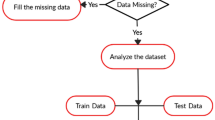
Abstract
Approximately 300 million people are afflicted with asthma around the world, with the estimated death rate of 250,000 cases, indicating the significance of this disease. If not treated, it can turn into a serious public health problem. The best method to treat asthma is to control it. Physicians recommend continuous monitoring on asthma symptoms and offering treatment preventive plans based on the patient’s control level. Therefore, successful detection of the disease control level plays a critical role in presenting treatment plans. In view of this objective, we collected the data of 96 asthma patients within a 9-month period from a specialized hospital for pulmonary diseases in Tehran. A new ensemble learning algorithm with combining physicians’ knowledge in the form of a rule-based classifier and supervised learning algorithms is proposed to detect asthma control level in a multivariate dataset with multiclass response variable. The model outcome resulting from the balancing operations and feature selection on data yielded the accuracy of 91.66%. Our proposed model combines medical knowledge with machine learning algorithms to classify asthma control level more accurately. This model can be applied in electronic self-care systems to support the real-time decision and personalized warnings on possible deterioration of asthma control level. Such tools can centralize asthma treatment from the current reactive care models into a preventive approach in which the physician’s therapeutic actions would be based on control level.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farion, K., Michalowski, W., Wilk, S., O’Sullivan, D., and Matwin, S., A tree-based decision model to support prediction of the severity of asthma exacerbations in children. J Med Syst 34(4):551–562, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-009-9268-7.
van Vliet, D., Alonso, A., Rijkers, G., Heynens, J., Rosias, P., Muris, J., Jobsis, Q., and Dompeling, E., Prediction of asthma exacerbations in children by innovative exhaled inflammatory markers: results of a longitudinal study. PLoS One 10(3):e0119434, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119434.
Bousquet, J., Mantzouranis, E., Cruz, A. A., Ait-Khaled, N., Baena-Cagnani, C. E., Bleecker, E. R., Brightling, C. E., Burney, P., Bush, A., Busse, W. W., Casale, T. B., Chan-Yeung, M., Chen, R., Chowdhury, B., Chung, K. F., Dahl, R., Drazen, J. M., Fabbri, L. M., Holgate, S. T., Kauffmann, F., Haahtela, T., Khaltaev, N., Kiley, J. P., Masjedi, M. R., Mohammad, Y., O'Byrne, P., Partridge, M. R., Rabe, K. F., Togias, A., van Weel, C., Wenzel, S., Zhong, N., and Zuberbier, T., Uniform definition of asthma severity, control, and exacerbations: document presented for the World Health Organization Consultation on Severe Asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126(5):926–938, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2010.07.019.
Luo, G., Stone, B. L., Fassl, B., Maloney, C. G., Gesteland, P. H., Yerram, S. R., and Nkoy, F. L., Predicting asthma control deterioration in children. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making 15(1):84, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-015-0208-9.
Bethesda (2007) Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (US), National Asthma Education and Prevention Program, Third Expert Panel on the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma.
Zhu H, Yang JB, Xu DL, Xu C Application of Evidential Reasoning rules to identification of asthma control steps in children. In: 2016 22nd International Conference on Automation and Computing (ICAC), 7–8 Sept. 2016 2016. pp 444–449. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/IConAC.2016.7604960
Ko, F. W., Hui, D. S., Leung, T. F., Chu, H. Y., Wong, G. W., Tung, A. H., Ngai, J. C., Ng, S. S., and Lai, C. K., Evaluation of the asthma control test: a reliable determinant of disease stability and a predictor of future exacerbations. Respirology 17(2):370–378, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.02105.x.
Zolnoori, M., Zarandi, M. H. F., and Moin, M., Application of Intelligent Systems in Asthma Disease: Designing a Fuzzy Rule-Based System for Evaluating Level of Asthma Exacerbation. Journal of Medical Systems 36(4):2071–2083, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-011-9671-8.
