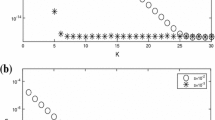
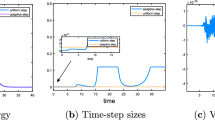
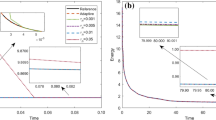
Abstract
We propose and analyze a BDF2 scheme with variable time steps for the Cahn–Hilliard equation with a logarithmic Flory–Huggins energy potential. The lumped mass method is adopted in the space discretization to ensure that the proposed scheme is uniquely solvable and positivity-preserving. Especially, a new second order viscous regularization term is added at the discrete level to guarantee the energy dissipation property. Furthermore, the energy stability is derived by a careful estimate under the condition that \(r\le r_{\max }\). To estimate the spatial and temporal errors separately, a spatially semi-discrete scheme is proposed and a new elliptic projection is introduced, and the super-closeness between this projection and the Ritz projection of the exact solution is attained. Based on the strict separation property of the numerical solution obtained by using the technique of combining the rough and refined error estimates, the convergence analysis in \(l^{\infty }(0,T;L_h^2(\varOmega ))\) norm is established when \(\tau \le Ch\) by using the technique of the DOC kernels. Finally, several numerical experiments are carried out to validate the theoretical results.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availibility
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abels, H.: On a diffuse interface model for two-phase flows of viscous, incompressible fluids with matched densities. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 194(2), 463–506 (2009)
Abels, H., Wilke, M.: Convergence to equilibrium for the Cahn–Hilliard equation with a logarithmic free energy. Nonlinear Anal.: Theory Methods Appl. 67(11), 3176–3193 (2007)
Adams, R., Fournier, J.: Sobolev Spaces. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2003)
Anderson, D.M., McFadden, G.B., Wheeler, A.A.: Diffuse-interface methods in fluid mechanics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30(1), 139–165 (1998)
Barrett, J.W., Blowey, J.F., Garcke, H.: Finite element approximation of the Cahn–Hilliard equation with degenerate mobility. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 37(1), 286–318 (1999)
Becker, J.: A second order backward difference method with variable steps for a parabolic problem. BIT Numer. Math. 38(4), 644–662 (1998)
Blowey, J.F., Copetti, M., Elliott, C.M.: Numerical analysis of a model for phase separation of a multicomponent alloy. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 16(1), 111–139 (1996)
Cahn, J.W., Elliott, C.M., Novick-Cohen, A.: The Cahn–Hilliard equation with a concentration dependent mobility: motion by minus the Laplacian of the mean curvature. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 7(3), 287–301 (1996)
Cahn, J.W., Hilliard, J.E.: Free energy of a nonuniform system. I. Interfacial free energy. J. Chem. Phys. 28(2), 258–267 (1958)
Cahn, J.W., Hilliard, J.E.: Spinodal decomposition: a reprise. Acta Metall. 19(2), 151–161 (1971)
Chen, W., Conde, S., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: A linear energy stable scheme for a thin film model without slope selection. J. Sci. Comput. 52(3), 546–562 (2012)
Chen, W., Jing, J., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: A modified Crank–Nicolson numerical scheme for the Flory–Huggins Cahn–Hilliard model. Commun. Comput. Phys. 31(1), 60–93 (2022)
Chen, W., Li, W., Luo, Z., Wang, C., Wang, X.: A stabilized second order exponential time differencing multistep method for thin film growth model without slope selection. ESAIM: Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 54(3), 727–750 (2020)
Chen, W., Li, W., Wang, C., Wang, S., Wang, X.: Energy stable higher-order linear ETD multi-step methods for gradient flows: application to thin film epitaxy. Res. Math. Sci. 7(3), 1–27 (2020)
