Abstract
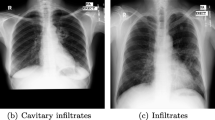
Chest radiography is the most preferred non-invasive imaging technique for early diagnosis of Tuberculosis (TB). However, lack of radiological expertise in TB detection leads to indiscriminate chest radiograph (CXR) screening. A modest classification approach based on the local image description to detect subtle characteristics of TB using CXRs is highly recommended. In this work, an attempt has been made to classify normal and TB CXR images using Bag of Features (BoF) approach with Speeded-Up Robust Feature (SURF) descriptor. The images are obtained from a public database. Lung fields segmentation is performed using Distance Regularized Level Set (DRLS) formulation. The results of segmentation are validated against the ground truth images using similarity, overlap and area correlation measures. BoF approach with SURF keypoint descriptors is implemented to categorize the images using Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) classifier. The obtained results demonstrate that the DRLS method is able to delineate lung fields from CXR images. The BoF with SURF keypoint descriptor is able to characterize local attributes of normal and TB images. The segmentation results are found to be in high correlation with ground truth. MLP classifier is found to provide high Recall, Specificity (Spec), Accuracy, F-score and Area Under the Curve (AUC) values of 87.7%, 85.9%, 87.8%, 87.6% and 94% respectively between normal and abnormal images. The proposed computer aided diagnostic approach is found to perform better as compared to the existing methods. Thus, the study can be of significant assistance to physicians at the point of care in resource constrained regions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Santosh, K. C., and Antani, S., Automated chest x-ray screening: Can lung region symmetry help detect pulmonary abnormalities? IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37:1168–1177, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2017.2775636.
Vajda, S., Karargyris, A., Jaeger, S., Santosh, K. C., Candemir, S., Xue, Z., Antani, S., and Thoma, G., Feature selection for automatic tuberculosis screening in frontal chest radiographs. J. Med. Syst. 42:146, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-0991-9.
Skoura, E., Zumla, A., and Bomanji, J., Imaging in tuberculosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 32:87–93, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2014.12.007.
Jaeger, S., Karargyris, A., Candemir, S., Siegelman, J., Folio, L., Antani, S., and Thoma, G., Automatic screening for tuberculosis in chest radiographs: A survey. Quant. Imaging. Med. Surg. 3:89–99, 2013. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2013.04.03.
Lopes, U. K., and Valiati, J. F., Pre-trained convolutional neural networks as feature extractors for tuberculosis detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 89:135–143, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.08.001.
Melendez, J., Hogeweg, L., Sánchez, C. I., Philipsen, R. H., Aldridge, R. W., Hayward, A. C., Abubakar, I., van Ginneken, B., and Story, A., Accuracy of an automated system for tuberculosis detection on chest radiographs in high-risk screening. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung. Dis. 22:567–571, 2018. https://doi.org/10.5588/ijtld.17.0492.
Hooda, R., Mittal, A., and Sofat, S., Segmentation of lung fields from chest radiographs-a radiomic feature-based approach. Biomed. Eng. Lett.:1–9, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-018-0086-z.
Shao, Y., Gao, Y., Guo, Y., Shi, Y., Yang, X., and Shen, D., Hierarchical lung field segmentation with joint shape and appearance sparse learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33:1761–1780, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2305691.
Candemir, S., Jaeger, S., Palaniappan, K., Musco, J. P., Singh, R. K., Xue, Z., Karargyris, A., Antani, S., Thoma, G., and McDonald, C. J., Lung segmentation in chest radiographs using anatomical atlases with nonrigid registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33:577–590, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2013.2290491.
Candemir, S., Jaeger, S., Palaniappan, K., Antani, S., Thoma, G., Graph-cut based automatic lung boundary detection in chest radiographs. IEEE Healthcare Technology Conference: Translational engineering in health & medicine: 31–34, 2012.
Qin, C., Yao, D., Shi, Y., and Song, Z., Computer-aided detection in chest radiography based on artificial intelligence: A survey. Biomed. Eng. Online 17:113, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-018-0544-y.
Hooda, R., Mittal, A., Sofat, S., A Survey of CAD Methods for Tuberculosis Detection in Chest Radiographs. Soft Computing: Theories and Applications. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. Springer:273–282, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-0589-4_25.
Lee, W. L., Chang, K., and Hsieh, K. S., Unsupervised segmentation of lung fields in chest radiographs using multiresolution fractal feature vector and deformable models. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 54:1409–1422, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1412-6.
Maintz, J. A., and Viergever, M. A., A survey of medical image registration. Med. Image Anal. 2:1–36, 1998. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1361-8415(01)80026-8.
Li, C., Xu, C., Gui, C., and Fox, M. D., Distance regularized level set evolution and its application to image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19:3243–3254, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2010.2069690.
Anandh, K.R., Sujatha, C.M., Ramakrishnan, S., Atrophy analysis of corpus callosum in Alzheimer brain MR images using anisotropic diffusion filtering and level sets. 36th IEEE Annual International Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society: 1945–1948. 2014.
