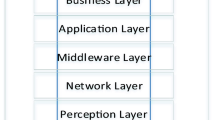
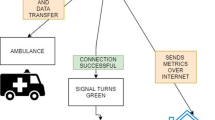
Abstract
The rapid introduction of Internet of Things (IoT) Technology has boosted the service deliverance aspects of health sector in terms of m-health, and remote patient monitoring. IoT Technology is not only capable of sensing the acute details of sensitive events from wider perspectives, but it also provides a means to deliver services in time sensitive and efficient manner. Henceforth, IoT Technology has been efficiently adopted in different fields of the healthcare domain. In this paper, a framework for IoT based patient monitoring in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) is presented to enhance the deliverance of curative services. Though ICUs remained a center of attraction for high quality care among researchers, still number of studies have depicted the vulnerability to a patient’s life during ICU stay. The work presented in this study addresses such concerns in terms of efficient monitoring of various events (and anomalies) with temporal associations, followed by time sensitive alert generation procedure. In order to validate the system, it was deployed in 3 ICU room facilities for 30 days in which nearly 81 patients were monitored during their ICU stay. The results obtained after implementation depicts that IoT equipped ICUs are more efficient in monitoring sensitive events as compared to manual monitoring and traditional Tele-ICU monitoring. Moreover, the adopted methodology for alert generation with information presentation further enhances the utility of the system.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Da Xu, L., He, W., and Li, S., Internet of Things in Industries: A Survey. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 10:2233–2243, 2014. doi:10.1109/TII.2014.2300753.
Zhang, P., Kogure, Y., Matsuoka, H., Akutagawa, M., Kinouchi, Y., and Zhang, Q., A Remote Patient Monitoring System using a Java-enabled 3G Mobile phone. Conference Proceedings of IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2007. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4353138.
Al-Fuqaha, A., Guizani, M., Mohammadi, M., Aledhari, M., and Ayyash, M., Internet of Things: A Survey on Enabling Technologies, Protocols and Applications. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials 17:2347–2376, 2015. doi:10.1109/COMST.2015.2444095.
Gubbi, J., Buyya, R., Marusic, S., and Palaniswami, M., Internet of Things (IoT): A Vision, Architectural elements, and Future directions. Future Generation Computer Systems 29:1645–1660, 2013. doi:10.1016/j.future.2013.01.010.
Varshney, U., A Model for Improving Quality of Decisions in Mobile Health. Decision Support Systems 62:66–77, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2014.03.005.
Xu, B., Xu, L., Cai, H., Jiang, L., Luo, Y., and Gu, Y., The Design of a M-Health Monitoring System based on a Cloud Computing Platform. Enterprise Information Systems, 2015. doi:10.1080/17517575.2015.1053416.
Fang, S., Da Xu, L., Member, S., Zhu, Y., Ahati, J., Pei, H., Yan, J., and Liu, Z., An Integrated System for Regional Environmental Monitoring and Management Based on Internet of Things. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 10:1596–1605, 2014. doi:10.1109/TII.2014.2302638.
Agoulmine, N., Ray, P., and Wu, T. H., Efficient and Cost-effective Communications in Ubiquitous Healthcare: Wireless sensors, Devices and Solutions. IEEE Communications Magazine 50:90–91, 2012. doi:10.1109/MCOM.2012.6194387.
Camiré, E., Moyen, E., and Stelfox, H. T., Medication Errors in Critical Care: Risk factors, prevention and disclosure. CMAJ 180:936–943, 2009. doi:10.1503/cmaj.080869.
Chalfin, D. B., Cohen, I. L., and Lambrinos, J., The Economics and Cost-effectiveness of Critical Care Medicine. Intensive Care Medicine 21:952–961, 1995. doi:10.1007/2FBF01712339.
Thomas, E. J., Lucke, J. F., Wueste, L., and Weavind, L., Association of Telemedicine for Remote Monitoring of Intensive Care Patients with Mortality, Complications, and Length of Stay. Journal of American Medical Association 302:2671–2678, 2013. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1902.
Kyriacou, E., Pattichis, M. S., Pattichis, C. S., Panayides, A., and Pitsillides, A., M-Health E-Emergency Systems: Current Status and Future Directions. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine 49:216–231, 2007. doi:10.1109/MAP.2007.371030.
Welters, I. D., Gibson, J., Mogk, M., and Wenstone, R., Major sources of Critical Incidents in Intensive Care. Critical Care, 2011. doi:10.1186/cc10474.
Vesin, A., Schwebel, C., Arnodo, P., et al., Selected Medical Errors in the Intensive Care Unit Results of the IATROREF Study: Parts I and II. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 181:134–142, 2010. doi:10.1164/rccm.200812-1820OC.
Johansson, L., Bergbom, I., Waye, K. P., Ryherd, E., and Lindahl, B., The Sound Environment in an ICU Patient Room- A Content Analysis of Sound Levels and Patient Experiences. Intensive and Critical Care Nursing 28:269–279, 2012. doi:10.1016/j.iccn.2012.03.004.
Thompson, D. R., Hamilton, D. K., Cadenhead, C. D., Swoboda, S. M., Schwindel, S. M., Anderson, D. C., et al., Guidelines for Intensive Care Unit Design. Critical Care Medicine 40:1586–1600, 2012. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182413bb2.
Ball, M. J., and Lillis, J., E-health: Transforming the Physician / Patient Relationship. International Journal of Medical Informatics 61:1–10, 2001. doi:10.1016/S1386-5056(00)00130-1.
Perera, C., Zaslavsky, A., Christen, P., and Georgakopoulos, D., Context Aware Computing for The Internet of Things: A Survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials 16:414–454, 2014. doi:10.1109/SURV.2013.042313.00197.
