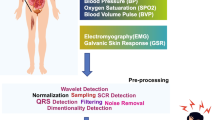
Abstract
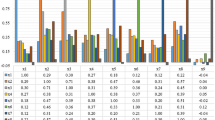
Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), usually observed commonly in females over age 30, is a rheumatic disease accompanied by extensive chronic pain. In the diagnosis of the disease non-objective psychological tests and physiological tests and laboratory test results are evaluated and clinical experiences stand out. However, these tests are insufficient in differentiating FMS with similar diseases that demonstrate symptoms of extensive pain. Thus, objective tests that would help the diagnosis are needed. This study analyzes the effect of sympathetic skin response (SSR) parameters on the auxiliary tests used in FMS diagnosis, the laboratory tests and physiological tests. The study was conducted in Suleyman Demirel University, Faculty of Medicine, Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinic in Turkey with 60 patients diagnosed with FMS for the first time and a control group of 30 healthy individuals. In the study all participants underwent laboratory tests (blood tests), certain physiological tests (pulsation, skin temperature, respiration) and SSR measurements. The test data and SSR parameters obtained were classified using artificial neural network (ANN). Finally, in the ANN framework, where only laboratory and physiological test results were used as input, a simulation result of 96.51 % was obtained, which demonstrated diagnostic accuracy. This data, with the addition of SSR parameter values obtained increased to 97.67 %. This result including SSR parameters – meaning a higher diagnostic accuracy – demonstrated that SSR could be a new auxillary diagnostic method that could be used in the diagnosis of FMS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boissevain, M.D., and McCain, G.A., Toward an integrated understanding of fibromyalgia syndrome. I. Medical and Pathophysiological Aspects. Pain. 45(3):227–238, 1991. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(91)90047-2.
Wolfe, F., Clauw, D.J., Fitzcharles, M.A., Goldenberg, D.L., Katz, R.S., Mease, P., Russell, A.S., Russell, I.J., Winfield, J.B., and Yunus, M.B., The American college of rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia and measurement of symptom severity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 62(5):600–610, 2010. doi:10.1002/acr.20140.
Ozkan, O., Yildiz, M., Bilgin, S., and Koklukaya, E., Measuring the sympathetic skin response on body and using as diagnosis-purposed for lung cancer patients by artificial neural networks. J Med Syst. 34(3):407–412, 2010. doi:10.1007/s10916-009-9253-1.
Ulas, U.H., Unlu, E., Hamamcioglu, K., Odabasi, Z., Cakci, A., and Vural, O., Dysautonomia in fibromyalgia syndrome: sympathetic skin responses and RR interval analysis. Rheumatol Int. 26(5):383–387, 2006. doi:10.1007/s00296-005-0007-1.
Yildiz, M., Ozkan, O., and Koklukaya, E., Investigating the effect of sympathetic skin response parameters on the psychological test scores in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome by using ANNs. SAU J. Sci. 17(1):27–32, 2013.
Ozgocmen, S., Yoldas, T., Yigiter, R., Kaya, A., and Ardicoglu, O., R-R interval variation and sympathetic skin response in fibromyalgia. Arch Med Res. 37(5):630–634, 2006. doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2005.11.008.
Tarvainen, M.P., Koistinen, A.S., Valkonen-Korhonen, M., Partanen, J., and Karjalainen, P.A., Analysis of galvanic skin responses with principal components and clustering techniques. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 48(10):1071–1079, 2001.
Tarvainen, M.P., Partanen, J., Karjalainen, P.A., Koistinen, A.S., and Valkonen-Korhonen, M., Principal component analysis of galvanic skin responses. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2000. Proceedings of the 22nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE 4:3011–3014, 2000. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2000.901513.
Everhart, D.E., and Harrison, D.W., Heart rate and fluency performance among high- and low-anxious men following autonomic stress. Int J Neurosci. 112(10):1149–1171, 2002. doi:10.1080/00207450290026120.
Ahuja ND, Agarwal AK, Mahajan NM, Mehta NH, Kapadia HN (2003) GSR and HRV: Its application in clinical diagnosis. Computer-Based Medical Systems, 2003. Proceedings. 16th IEEE Symposium 1:279–283. doi:10.1109/CBMS.2003.1212802
Ozkan, O., Yildiz, M., and Koklukaya, E., The correlation of laboratory tests and sympathetic skin response parameters by using artificial neural networks in fibromyalgia patients. J Med Syst. 36(3):1841–1848, 2012. doi:10.1007/s10916-010-9643-4.
Berger, M.J., Hubli, M., and Krassioukov, A.V., Sympathetic skin responses and autonomic dysfunction in spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 31(18):1531–1539, 2014. doi:10.1089/neu.2014.3373.
Saba, E., and Sultan, H., Autonomic nervous system changes associated with rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and electrophysiological study. The Egyptian Rheumatologist. 36(4):157–163, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.ejr.2014.03.002.
Dag, Z.O., Alpua, M., Turkel, Y., and Isik, Y., Autonomic dysfunction in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 54(4):381–384, 2015. doi:10.1016/j.tjog.2015.03.002.
Ozkan, O., Yildiz, M., and Koklukaya, E., Improving diagnostic accuracy by supporting the laboratory tests which used for diagnosis of fibromyalgia syndrome with the sympathetic skin response parameters. SAU J. Sci. 15(1):1–7, 2011.
Zhai, J., Barreto, A.B., Chin, C., and Li, C., Realization of stress detection using psychophysiological signals for improvement of human-computer interactions”. Proceedings of the IEEE Southeastcon. 1:415–420, 2005. doi:10.1109/SECON.2005.1423280.
Evcik, D., Kizilay, B., and Gokcen, E., The effects of balneotherapy on fibromyalgia patients. Rheumatol Int. 22(2):56–59, 2002. doi:10.1007/s00296-002-0189-8.
Oztemel, E., Yapay sinir aglari. Papatya Publishing, Istanbul, 2012.
Askin, D., Iskender, I., and Mamizadeh, A., Dry type transformer winding thermal analysis using different neural network methods. J. Fac. Eng. Arch. Gazi Univ. 26(4):905–913, 2011.
Altun, A.A., and Allahverdi, N., A new approach to recognition of fingerprints enhanced by filtering techniques with artificial neural networks. J. Fac. Eng. Arch. Gazi Univ. 22(2):227–236, 2007.
MATLAB® Documentation Neural Network Toolbox Help (2015) http://www.mathworks.com/help/nnet/index.html. Accessed 26 Feb. 2015
Oz C, Koker R, Cakar S (2002) Yapay Sinir Agları ile Karakter Tabanlı Plaka Tanıma. Elektrik – Elektronik – Bilgisayar Mühendisligi Sempozyumu (ELECO), Bursa
Acknowledgments
This research is funded by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) and Sakarya University (Project code: 2009-50-02-016) within the context of the project code: 108E036, and titled “Evaluation of HRV, SSR and Psychological Tests using Wavelet Transform and Artificial Neural Nets for the diagnosis of Fibromyalgia Syndrome and Determination of Relations”. Relevant reference number of ethic committee report is B.30.2.SDU.0.01.00.01.301.01/19-271.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozkan, O., Yildiz, M., Arslan, E. et al. A Study on the Effects of Sympathetic Skin Response Parameters in Diagnosis of Fibromyalgia Using Artificial Neural Networks. J Med Syst 40, 54 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0406-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0406-0