Abstract
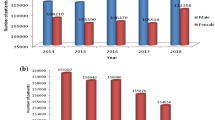
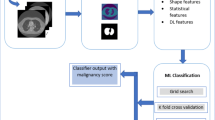
As “the second eyes” of radiologists, computer-aided diagnosis systems play a significant role in nodule detection and diagnosis for lung cancer. In this paper, we aim to provide a systematic survey of state-of-the-art techniques (both traditional techniques and deep learning techniques) for nodule diagnosis from computed tomography images. This review first introduces the current progress and the popular structure used for nodule diagnosis. In particular, we provide a detailed overview of the five major stages in the computer-aided diagnosis systems: data acquisition, nodule segmentation, feature extraction, feature selection and nodule classification. Second, we provide a detailed report of the selected works and make a comprehensive comparison between selected works. The selected papers are from the IEEE Xplore, Science Direct, PubMed, and Web of Science databases up to December 2018. Third, we discuss and summarize the better techniques used in nodule diagnosis and indicate the existing future challenges in this field, such as improving the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve and accuracy, developing new deep learning-based diagnosis techniques, building efficient feature sets (fusing traditional features and deep features), developing high-quality labeled databases with malignant and benign nodules and promoting the cooperation between medical organizations and academic institutions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., and Jemal, A., Cancer statistics, 2018. Ca-Cancer J Clin 60(5):277–300, 2018.
Siegel, R., Naishadham, D., and Jemal, A., Cancer statistics, 2013. Ca-Cancer J Clin, 2013.
McGuire, S., World cancer report 2014. World Health Organization 7(2):418–419, 2015.
Henschke, C. I., Mccauley, D. I., Yankelevitz, D. F., Naidich, D. P., Mcguinness, G., Miettinen, O. S., Libby, D. M., Pasmantier, M. W., Koizumi, J., and Altorki, N. K., Early Lung Cancer Action Project: overall design and findings from baseline screening. Cancer-Am Cancer Soc 354(9173):2474–2482, 1999.
Gibaldi, A., Barone, D., Gavelli, G., Malavasi, S., and Bevilacqua, A., Effects of Guided Random Sampling of TCCs on Blood Flow Values in CT Perfusion Studies of Lung Tumors. Acad. Radiol. 22(1):58–69, 2015.
Ng, Q. S., and Goh, V., Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: imaging with perfusion computed tomography. J Thorac Inag 25(2):142, 2010.
Aberle, D. R., Adams, A. M., Berg, C. D., Black, W. C., Clapp, J. D., Fagerstrom, R. M., Gareen, I. F., Gatsonis, C., Marcus, P. M., and Sicks, J. D., Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. New Engl J Med 365(5):395–409, 2011.
Gould, M. K., Maclean, C. C., Kuschner, W. G., Rydzak, C. E., and Owens, D. K., Accuracy of positron emission tomography for diagnosis of pulmonary nodules and mass lesions: a meta-analysis. Jama-J Am Med Assoc 285(7):914–924, 2001.
Doi, K., Computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging: Historical review, current status and future potential. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 31(4):198–211, 2007.
Ma, Z., Tavares, J. M. R. S., and Jorge, R. M. N., A review on the current segmentation algorithms for medical images. In: 1st International Conference on Imaging Theory and Applications (IMAGAPP), INSTICC Press, Lisbon, 135–140, 2015.
Ma, Z., Tavares, J. M. R. S., Jorge, R. N., and Mascarenhas, T., A review of algorithms for medical image segmentation and their applications to the female pelvic cavity. Comput Method Biomec 13(2):235–246, 2010.
Zhang, J. J., Xia, Y., Cui, H. F., and Zhang, Y. N., Pulmonary nodule detection in medical images: A survey. Biomed Signal Proces 43:138–147, 2018.
Zhang, G. B., Jiang, S., Yang, Z. Y., Gong, L., Ma, X. D., Zhou, Z. Y., Bao, C., and Liu, Q., Automatic nodule detection for lung cancer in CT images: A review. Comput. Biol. Med. 103:287–300, 2018.
El-Regaily, S. A., Salem, M. A., Aziz, M. H. A., and Roushdy, M. I., Survey of Computer Aided Detection Systems for Lung Cancer in Computed Tomography. Curr Med Imaging Rev 14(1):3–18, 2018.
