Abstract
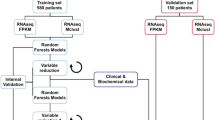
The use of data issued from high throughput technologies in drug target problems is widely widespread during the last decades. This study proposes a meta-heuristic framework using stochastic local search (SLS) combined with random forest (RF) where the aim is to specify the most important genes and proteins leading to the best classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) patients. First we use a stochastic local search meta-heuristic as a feature selection technique to select the most significant proteins to be used in the classification task step. Then we apply RF to classify new patients into their corresponding classes. The evaluation technique is to run the RF classifier on the training data to get a model. Then, we apply this model on the test data to find the appropriate class. We use as metrics the balanced accuracy (BAC) and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) to measure the performance of our model. The proposed method is evaluated on the dataset issued from DREAM 9 challenge. The comparison is done with a pure random forest (without feature selection), and with the two best ranked results of the DREAM 9 challenge. We used three types of data: only clinical data, only proteomics data, and finally clinical and proteomics data combined. The numerical results show that the highest scores are obtained when using clinical data alone, and the lowest is obtained when using proteomics data alone. Further, our method succeeds in finding promising results compared to the methods presented in the DREAM challenge.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
These data were provided by Dr. Steven Kornblau from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and were obtained through Synapse syn2455683 as part of the AML DREAM Challenge.
References
Boughaci, D.: Metaheuristic approaches for the winner determination problem in combinatorial auction. In: Artificial Intelligence, Evolutionary Computing and Metaheuristics - In the Footsteps of Alan Turing, pp. 775–791, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29694-9_29.
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1):5–32, 2001. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Cerami, E.G., Gross, B.E., Demir, E., Rodchenkov, I., Babur, O., Anwar, N., Schultz, N., Bader, G.D., and Sander, C.: Pathway commons, a web resource for biological pathway data. Nucleic Acids Res. 39(suppl_1):D685–D690, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq1039
Croft, D., O’Kelly, G., Wu, G., Haw, R., Gillespie, M., Matthews, L., Caudy, M., Garapati, P., Gopinath, G., Jassal, B., Jupe, S., Kalatskaya, I., Mahajan, S., May, B., Ndegwa, N., Schmidt, E., Shamovsky, V., Yung, C., Birney, E., Hermjakob, H., D’Eustachio, P., and Stein, L.: Reactome: a database of reactions, pathways and biological processes. Nucleic Acids Res. 39(suppl_1):D691–D697, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq1018
Croft, D., Mundo, A.F., Haw, R., Milacic, M., Weiser, J., Wu, G., Caudy, M., Garapati, P., Gillespie, M., Kamdar, M.R., Jassal, B., Jupe, S., Matthews, L., May, B., Palatnik, S., Rothfels, K., Shamovsky, V., Song, H., Williams, M., Birney, E., Hermjakob, H., Stein, L., and D’Eustachio, P., The reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 42(Database-Issue):472–477, 2014.
Dexter, P., Jing, C., David, W., Ricardo, R., Rudolf, P., Vladimir, R., Keiichiro, O., Carol, M., Lyndon, H., Sandor, S., Aleksandar, S., Radu, D., Michael, B., Jan, K., Barry, D., and Trey, I.: Ndex, the network data exchange. Cell Systems 1:302–305, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2015.10.001
Dhaenens, C., and Jourdan, L., On the use of metaheuristics for feature selection in classification, pp. 135–145. Hoboken: Wiley, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119347569.ch7.
Gawehn, E., Hiss, J.A., and Schneider, G.: Deep learning in drug discovery. Mol. Inf. 35(1):3–14, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/minf.201501008
Ghaemi, M., and Feizi Derakhshi, M.R.: Classifying different feature selection algorithms based on the search strategies. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, Electrical and Mechanical Engineering (ICMLEME’2014), At Dubai (UAE), pp. 17–21, 2014.