Chen, W., Liu, Q., Shen, J.: Error estimates and blow-up analysis of a finite-element approximation for the parabolic-elliptic Keller–Segel system. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 19(2–3), 275–298 (2022)
Chen, W., Liu, Y., Wang, C., Wise, S.: Convergence analysis of a fully discrete finite difference scheme for the Cahn–Hilliard–Hele–Shaw equation. Math. Comput. 85(301), 2231–2257 (2016)
Chen, W., Wang, C., Wang, S., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: Energy stable numerical schemes for ternary Cahn–Hilliard system. J. Sci. Comput. 84(2), 1–36 (2020)
Chen, W., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: Positivity-preserving, energy stable numerical schemes for the Cahn–Hilliard equation with logarithmic potential. J. Comput. Phys.: X 3, 100031 (2019)
Chen, W., Wang, X., Yan, Y., Zhang, Z.: A second order BDF numerical scheme with variable steps for the Cahn–Hilliard equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 57(1), 495–525 (2019)
Cheng, K., Wang, C., Wise, S.M., Wu, Y.: A third order accurate in time, BDF-type energy stable scheme for the Cahn–Hilliard equation. Numer. Math.: Theory Methods Appl. 15(2), 279–303 (2022)
Cherfils, L., Miranville, A., Zelik, S.: The Cahn–Hilliard equation with logarithmic potentials. Milan J. Math. 79(2), 561–596 (2011)
Choksi, R.: Scaling laws in microphase separation of diblock copolymers. J. Nonlinear Sci. 11(3), 223–236 (2001)
Copetti, M.I.M., Elliott, C.M.: Numerical analysis of the Cahn–Hilliard equation with a logarithmic free energy. Numer. Math. 63(1), 39–65 (1992)
Debussche, A., Dettori, L.: On the Cahn–Hilliard equation with a logarithmic free energy. Nonlinear Anal.: Theory Methods Appl. 24(10), 1491–1514 (1995)
Diegel, A.E., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: Convergence analysis and error estimates for a second order accurate finite element method for the Cahn–Hilliard–Navier–Stokes system. Numer. Math. 137(3), 495–534 (2017)
Doi, M.: Soft Matter Physics. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2013)
Dong, L., Wang, C., Wise, S.M., Zhang, Z.: A positivity-preserving, energy stable scheme for a ternary Cahn–Hilliard system with the singular interfacial parameters. J. Comput. Phys. 442, 110451 (2021)
Dong, L., Wang, C., Zhang, H., Zhang, Z.: A positivity-preserving, energy stable and convergent numerical scheme for the Cahn–Hilliard equation with a Flory–Huggins–Degennes energy. Commun. Math. Sci. 17(4), 921–939 (2019)
Dong, L., Wang, C., Zhang, H., Zhang, Z.: A positivity-preserving second-order BDF scheme for the Cahn–Hilliard equation with variable interfacial parameters. Commun. Comput. Phys. 28(3), 967–998 (2020). https://doi.org/10.4208/cicp.oa-2019-0037
Elliott, C.M., Garcke, H.: On the Cahn–Hilliard equation with degenerate mobility. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 27(2), 404–423 (1996)
Eyre, D.J.: Unconditionally gradient stable time marching the Cahn–Hilliard equation. MRS Online Proc. Libr. (OPL) 529, 39 (1998)
Feng, X., Prohl, A.: Error analysis of a mixed finite element method for the Cahn–Hilliard equation. Numer. Math. 99(1), 47–84 (2004)
Giacomelli, L., Otto, F.: Variatonal formulation for the lubrication approximation of the Hele–Shaw flow. Calc. Var. Partial Differ. Equ. 13(3), 377–403 (2001)
Grigorieff, R.D.: Stability of multistep-methods on variable grids. Numer. Math. 42(3), 359–377 (1983)
Gurtin, M.E., Polignone, D., Vinals, J.: Two-phase binary fluids and immiscible fluids described by an order parameter. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 6(06), 815–831 (1996)
Hou, D., Qiao, Z.: A linear adaptive BDF2 scheme for phase field crystal equation (2022). arXiv:2206.07625
Huang, J., Yang, C., Wei, Y.: Parallel energy-stable solver for a coupled Allen–Cahn and Cahn–Hilliard system. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 42(5), C294–C312 (2020)
Ji, G., Yang, Y., Zhang, H.: Modeling and simulation of a ternary system for macromolecular microsphere composite hydrogels. East Asian J. Appl. Math. 11(1), 93–118 (2021)
