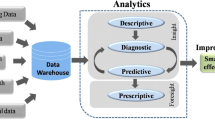
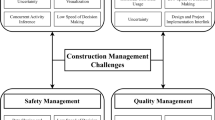
Abstract
To introduce smart health in Wuhan, and provide some references for other cities. As the largest mega-city in central China, Wuhan is investing large amounts of resources to push forward the development of Smart Wuhan and Health Wuhan, and it has unique features. It is one of the centerpieces of China’s New Healthcare Reform, and great hope is put on it to help solve the conflict between limited healthcare resources and the large population of patients. How to plan and design smart health is important. The construction of Wuhan Smart Health includes some aspects as follows, like requirement analysis, the establishment of objectives and blueprint, the architecture design of regional health information platform, evaluation and implementation, problems and solutions, and so on. Wuhan Smart Health has obtained some achievements in health network, information systems, resident’s health records, information standard, and the first phase of municipal health information platform. The focus of this article is the whole construction process of smart health in Wuhan. Although there are some difficulties during this period, some smart health services and management have been reflected. Compared with other cities or countries, Wuhan Smart Health has its own advantages and disadvantages. This study aims to provide a reference for other cities. Because smart health of Wuhan is characteristic in construction mode. Though still in the initial stage, it has great potentials in the future.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caine, K., and Hanania, R., Patients want granular privacy control over health information in electronic medical records. Jamia. 20(1):7–15, 2013.
Dobalian, A., Claver, M.L., Pevnick, J.M., Stutman, H.R., Tomines, A., and Fu Jr., P., Organizational challenges in developing one of the nationwide health information network trial implementation awardees. J. Med. Syst. 36(2):933–940, 2012.
Moghaddasi, H., Asadi, F., Hosseini, A., and Ebnehoseini, Z., E-health: a global approach with extensive semantic variation. J. Med. Syst. 36(5):3173–3176, 2012.
Ramanathan, N., Swendeman, D., Comulada, W. S., et al., Identifying preferences for mobile health applications for self-monitoring and self-management: Focus group findings from HIV-positive persons and young mothers. Int. J. Med. Inform. 82(4):e38–e46, 2013.
Provost, F., and Fawcett, T., Data science and its relationship to big data and data-driven decision making. Big Data. 1(1):51–59, 2013.
Merrell, R.C., and Doarn, C.R., M-health. Telemed J. e-Health. 20(2):99–101, 2014.
Toubiana, L., and Cuggia, M., Big data and smart health strategies: findings from the health information systems perspective. Yearb. Med. Inform. 9(1):125–127, 2014.
Albino, V., Berardi, U., and Dangelico, R.M., Smart cities: definitions, dimensions, performance, and initiatives. J. Urban Technol. 22(1):3–21, 2015.
Lombardi, P., Giordano, S., Farouh, H., et al., Modelling the smart city performance. Innovation-Abingdon. 25(2):137–149, 2012.
Komninos, N., Pallot, M., and Schaffers, H., Special issue on smart cities and the future internet in Europe. J. Knowl. Econ. 4(2):119–134, 2013.
Hao, L., Lei, X., Yan, Z., & ChunLi, Y., The application and Implementation research of Smart City in China. In System Science and Engineering (ICSSE), 2012 International Conference on (pp. 288–292). IEEE, 2012.
Hvistendahl, M., China pushes the “internet of things”. Science. 336(6086):1223–1223, 2012.
Chen, C.C., The trend towards “smart cities”. Int. J. Autom. Smart Technol. 4(2):63–66, 2014.
Zhen, F., Wang, X., Yin, J., et al., An empirical study on Chinese city network pattern based on producer services. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 23(3):274–285, 2013.
Chen, X., A sustainability analysis on the Wuhan-Guangzhou high-speed railway in China. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 9(5):348–363, 2015.
Cheng, J., and Masser, I., Urban growth pattern modeling: a case study of Wuhan city. Pr China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 62(4):199–217, 2003.
State Council of China. Opinions of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on deepening the healthcare system reform. March 2009. URL http://www.gov.cn/jrzg/2009-04/06/content_1278721.htm.
Gao, X., Xu, J., Sorwar, G., et al., Implementation of E-health record systems and E-medical record systems in China. Int. Technol. Manag. Review. 3(2):127–139, 2013.
O’Malley, A.S., Tapping the unmet potential of health information technology. N. Engl. J. Med. 364(12):1090–1091, 2011.
Li, B., and Yu, J., Research and application on the smart home based on component technologies and internet of things. Procedia Eng. 15:2087–2092, 2011.
Kuperman, G.J., Health-information exchange: why are we doing it, and what are we doing? J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc.. 18(5):678–682, 2011.
Yoo, I., et al., “data mining in healthcare and biomedicine: a survey of the literature.”. J. Med. Syst. 36(4):2431–2448, 2012.
Khan, W.A., Khattak, A.M., Hussain, M., et al., An adaptive semantic based mediation system for data interoperability among health information systems. J. Med. Syst. 38(8):1–18, 2014.
Saboury, A., Ghaffari-Nasab, N., Barzinpour, F., et al., Applying two efficient hybrid heuristics for hub location problem with fully interconnected backbone and access networks. Comput. Oper. Res. 40(10):2493–2507, 2013.
Jedermann, R., Becker, M., Gorg, C., et al., Testing network protocols and signal attenuation in packed food transports. Int. J. Sensor Networks. 9(3–4):170–181, 2011.
Zheng, X., and Rodríguez-Monroy, C., The development of intelligent healthcare in China. Telemed. e-Health. 21(5):443–448, 2015.
Baig, M.M., and Gholamhosseini, H., Smart health monitoring systems: an overview of design and modeling. J. Med. Syst. 37(2):1–14, 2013.
Mandl, K.D., Mandel, J.C., Murphy, S.N., et al., The SMART Platform: early experience enabling substitutable applications for electronic health records. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 19(4):597–603, 2012.
Lymberis, A., Research and development of smart wearable health applications: the challenge ahead. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 108:155–161, 2004.
Park, H.S., Shin, Y., Choi, S.W., et al., An integrative structural health monitoring system for the local/global responses of a large-scale irregular building under construction. Sensors. 13(7):9085–9103, 2013.
Solanas, A., Patsakis, C., Conti, M., et al., Smart health: a context-aware health paradigm within smart cities. IEEE Commun. Mag. 52(8):74–81, 2014.
Wang, B.R., Park, J.Y., Chung, K., et al., Influential factors of smart health users according to usage experience and intention to use. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 79(4):2671–2683, 2014.
Dünnebeil, S., Sunyaev, A., Blohm, I., et al., Determinants of physicians’ technology acceptance for e-health in ambulatory care. Int. J. Med. Inform. 81(11):746–760, 2012.
Kourtesis, D., Alvarez-Rodríguez, J.M., and Paraskakis, I., Semantic-based QoS management in cloud systems: current status and future challenges. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 32:307–323, 2014.
Acknowledgments
MC and MF conceived the study. MF searched and checked the databases according to keywords and terms, extracted retrieval results and assessed their quality. MC and MF made questionnaire, and completed the survey. JS and BZ provided the important materials. MC and MF wrote the draft of the paper. All authors contributed to writing, reviewing or revising the paper and read and approved the final manuscript. MC is the guarantor of this work and had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for its integrity and the accuracy of the data analysis. The authors would like to thank all the anonymous reviewers for their helpful advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Mobile Systems
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, M., Sun, J., Zhou, B. et al. The Smart Health Initiative in China: The Case of Wuhan, Hubei Province. J Med Syst 40, 62 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0416-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0416-y