Rehman, M. Z. U., Javaid, M., Shah, S. I. A., Gilani, S. O., Jamil, M., and Butt, S. I., An appraisal of nodules detection techniques for lung cancer in CT images. Biomed Signal Proces 41:140–151, 2018.
Naqi, S. M., and Sharif, M., Recent Developments in Computer Aided Diagnosis for Lung Nodule Detection from CT images: A Review. Curr Med Imaging Rev 13(1):3–19, 2017.
Valente, I. R. S., Cortez, P. C., Neto, E. C., Soares, J. M., Albuquerque, V. H. C. D., and Tavares, J. M. R. S., Automatic 3D pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: A survey. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 124(C):91–107, 2016.
Lee, S. L. A., Kouzani, A. Z., and Hu, E. J., Automated detection of lung nodules in computed tomography images: a review. Mach. Vis. Appl. 23(1):151–163, 2012.
El-Baz, A., Elnakib, A., Abou, E.-G. M., Gimel'Farb, G., Falk, R., and Farag, A., Automatic Detection of 2D and 3D Lung Nodules in Chest Spiral CT Scans. International Journal of Biomedical Imaging 2013(1):517632, 2013.
Eadie, L. H., Paul, T., and Gibson, A. P., A systematic review of computer-assisted diagnosis in diagnostic cancer imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 81(1):e70–e76, 2012.
Firmino, M., Morais, A. H., Mendoça, R. M., Dantas, M. R., Hekis, H. R., and Valentim, R., Computer-aided detection system for lung cancer in computed tomography scans: Review and future prospects. Biomed. Eng. Online 13(1):41, 2014.
Yang, Y. X., Feng, X. Y., Chi, W. H., Li, Z. Y., Duan, W. Z., Liu, H. P., Liang, W. H., Wang, W., Chen, P., He, J. X., and Liu, B., Deep learning aided decision support for pulmonary nodules diagnosing: a review. J Thorac Dis 10:S867–S875, 2018.
Hu, Z., Tang, J., Wang, Z., Kai, Z., Lin, Z., and Sun, Q., Deep Learning for Image-based Cancer Detection and Diagnosis — A Survey. Pattern Recogn. 83:134–149, 2018.
Paulraj, T., and Chellliah, K. S. V., Computer-Aided Diagnosis of lung cancer in Computed Tomography scans: A Review. Curr Med Imaging Rev 14(3):374–388, 2018.
Dean, J. C., and Ilvento, C. C., Improved cancer detection using computer-aided detection with diagnostic and screening mammography: prospective study of 104 cancers. Breast Diseases A Year Book Quarterly 187(1):20–28, 2006.
Singh, S., Maxwell, J., Baker, J. A., and Nicholas, J. L., Computer -aided classification of breast masses: performance and interobserver variability of expert radiologists versus residents. International Journal of Medical Radiology 258(1):73–80, 2011.
Berkman, S., Heang-Ping, C., Roubidoux, M. A., Hadjiiski, L. M., Helvie, M. A., Chintana, P., Janet, B., Nees, A. V., and Caroline, B., Malignant and benign breast masses on 3D US volumetric images: effect of computer-aided diagnosis on radiologist accuracy. Radiology 242(3):716–724, 2007.
Giger, M. L., Karssemeijer, N., and Schnabel, J. A., Breast Image Analysis for Risk Assessment, Detection, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Cancer. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 15(1):327–357, 2013.
Reeves, A. P., Biancardi, A. M., Apanasovich, T. V. et al., The Lung Image Database Consortium (LIDC): A comparison of different size metrics for pulmonary nodule measurements. Acad. Radiol. 14(12):1475–1485, 2007.
Armato, S. G., Geoffrey, M. L., Mcnitt-Gray, M. F., Meyer, C. R., David, Y., Aberle, D. R., Henschke, C. I., Hoffman, E. A., Kazerooni, E. A., and Heber, M. M., Lung image database consortium: developing a resource for the medical imaging research community. Radiology 232(3):739–748, 2004.
Clark, K., Vendt, B., Smith, K., Freymann, J., Kirby, J., Koppel, P., Moore, S., Phillips, S., Maffitt, D., and Pringle, M., The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository. J. Digit. Imaging 26(6):1045–1057, 2013.