Toti, G., Vilalta, R., Lindner, P., Lefer, B., Macias, C., and Price, D., Analysis of correlation between pediatric asthma exacerbation and exposure to pollutant mixtures with association rule mining. Artif Intell Med 74:44–52, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2016.11.003.
Kupczyk, M., Haque, S., Sterk, P. J., Nizankowska-Mogilnicka, E., Papi, A., Bel, E. H., Chanez, P., Dahlen, B., Gaga, M., Gjomarkaj, M., Howarth, P. H., Johnston, S. L., Joos, G. F., Kanniess, F., Tzortzaki, E., James, A., Middelveld, R. J., and Dahlen, S. E., Detection of exacerbations in asthma based on electronic diary data: results from the 1-year prospective BIOAIR study. Thorax 68(7):611–618, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2012-201815.
Bateman, E. D., Buhl, R., O'Byrne, P. M., Humbert, M., Reddel, H. K., Sears, M. R., Jenkins, C., Harrison, T. W., Quirce, S., Peterson, S., and Eriksson, G., Development and validation of a novel risk score for asthma exacerbations: The risk score for exacerbations. J Allergy Clin Immunol 135(6):1457–1464.e1454, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2014.08.015.
Finkelstein, J., and Wood, J., Predicting asthma exacerbations using artificial intelligence. Stud Health Technol Inform 190:56–58, 2013.
Farion, K. J., Wilk, S., Michalowski, W., O'Sullivan, D., and Sayyad-Shirabad, J., Comparing predictions made by a prediction model, clinical score, and physicians: pediatric asthma exacerbations in the emergency department. Appl Clin Inform 4(3):376–391, 2013. https://doi.org/10.4338/aci-2013-04-ra-0029.
Lee, C. H., Chen, J. C., and Tseng, V. S., A novel data mining mechanism considering bio-signal and environmental data with applications on asthma monitoring. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 101(1):44–61, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2010.04.016.
Xu, M., Tantisira, K. G., Wu, A., Litonjua, A. A., Chu, J. H., Himes, B. E., Damask, A., and Weiss, S. T., Genome Wide Association Study to predict severe asthma exacerbations in children using random forests classifiers. BMC Med Genet 12:90, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-12-90.
Wu, A. C., Gregory, M., Kymes, S., Lambert, D., Edler, J., Stwalley, D., and Fuhlbrigge, A. L., Modeling asthma exacerbations through lung function in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol 130(5):1065–1070, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2012.08.009.
Honkoop PJ, Simpson A, Bonini M, Snoeck-Stroband JB, Meah S, Fan Chung K, Usmani OS, Fowler S, Sont JK (2017) MyAirCoach: the use of home-monitoring and mHealth systems to predict deterioration in asthma control and the occurrence of asthma exacerbations; study protocol of an observational study. 7 (1):e013935. doi:https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013935%J BMJ Open
Arvanitis G, Kocsis O, Lalos AS, Nousias S, Moustakas K, Fakotakis N (2018) 3-Class Prediction of Asthma Control Status Using a Gaussian Mixture Model Approach. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 10th Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Patras, Greece
Kocsis O, Arvanitis G, Lalos A, Moustakas K, Sont JK, Honkoop PJ, Chung KF, Bonini M, Usmani OS, Fowler S, Simpson A Assessing machine learning algorithms for self-management of asthma. In: 2017 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB), 22–24 June 2017 2017. pp 571–574. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/EHB.2017.7995488
Tyagi, A., and Singh, P., Asthma diagnosis and level of control using decision tree and fuzzy system. International Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Technology 16(2):169–181, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijbet.2014.065658.
Rokach LJAIR (2010) Ensemble-based classifiers. 33 (1):1–39. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-009-9124-7
Serpen, G., Tekkedil, D. K., and Orra, M., A knowledge-based artificial neural network classifier for pulmonary embolism diagnosis. Computers in biology and medicine 38(2):204–220, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2007.10.001.