Hall, M., Frank, E., Holmes, G., Pfahringer, B., Reutemann, P., and Witten, I.H.: The weka data mining software: an update. SIGKDD Explor Newsl. 11(1):10–18, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1145/1656274.1656278
Hall, M.A., Correlation-based feature selection for machine learning. Hamilton: Tech. rep. The University of Waikato, 1999.
Hoos, H.H., and Stützle, T.: 2 - {SLS} {METHODS}. In: Hoos, H.H., and Stützle, T. (Eds.) Stochastic Local Search, The Morgan Kaufmann Series in Artificial Intelligence, Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, pp. 61–112, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-155860872-6/50019-6. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781558608726500196
Hoos, H.H., and Stützle, T., Stochastic Local Search Algorithms: An Overview, pp. 1085–1105. Berlin: Springer, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-43505-2_54.
Kanehisa, M., and Goto, S.: Kegg: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28(1):27–30, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Kuhn, M., Yates, P., and Hyde, C., Statistical methods for drug discovery, pp. 53–81. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23558-5_4.
Liaw, A., and Wiener, M., Classification and regression by randomforest. R News 2(3):18–22, 2002. http://CRAN.R-project.org/doc/Rnews/.
Lima, A.N., Philot, E.A., Trossini, G.H.G., Scott, L.P.B., Maltarollo, V.G., and Honorio, K.M.: Use of machine learning approaches for novel drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discovery. 11(3):225–239, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1517/17460441.2016.1146250. pMID: 26814169
Liu, L., Chang, Y., Yang, T., Noren, D.P., Long, B., Kornblau, S., Qutub, A., and Ye, J.: Evolution-informed modeling improves outcome prediction for cancers. Evol. Appl. 10(1):68–76, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1111/eva.12417
Miannay, B., Minvielle, S., Roux, O., Drouin, P., Avet-Loiseau, H. , Guerin-Charbonnel, C., Gouraud, W., Attal, M., Facon, T., Munshi, N.C., Moreau, P. , Campion, L., Magrangeas, F., and Guziolowski, C.: Logic programming reveals alteration of key transcription factors in multiple myeloma. Sci Rep 7(1):9257, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09378-9
Murphy, R.F.: An active role for machine learning in drug development. Nat Chem Biol 7:327–330, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.576
Noren, D., Long, B., Norel, R., Rrhissorrakrai, K., Hess, K., Hu, C., Bisberg, A., Schultz, A., Engquist, E., Liu, L., Lin, X., Chen, G., Xie, H., Hunter, G., Boutros, P., Stepanov, O., Norman, T., Friend, S., Stolovitzky, G., Kornblau, S., and Qutub, A.: DREAM 9 AML-OPC Consortium, A crowdsourcing approach to developing and assessing prediction algorithms for aml prognosis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 12(6), 2016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004890
Turei, D., Korcsmaros, T., and Saez-Rodriguez, J.: Omnipath: guidelines and gateway for literature-curated signaling pathway resources. Nat Meth 13:966–967, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4077
Yuanyuan, W.M.: Statistical methods for high throughput screening drug discovery data. PhD thesis, 2005, http://hdl.handle.net/10012/1204.
Witten, I.H., Frank, E., Hall, M.A., and Pal, C.J., Data mining fourth edition: Practical machine learning tools and techniques. 4 ed. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 2016.
Yusta, S.C.: Different metaheuristic strategies to solve the feature selection problem. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 30(5):525–534, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2008.11.012. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167865508003565
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank DREAM 9 Challenge for providing data in public. Also PROFAS B + as well as the 1 month program stay provided by the university of Tizi Ouzou. We are most grateful to the bioinformatics core facility of Nantes (BiRD - Biogenouest) for its technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
Author L. CHEBOUBA declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author D. BOUGHACI declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author C. GUZIOLOWSKI declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chebouba, L., Boughaci, D. & Guziolowski, C. Proteomics Versus Clinical Data and Stochastic Local Search Based Feature Selection for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients’ Classification. J Med Syst 42, 129 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-0972-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-0972-z