous galerkin methods for the allen-cahn equation and the mean curvature flow. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 35(4), 1622–1651 (2014)
Feng, X., Prohl, A.: Numerical analysis of the allen-cahn equation and approximation for mean curvature flows. Numer. Math. 94(1), 33–65 (2003)
Fernandez, P., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: The hybridized discontinuous galerkin method for implicit large-eddy simulation of transitional turbulent flows. J. Comput. Phys. 336, 308–329 (2017)
Giorgiani, G., Fernández-Méndez, S., Huerta, A.: Hybridizable discontinuous galerkin with degree adaptivity for the incompressible navier-stokes equations. Comput. Fluids 98, 196–208 (2014)
Gokieli, M., Marcinkowski, L.: Modelling phase transitions in alloys. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 63(5–7), e1143–e1153 (2005)
Gong, Y., Zhao, J., Yang, X., Wang, Q.: Fully discrete second-order linear schemes for hydrodynamic phase field models of binary viscous fluid flows with variable densities. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 40(1), B138–B167 (2018)
Guan, Z., Lowengrub, J., Wang, C., Wise, S.: Second order convex splitting schemes for periodic nonlocal cahn-hilliard and allen-cahn equations. J. Comput. Phys. 277, 48–71 (2014)
Guo, R., Ji, L., Xu, Y.: High order local discontinuous galerkin methods for the allen-cahn equation: analysis and simulation. J. Comput. Math. 34(2), 135–158 (2016)
Karasozen, B., Sariaydin-Filibelioglu, A., Uzunca, M., Yucel, H.: Energy stable discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for the Allen-Cahn equation. Int. J. Comput. Methods 1503, 1850013 (2018)
Li, B., Sun, W.: Unconditional convergence and optimal error estimates of a galerkin-mixed fem for incompressible miscible flow in porous media. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51(4), 1959–1977 (2013)
Liu, F., Shen, J.: Stabilized semi-implicit spectral deferred correction methods for Allen-Cahn and Cahn-Hilliard equations. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 38(18), 4564–4575 (2015)
Nguyen, N.C., Cockburn, B., Peraire, J.: Hybridizable discontinuous galerkin methods for the time-harmonic maxwell’s equations. J. Comput. Phys. 230(19), 7151–7175 (2011)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: Hybridizable discontinuous galerkin methods for partial differential equations in continuum mechanics. J. Comput. Phys. 231(18), 5955–5988 (2012)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: An implicit high-order hybridizable discontinuous galerkin method for linear convection-diffusion equations. J. Comput. Phys. 228(9), 3232–3254 (2009)
Paipuri, M., Fernández-Méndez, S., Tiago, C.: Comparison of high-order continuous and hybridizable discontinuous galerkin methods for incompressible fluid flow problems. Math. Comput. Simul. 153, 35–58 (2018)
Reed, W., Hill, T.: Triangular mesh methods for the neutron transport equation. Technical report, Los Alamos Scientific Lab., N. Mex.(USA), (1973)
Sheldon, J., Miller, S., Pitt, J.: A hybridizable discontinuous galerkin method for modeling fluid-structure interaction. J. Comput. Phys. 326, 91–114 (2016)
Shen, J., Xu, J., Yang, J.: The scalar auxiliary variable (sav) approach for gradient flows. J. Comput. Phys. 353, 407–416 (2018)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: Numerical approximations of allen-cahn and cahn-hilliard equations. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 28(4), 1669–1691 (2010)
Shin, J., Lee, H., Lee, J.: Unconditionally stable methods for gradient flow using convex splitting runge-kutta scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 347, 367–381 (2017)
Ueckermann, M.P., Lermusiaux, P.: Hybridizable discontinuous galerkin projection methods for navier-stokes and boussinesq equations. J. Comput. Phys. 306, 390–421 (2016)
Vidal-Codina, F., Nguyen, N.C., Oh, S.-H., Peraire, J.: A hybridizable discontinuous galerkin method for computing nonlocal electromagnetic effects in three-dimensional metallic nanostructures. J. Comput. Phys. 355, 548–565 (2018)
Wang, B., Khoo, B.C.: Hybridizable discontinuous galerkin method (hdg) for stokes interface flow. J. Comput. Phys. 247, 262–278 (2013)
Wheeler, A., Boettinger, W., McFadden, G.: Phase-field model for isothermal phase transitions in binary alloys. Phys. Rev. A 45(10), 7424 (1992)
Xia, Y., Xu, Y., Shu, C.: Application of the local discontinuous galerkin method for the allen-cahn/cahn-hilliard system. Commun. Comput. Phys. 5, 821–835 (2009)
Xiao, X., Feng, X., Yuan, J.: The stabilized semi-implicit finite element method for the surface allen-cahn equation. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 22(7), 2857 (2017)
Xu, Z., Yang, X., Zhang, H., Xie, Z.: Efficient and linear schemes for anisotropic cahn-hilliard model using the stabilized-invariant energy quadratization (s-ieq) approach. Comput. Phys. Commun. 238, 36–49 (2019)
Yang, X.: Linear, first and second order and unconditionally energy stable numerical schemes for the phase field model of homopolymer blends. J. Comput. Phys. 327, 294–316 (2016)
Yang, X.: Efficient Linear, stabilized, second order time marching schemes for an anisotropic phase field dendritic crystal growth model. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engrg. 347, 316–339 (2019)
Yang, X., Yu, H.: Efficient Second Order Unconditionally Stable Schemes for a Phase Field Moving Contact Line Model Using an Invariant Energy Quadratization Approach. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 40, B889–B914 (2018)
Yang, X., Zhang, G.: Convergence analysis for the invariant energy quadratization (ieq) schemes for solving the cahn-hilliard and allen-cahn equations with general nonlinear potential. J. Sci. Comput. 82, 55 (2020)
Yang, X., Zhao, J., Wang, Q., Shen, J.: Numerical approximations for a three components Cahn-Hilliard phase-field model based on the invariant energy Quadratization method. M3AS Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 27, 1993–2030 (2017)
Zhang, J., Chen, C., Wang, J., Yang, X.: Efficient, second oder accurate, and unconditionally energy stable numerical scheme for a new hydrodynamics coupled binary phase-field surfactant system. Comput. Phys. Commun., p 107122, (2019)
Zhang, J., Chen, C., Yang, X.: A novel Decoupled and stable scheme for an anisotropic phase-field dendritic crystal growth model. Appl. Math. Lett. 95, 122–129 (2019)
Zhang, J., Yang, X.: Unconditionally energy stable large time stepping method for the l2-gradient flow based ternary phase-field model with precise nonlocal volume conservation. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 361, 112743 (2020)
Zhao, J., Wang, Q., Yang, X.: Numerical approximations for a phase field dendritic crystal growth model based on the invariant energy quadratization approach. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 110(3), 279–300 (2017)
Zhao, J., Yang, X., Li, J., Wang, Q.: Energy stable numerical schemes for a hydrodynamic model of nematic liquid crystals. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 38(5), A3264–A3290 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous referees for the valuable comments and constructive suggestions to improve this paper.
Funding
The work of J. Wang was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11801171). The work of K. Pan was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41874086) and Science Challenge Project (Grant No. TZ2016002). The work of X. Yang was partially supported by National Science Foundation of USA with grant number DMS-2012490.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Pan, K. & Yang, X. Convergence Analysis of the Fully Discrete Hybridizable Discontinuous Galerkin Method for the Allen–Cahn Equation Based on the Invariant Energy Quadratization Approach. J Sci Comput 91, 49 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-01822-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-01822-x