Messay, T., Hardie, R. C., and Tuinstra, T. R., Segmentation of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography using a regression neural network approach and its application to the Lung Image Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative dataset. Med. Image Anal. 22(1):48–62, 2015.
Setio, A. A. A., Traverso, A., de Bel, T. et al., Validation, comparison, and combination of algorithms for automatic detection of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography images: the luna16 challenge. Med. Image Anal. 42:1–13, 2017.
Henschke, C. I., Yankelevitz, D. F., Libby, D. M., Pasmantier, M. W., Smith, J. P., and Miettinen, O. S., Survival of patients with stage I lung cancer detected on CT screening. New Engl J Med 355(17):1763–1771, 2006.
Rowena, Y., Henschke, C. I., Yankelevitz, D. F., and Smith, J. P., CT screening for lung cancer: alternative definitions of positive test result based on the national lung screening trial and international early lung cancer action program databases. Radiology 273(2):591–596, 2014.
Carrilloa, M. C., and Katz, R. G., Maximizing the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative II. Alzheimers & Dementia the Journal of the Alzheimers Association 5(3):271–275, 2009.
Weisheng, W., Jiawei, L., Xuedong, Y., and Hongli, L., Data analysis of the Lung Imaging Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative. Acad. Radiol. 22(4):488–495, 2015.
Armato, S. G., McLennan, G., Bidaut, L. et al., The Lung Image Database Consortium, (LIDC) and Image Database Resource Initiative (IDRI): A Completed Reference Database of Lung Nodules on CT Scans. Med. Phys. 38(2):915–931, 2011.
Filho, A. O. D. C., Silva, A. C., Paiva, A. C. D., Nunes, R. A., and Gattass, M., Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Lung Nodules in Computed Tomography by Using Phylogenetic Diversity, Genetic Algorithm, and SVM. J. Digit. Imaging 30(6):812–822, 2017.
Costa, R. W. D. S., Silva, G. L. F. D., Filho, A. O. D. C., Silva, A. C., Paiva, A. C. D., and Gattass, M., Classification of malignant and benign lung nodules using taxonomic diversity index and phylogenetic distance. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 56(11):2125–2136, 2018.
Kumar, D., Wong, A., and Clausi, D. A., Lung Nodule Classification Using Deep Features in CT Images. Conference on Computer & Robot Vision:133–138, 2015.
Wu, P., Xia, K., and Yu, H., Relevance Vector Machine Based Pulmonary Nodule Classification. J Med Imag Health In 6(1):163–169, 2016.
Akram, S., Javed, Y., Akram, U., Qamar, U., and Hassan, A., Pulmonary Nodules Detection and Classification Using Hybrid Features from Computerized Tomographic Images. J Med Imag Health In 6(1):252–259, 2016.
Akram, S., Javed, M. Y., Hussain, A., Riaz, F., and Akram, M. U., Intensity-based statistical features for classification of lungs CT scan nodules using artificial intelligence techniques. J Exp Theor Artif In 27(6):737–751, 2015.
Filho, A. O. D. C., Silva, A. C. E., Paiva, A. C. D., Nunes, R. A., and Gattass, M., Classification of patterns of benignity and malignancy based on CT using topology-based phylogenetic diversity index and convolutional neural network. Pattern Recogn. 81:200–212, 2018.
Filho, A. O. D. C., Silva, A. C., Paiva, A. C. D., Nunes, R. A., and Gattass, M., Computer-aided diagnosis system for lung nodules based on computed tomography using shape analysis, a genetic algorithm, and SVM. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 55(8):1129–1146, 2017.
Sweetlin, J. D., Nehemiah, H. K., and Kannan, A., Computer aided diagnosis of pulmonary hamartoma from CT scan images using ant colony optimization based feature selection. Alexandria Engineering Journal 57(3):1557–1567, 2017.
Firmino, M., Angelo, G., Morais, H., Dantas, M. R., and Valentim, R., Computer-aided detection (CADe) and diagnosis (CADx) system for lung cancer with likelihood of malignancy. Biomed. Eng. Online 15(1):2, 2016.
Orozco, H. M., Villegas, O. O. V., Sánchez, V. G. C., Domínguez, H. D. J. O., and Alfaro, M. D. J. N., