Abstract
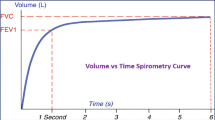
In this work, an attempt has been made to enhance the diagnostic relevance of spirometric pulmonary function test using neural networks and Principal Component Analysis (PCA). For this study, flow–volume curves (N = 175) using spirometers were generated under standard recording protocol. A method based on neural network is used to predict the most significant parameter, FEV1. Further, PCA is used to analyze the interdependency of the parameters in the measured and predicted datasets. Results show that the back propagation neural network is able to predict FEV1 both in normal and abnormal cases. The variation in the magnitude and direction of parameters in the contribution of the principal components shows that FEV1 is a significant discriminator of normal and abnormal datasets and is further confirmed by the percentage variance in the first few principal components. It appears that this method of prediction and principal component analysis on the measured and predicted datasets could be useful for spirometric pulmonary function test with incomplete data.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crapo, R. O., Pulmonary—function testing. N. Eng. J. Med. 331:25–30, 1994.
Miller, M. R., Hankinson, J., Brusasco, V., Burgos, F., Casaburi, R., Coates, A., Crapo, R., Enright, P., van der Grinten, C. P. M., Gustafsson, P., Jensen, R., Johnson, D. C., MacIntyre, N., McKay, R., Navajas, D., Pedersen, O. F., Pellegrino, R., Viegi, G., and Wanger, J., Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Resp. J. 26:319–338, 2005.
Wagner, N. L., Beckett, W. S., and Steinberg, R., Using spirometry results in occupational medicine and research: common errors and good practice in statistical analysis and reporting. Ind. J. Occ. Environ. Med. 10:5–10, 2006.
Arora, V. K., and Raghu, S., Flow volume curves: clinical significance. Lung Ind. 14:169–171, 2000.
Feyrouz, A., Reena, M., and Peter, J. M., Interpreting pulmonary function tests: recognise the pattern, and the diagnosis will follow. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 70:866–880, 2003.
Pierce, R., Spirometer: an essential clinical measurement. Aust. Fam. Phys. 34:535–539, 2004.
David, P. J., and Rob, P., Spirometry—The measurement and interpretation of ventilatory function in clinical practice. Spirometry Handbook, 3rd edition. 1–24, 2008.
Timothy, J. B., and Irene, P., An approach to interpreting spirometry. Am. Fam. Phys. 69:1108–1114, 2004.
Dimitrios, P., Georgios, E., Kiriakos, K., Nikolas, Z., Panos, G., and Kostas, S., Lung function measurements in traditional bakers. Acta Biomed. 79:197–203, 2008.
Ulmer, W. T., Lung function—clinical importance, problems and new results. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 54:11–13, 2003.
Jesu, C. J., and Ramakrishnan, S., Assessment and classification of mechanical strength components of human trabecular bone using digital image processing and neural networks. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 7:315–324, 2007.
Sujatha, C. M., and Ramakrishnan, S., Prediction of forced expiratory volume in pulmonary function test using radial basis neural networks and k-means clustering. J. Med. Syst. (Under Print— 10.1007/s10916-008-9196-y), 2008.
Sachin, M. B., SangChul, P., and Gi-Nam, W., Predicting extrusion process parameters using neural networks. Int. J. Mech. Syst. Sci. Eng. 1:161–167, 2007.
Benardos, P. G., and Vosniakos, G. C., Optimizing feed forward artificial neural network architecture. Eng. App Art. Int. 20:365–382, 2007.
Rakesh, K. S., Artificial neural network and wavelet based automated detection of sleep spindles, REM sleep and wake states. J. Med. Syst. 32:291–299, 2008.
Gaetano, P., Marieann, H., Christian, R., Rocco, G., Tommaso, F., and Goron, H., Assessment of respiratory system mechanics by artificial neural networks: an exploratory study. J. App. Physiol. 90:1817–1824, 2001.
Lisboa, P. J. G., Emmanuel, C., Ifeachor, and Piotr, S. S., Artificial neural networks in biomedicine. Art. Int. Med. 25:211–214, 2002.
Mahesh, V., Sujatha, C. M., and Ramakrishnan, S., Experimental analysis on human respiratory dynamics using flow volume spirometry and combined neural networks. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 8:541–548, 2008.
Ferrigno, G., and Carnevali, P., Principal component analysis of chest wall movement in selected pathologies. Med. Biol. Eng. Comp. 36:445–451, 1998.
Salaffi, F., Manganelli, P., Carotti, M., and Baldelli, S., The differing patterns of subclinical pulmonary involvement in connective tissue diseases as shown by application of factor analysis. Clin. Rheumat. 19:35–41, 2000.
Marek, S., Pniewski, Emilia, K., Pawel, Z., Katarzyna, S., Agata, P., Mariusz, K., and Bogdan, B., Pattern recognition methods in evaluation of the structure of the laboratory data biominerals, antioxidant enzymes, selected biochemical parameters, and pulmonary function of welders. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 93:39–46, 2003.
Arnaz, M., and Robert, X. G., PCA-based feature selection scheme for machine defect classification. IEEE Trans. Inst. Meas. 53:1517–1525, 2004.
Terry, E. R., Ann, N. L., William, H. N., Francis, G. B., Frandics, P. C., Daniel, A. B., Tyson, H. H., and Richard, B. M., Composite spirometric–computed tomography outcome measure in early cystic fibrosis lung disease. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Car. Med. 188:688–693, 2003.
Jenkins, C. R., Thien, F. C. K., Wheatley, J. R., and Reddel, H. K., Traditional and patient—centred outcomes with three classes of asthma medication. Eur. Resp. J. 26:36–44, 2005.
Cooper, B. G., and Madsen, F. Eur. Resp. buyers guide. 3:40–43, 2000.
Igor, B., Principal component analysis is a powerful instrument in occupational hygiene enquiries. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 48:655–661, 2004.
Samanwoy, G. D., Hojjat, A., and Nahid, D., Principal component analysis—enhanced cosine radial basis function neural network for robust epilepsy and seizure detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 50:512–518, 2008.
Aguado, D., Montoy, T., Borras, L., Seco, A., and Ferrer, J., Using SOM and PCA for analyzing and interpreting data from a P-removal SBR. Eng. App. Art. Int. 21:919–930, 2008.
Gabriel, The biplot graphic display of matrices with application to principal component analysis. Biometrika. 58:453–467, 1971.
Daniel, C. G., and Jonathan, D. T., Clinical review: respiratory mechanics in spontaneous and assisted ventilation. Crit. Car. 9:472–484, 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kavitha, A., Sujatha, M. & Ramakrishnan, S. Evaluation of Flow–Volume Spirometric Test Using Neural Network Based Prediction and Principal Component Analysis. J Med Syst 35, 127–133 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-009-9349-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-009-9349-7