Kang, Y., Liao, Hl.: Energy stability of BDF methods up to fifth-order for the molecular beam epitaxial model without slope selection. J. Sci. Comput. 91(2), 1–22 (2022)
Kim, J.: Phase-field models for multi-component fluid flows. Commun. Comput. Phys. 12(3), 613–661 (2012)
Larson, R.: Arrested tumbling in shearing flows of liquid-crystal polymers. Macromolecules 23(17), 3983–3992 (1990)
Larson, R., Ottinger, H.: Effect of molecular elasticity on out-of-plane orientations in shearing flows of liquid-crystalline polymers. Macromolecules 24(23), 6270–6282 (1991)
Leslie, F.M.: Theory of flow phenomena in liquid crystals. In: Advances in Liquid Crystals, vol. 4, pp. 1–81. Elsevier (1979)
Li, D., Qiao, Z.: On second order semi-implicit Fourier spectral methods for 2D Cahn–Hilliard equations. J. Sci. Comput. 70(1), 301–341 (2017)
Li, X., Qiao, Z., Wang, C.: Stabilization parameter analysis of a second-order linear numerical scheme for the nonlocal Cahn–Hilliard equation. IMA J. Numer. Anal. (2022)
Li, X., Qiao, Z., Zhang, H.: An unconditionally energy stable finite difference scheme for a stochastic Cahn–Hilliard equation. Sci. China Math. 59(9), 1815–1834 (2016)
Liao, H., Ji, B., Wang, L., Zhang, Z.: Mesh-robustness of the variable steps BDF2 method for the Cahn–Hilliard model (2021). arXiv:2102.03731
Liao, H., Ji, B., Zhang, L.: An adaptive BDF2 implicit time-stepping method for the phase field crystal model. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 42(1), 649–679 (2022)
Liao, H., Kang, Y., Han, W.: Discrete gradient structures of BDF methods up to fifth-order for the phase field crystal model (2022). arXiv:2201.00609
Liao, H., Tang, T., Zhou, T.: A new discrete energy technique for multi-step backward difference formulas (2021). arXiv:2102.04644
Liao, H., Tang, T., Zhou, T.: Discrete energy analysis of the third-order variable-step BDF time-stepping for diffusion equations (2022). arXiv:2204.12742
Liu, C., Wang, C., Wise, S., Yue, X., Zhou, S.: A positivity-preserving, energy stable and convergent numerical scheme for the Poisson–Nernst–Planck system. Math. Comput. 90(331), 2071–2106 (2021)
Liu, Y., Chen, W., Wang, C., Wise, S.M.: Error analysis of a mixed finite element method for a Cahn–Hilliard–Hele–Shaw system. Numer. Math. 135(3), 679–709 (2017)
Lowengrub, J., Truskinovsky, L.: Quasi-incompressible Cahn–Hilliard fluids and topological transitions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 454(1978), 2617–2654 (1998)
Miranville, A.: On a phase-field model with a logarithmic nonlinearity. Appl. Math. 57(3), 215–229 (2012)
Miranville, A., Zelik, S.: Robust exponential attractors for Cahn–Hilliard type equations with singular potentials. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 27(5), 545–582 (2004)
Otto, F.: Lubrication approximation with prescribed nonzero contact anggle. Commun. Partial Differ. Equ. 23(11–12), 2077–2164 (1998)
Qiao, Z., Zhang, Z., Tang, T.: An adaptive time-stepping strategy for the molecular beam epitaxy models. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 33(3), 1395–1414 (2011)
Shen, J., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: Second-order convex splitting schemes for gradient flows with Ehrlich–Schwoebel type energy: application to thin film epitaxy. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(1), 105–125 (2012)
Shen, J., Xu, J., Yang, J.: The scalar auxiliary variable (SAV) approach for gradient flows. J. Comput. Phys. 353, 407–416 (2018)
Shen, J., Xu, J., Yang, J.: A new class of efficient and robust energy stable schemes for gradient flows. SIAM Rev. 61(3), 474–506 (2019)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: Numerical approximations of Allen–Cahn and Cahn–Hilliard equations. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Systems. 28(4), 1669 (2010)