Shrestha GM, Niggemann O Hybrid approach combining Bayesian network and rule-based systems for resource optimization in industrial cleaning processes. In: 2015 IEEE 20th Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation (ETFA), 8–11 Sept. 2015 2015. pp 1–4. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ETFA.2015.7301543
Villena-Román J, Collada-Pérez S, Serrano S, Gonzalez-Cristobal J (2011) Hybrid Approach Combining Machine Learning and a Rule-Based Expert System for Text Categorization.
Rokach, L., Ensemble-based classifiers. Artificial Intelligence Review 33(1):1–39, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-009-9124-7.
Seiffert C, Khoshgoftaar TM, Hulse JV, Napolitano A Resampling or Reweighting: A Comparison of Boosting Implementations. In: 2008 20th IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, 3–5 Nov. 2008 2008. pp 445–451. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTAI.2008.59
Shearer C (2000) The CRISP-DM model: the new blueprint for data mining, vol 5.
Global initiative for asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention (2018)
Greenberg, S., Liu, N., Kaur, A., Lakshminarayanan, M., Zhou, Y., Nelsen, L., Gates, Jr., D. F., Kuo, W. L., Smugar, S. S., Reiss, T. F., Barnes, N., Fuhlbrigge, A., Milgrom, H., Schatz, M., and Knorr, B., The asthma disease activity score: a discriminating, responsive measure predicts future asthma attacks. J Allergy Clin Immunol 130(5):1071–1077.e1010, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.057.
Aguinis, H., Gottfredson, R. K., and Joo, H., Best-Practice Recommendations for Defining, Identifying, and Handling Outliers. Organizational Research Methods 16(2):270–301, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428112470848.
Liu, Y., and De, A., Multiple Imputation by Fully Conditional Specification for Dealing with Missing Data in a Large Epidemiologic Study. International journal of statistics in medical research 4(3):287–295, 2015. https://doi.org/10.6000/1929-6029.2015.04.03.7.
Liu, X. Y., Wu, J., and Zhou, Z. H., Exploratory Undersampling for Class-Imbalance Learning. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics) 39(2):539–550, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2008.2007853.
Chawla, N. V., Bowyer, K. W., Hall, L. O., and Kegelmeyer, W. P., SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Int Res 16(1):321–357, 2002.
Friedman, J. H., Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines. Ann Statist 19(1):1–67, 1991. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176347963.
Chen X, Jeong JC Enhanced recursive feature elimination. In: Sixth International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA 2007), 13–15 Dec. 2007 2007. 429–435. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMLA.2007.35
Hong H, Xiaoling G, Hua Y Variable selection using Mean Decrease Accuracy and Mean Decrease Gini based on Random Forest. In: 2016 7th IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science (ICSESS), 26–28 Aug. 2016 2016. pp 219–224. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSESS.2016.7883053
Dhir CS, Iqbal N, Lee S Efficient feature selection based on information gain criterion for face recognition. In: 2007 International Conference on Information Acquisition, 8–11 July 2007 2007. pp 523–527. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIA.2007.4295788
McHugh, M. L., The chi-square test of independence. Biochemia medica 23(2):143–149, 2013. https://doi.org/10.11613/BM.2013.018.
Sokolova, M., and Lapalme, G., A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Information Processing & Management 45(4):427–437, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2009.03.002.
Dubey, R., Zhou, J., Wang, Y., Thompson, P. M., and Ye, J., Analysis of sampling techniques for imbalanced data: An n = 648 ADNI study. Neuroimage 87:220–241, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.10.005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical approval
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khasha, R., Sepehri, M.M. & Mahdaviani, S.A. An ensemble learning method for asthma control level detection with leveraging medical knowledge-based classifier and supervised learning. J Med Syst 43, 158 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1259-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1259-8