Guo, B., Zhang, D., Wang, Z., Yu, Z., and Zhou, X., Opportunistic IoT: Exploring the Harmonious Interaction between Human and the Internet of Things. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 36:1531–1539, 2013. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2012.12.028.
Sneha, S., and Varshney, U., Enabling ubiquitous patient monitoring: Model, Decision Protocols, Opportunities and Challenges. Decision Support Systems 46:606–619, 2009. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2008.11.014.
Varshney, U., A Framework for Supporting Emergency Messages in Wireless Patient Monitoring. Decision Support Systems 45:981–996, 2008. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2008.03.006.
Giger, J. T., Pope, N. D., Vogt, H. B., Gutierrez, C., Newland, L., Lemke, J., et al., Remote patient monitoring acceptance trends among older adults residing in a frontier state. Computers in Human Behavior 44:174–182, 2015. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2014.11.044.
Clarke, M., Schluter, P., Reinhold, B., and Reinhold, B., Designing Robust and Reliable Timestamps for Remote Patient Monitoring. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 19:1718–1723, 2014. doi:10.1109/JBHI.2014.2343632.
Hande, A., Polk, T., Walker, W., and Bhatia, D., Self-powered Wireless Sensor Networks for Remote Patient Monitoring in Hospitals. Sensors 6:1102–1117, 2006. doi:10.3390/s6091102.
Suh, M., Chen, A., Woodbridge, J., Tu, M. K., Kim, J. I., Nahapetian, A., Evangelista, L. S., and Sarrafzadeh, M., A Remote Patient Monitoring System for Congestive Heart Failure. Journal of Medical Systems 35:1165–1179, 2011. doi:10.1007/s10916-011-9733-y.
Fanucci, L., Saponara, S., Bacchillone, T., Donati, M., Barba, P., Sanchez-Tato, I., and Carmona, C., Sensing Devices and Sensor Signal Processing for Remote Monitoring of Vital Signs in CHF Patients. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 62:553–569, 2013. doi:10.1109/TIM.2012.2218681.
Sund, Z. M., Powell, T., Greenwood, R., and Jarad, N. A., Remote Daily Real-time Monitoring in Patients with COPD-A Feasibility Study using a Novel Device. Respiratory Medicine 103:1320–1328, 2009. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2009.03.017.
Kumar, S., Merchant, S., and Reynolds, R., Tele-ICU: Efficacy and Cost-effectiveness of Remotely Managing Critical Care. Perspectives in Health Information Management 10:24–29, 2013. doi:10.2174/1874431101307010024.
Hoonakker, P. L. T., Carayon, P., McGuire, K., Khunlertkit, A., Wiegmann, D. A., Alyousef, B., Xie, A., and Wood, K. E., Motivation and Job Satisfaction of Tele-ICU Nurses. Journal of Critical Care 28:315. e13–315.e21, 2013. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2012.10.001.
Khunlertkit, A., and Carayon, P., Contributions of Tele-Intensive Care Unit (Tele-ICU) Technology to Quality of Care and Patient Safety. Journal of Critical Care 28:315.e1–315.e12, 2013. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2012.10.005.
Ramnath, V. R., and Khazeni, N., Centralized monitoring and virtual consultant models of tele-ICU care: a side-by-side review. Telemedicine and E-Health 20:962–971, 2014. doi:10.1089/tmj.2014.0024.
Sultan, N., Making use of Cloud Computing for healthcare provision: Opportunities and Challenges. International Journal of Information Management 34:177–184, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2013.12.011.
He, C., Fan, X., and Li, Y., Toward Ubiquitous Healthcare Services with a Novel Efficient Cloud platform. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 60:230–234, 2013. doi:10.1109/TBME.2012.2222404.
Bahga, A., and Madisetti, V. K., Healthcare Data Integration and Informatics in the Cloud. Computer 48:50–57, 2015. doi:10.1109/MC.2015.46.
Poon, C. C. Y., Zhang, Y. T., and Di Bao, S., A Novel Biometrics Method to Secure Wireless Body Area Sensor Networks for Telemedicine and M-health. IEEE Communications Magazine 44:73–81, 2006. doi:10.1109/MCOM.2006.1632652.
Sahoo, P., Efficient Security Mechanisms for mHealth Applications using Wireless Body Sensor Networks. Sensors 12:12606–12633, 2012. doi:10.3390/s120912606.
Jerome, G., How Doctors Think. Houghton Mifflin, Boston, 2007.
Kushniruk, A. W., and Patel, V. L., Cognitive Evaluation of Decision Making Processes and Assessment of Information Technology in Medicine. International Journal of Medical Informatics 51:83–90, 1998. doi:10.1016/S1386-5056(98)00106-3.
Amazon Cloud Services. https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/. Accessed 14 January 2016.
IBM SPSS Statistics Software. http://www01.ibm.com/software/analytics/spss/. Accessed 30 January 2016
Mari, D., An Overview of the Internet of Things for People with Disabilities. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 35:584–596, 2012. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2011.10.015.
Atzori, L., Lera, A., and Morabito, G., The Internet of Things: A Survey. Computer Networks 54:2787–2805, 2010. doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2010.05.010.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank Dr. Navdeep K. Bhatia and Dr. Pankaj Sood for data collection and other support services inside ICUs. Moreover, heartily thanks to all patients and their family members for their immense cooperation during the entire implementation procedure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Mobile Systems
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, M., Sood, S.K. Temporal Informative Analysis in Smart-ICU Monitoring: M-HealthCare Perspective. J Med Syst 40, 190 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0547-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0547-9