Thomée, V.: Galerkin Finite Element Methods for Parabolic Problems, vol. 25. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Wang, W., Chen, Y., Fang, H.: On the variable two-step IMEX BDF method for parabolic integro-differential equations with nonsmooth initial data arising in finance. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 57(3), 1289–1317 (2019)
Wang, W., Mao, M., Huang, Y.: Optimal a posteriori estimators for the variable step-size BDF2 method for linear parabolic equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 413, 114306 (2022)
Wang, W., Mao, M., Wang, Z.: Stability and error estimates for the variable step-size BDF2 method for linear and semilinear parabolic equations. Adv. Comput. Math. 47(1), 1–28 (2021)
Wight, C.L., Zhao, J.: Solving Allen–Cahn and Cahn–Hilliard equations using the adaptive physics informed neural networks (2020). arXiv:2007.04542
Yan, Y., Chen, W., Wang, C., Wise, S.M.: A second-order energy stable BDF numerical scheme for the Cahn–Hilliard equation. Commun. Comput. Phys. 23(2), 572–602 (2018)
Yan, Y., Li, W., Chen, W., Wang, Y.: Optimal convergence analysis of a mixed finite element method for fourth-order elliptic problems. Commun. Comput. Phys. 24(2), 510–530 (2018)
Yang, X.: Linear, first and second-order, unconditionally energy stable numerical schemes for the phase field model of homopolymer blends. J. Comput. Phys. 327, 294–316 (2016)
Yang, X.: On a novel fully decoupled, second-order accurate energy stable numerical scheme for a binary fluid-surfactant phase-field model. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 43(2), B479–B507 (2021)
Yang, X., Zhao, J.: On linear and unconditionally energy stable algorithms for variable mobility Cahn–Hilliard type equation with logarithmic Flory–Huggins potential. Commun. Comput. Phys. 25(3), 703–728 (2017)
Yang, X., Zhao, J., Wang, Q., Shen, J.: Numerical approximations for a three-component Cahn–Hilliard phase-field model based on the invariant energy quadratization method. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 27(11), 1993–2030 (2017)
Yuan, M., Chen, W., Wang, C., Wise, S.M., Zhang, Z.: An energy stable finite element scheme for the three-component Cahn–Hilliard-type model for macromolecular microsphere composite hydrogels. J. Sci. Comput. 87(3), 1–30 (2021)
Yuan, M., Chen, W., Wang, C., Wise, S.M., Zhang, Z.: A second order accurate in time, energy stable finite element scheme for the Flory–Huggins–Cahn–Hilliard equation. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 14(6), 1477–1508 (2022)
Yue, P., Feng, J.J., Liu, C., Shen, J.: A diffuse-interface method for simulating two-phase flows of complex fluids. J. Fluid Mech. 515, 293–317 (2004)
Zhang, Z., Ma, Y., Qiao, Z.: An adaptive time-stepping strategy for solving the phase field crystal model. J. Comput. Phys. 249, 204–215 (2013)
Zhao, J., Wang, Q., Yang, X.: Numerical approximations for a phase field dendritic crystal growth model based on the invariant energy quadratization approach. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 110(3), 279–300 (2017)
Zhu, J., Chen, L.Q., Shen, J., Tikare, V.: Coarsening kinetics from a variable-mobility Cahn–Hilliard equation: application of a semi-implicit Fourier spectral method. Phys. Rev. E 60(4), 35–64 (1999)
Acknowledgements
W. Chen is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) 12241101 and NSFC 12071090. The authors would like to thank anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions that have improved the manuscript.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Jing, J., Yuan, M. et al. A Positivity-Preserving, Energy Stable BDF2 Scheme with Variable Steps for the Cahn–Hilliard Equation with Logarithmic Potential. J Sci Comput 95, 37 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02163-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02163-z
Keywords
- Variable-step BDF2 scheme
- Cahn–Hilliard equation
- Logarithmic potential
- Lumped mass method
- Energy dissipation
- Convergence analysis