Yang, F., Qin, W., Xie, Y., Wen, T., and Gu, J., A shape-optimized framework for kidney segmentation in ultrasound images using NLTV denoising and DRLSE. Biomed. Eng. Online 11:82, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-925X-11-82.
Ngo, T.A., Carneiro, G., Fully Automated Segmentation Using Distance Regularised Level Set and Deep-Structured Learning and Inference. Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks for Medical Image Computing. Springer:197–224, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42999-1_12.
Karargyris, A., Siegelman, J., Tzortzis, D., Jaeger, S., Candemir, S., Xue, Z., Santosh, K. C., Vajda, S., Antani, S., Folio, L., and Thoma, G. R., Combination of texture and shape features to detect pulmonary abnormalities in digital chest X-rays. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 11:99–106, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1242-x.
Bay, H., Ess, A., Tuytelaars, T., and Van Gool, L., Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 110:346–359, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2007.09.014.
Schmitt, D., and McCoy, N., Object classification and localization using SURF descriptors. CS 229:1–5, 2011.
Alfadhli, F.H., Mand, A.A., Sayeed, M.S., Sim, K.S., Al-Shabi, M., Classification of tuberculosis with SURF spatial pyramid features. IEEE International Conference on Robotics, Automation and Sciences: 1–5. 2017.
Csurka, G., Dance, C., Fan, L., Willamowski, J., and Bray, C., Visual categorization with bags of keypoints. ECCV Workshop Stat. Learn. Comput. Vis. 1:1–22, 2004.
O'Hara, S., Draper, B.A., Introduction to the bag of features paradigm for image classification and retrieval. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1101.3354. 2011.
Dardas, N. H., and Georganas, N. D., Real-time hand gesture detection and recognition using bag-of-features and support vector machine techniques. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 60:3592–3607, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2011.2161140.
Rueda, A., Arevalo, J., Cruz, A., Romero, E., González, F.A., Bag of features for automatic classification of Alzheimer’s disease in magnetic resonance images. Progress in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer Vision, and Applications. Springer:559–566, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33275-3_69.
Cruz-Roa, A., Caicedo, J. C., and González, F. A., Visual pattern mining in histology image collections using bag of features. Artif. Intell. Med. 52:91–106, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2011.04.010.
Islam, M., Dinh, A. V., and Wahid, K. A., Automated diabetic retinopathy detection sing bag of words approach. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 10:86–96, 2017. https://doi.org/10.4236/jbise.2017.105B010.
Avni, U., Greenspan, H., Sharon, M., Konen, E., Goldberger, J., X-ray image categorization and retrieval using patch-based visual words representation. IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro: 350–353. 2009.
Avni, U., Goldberger, J., Sharon, M., Konen, E., and Greenspan, H., Chest x-ray characterization: From organ identification to pathology categorization. ACM Proc. Int. Conf. Multimed. Inform. Retriev.:155–164, 2010.
Jaeger, S., Karargyris, A., Candemir, S., Folio, L., Siegelman, J., Callaghan, F. M., Xue, Z., Palaniappan, K., Singh, R. K., Antani, S. K., and Thoma, G. R., Automatic tuberculosis screening using chest radiographs. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33:233–245, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2013.2284099.
Anandh, K. R., Sujatha, C. M., and Ramakrishnan, S., A method to differentiate mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer in MR images using eigen value descriptors. J. Med. Syst. 40:25, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0396-y.
Kashif, M., Deserno, T. M., Haak, D., and Jonas, S., Feature description with SIFT, SURF, BRIEF, BRISK, or FREAK? A general question answered for bone age assessment. Comput. Biol. Med. 68:67–75, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2015.11.006.
Bishop, C.M., Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford university press. 1995.
Yan, H., Jiang, Y., Zheng, J., Peng, C., and Li, Q., A multilayer perceptron-based medical decision support system for heart disease diagnosis. Expert Syst. Appl. 30:272–281, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2005.07.022.
Lin, C. C., Ou, Y. K., Chen, S. H., Liu, Y. C., and Lin, J., Comparison of artificial neural network and logistic regression models for predicting mortality in elderly patients with hip fracture. Injury 41:869–873, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2010.04.023.
Kavitha, J. C., and Suruliandi, A., Feature extraction using dominant local texture-color patterns (DLTCP) and classification of color images. J. Med. Syst. 42:220, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-1067-6.
Santosh, K. C., Vajda, S., Antani, S., and Thoma, G. R., Edge map analysis in chest X-rays for automatic pulmonary abnormality screening. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 11:1637–1646, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1359-6.
Acknowledgements
The authors extend sincere thanks to the Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology, (Government of India) for supporting this study.
Funding
This study is funded by Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science & Technology, Government of India (SERB-SB/S3/EECE/291/201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Govindarajan, S., Swaminathan, R. Analysis of Tuberculosis in Chest Radiographs for Computerized Diagnosis using Bag of Keypoint Features. J Med Syst 43, 87 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1222-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1222-8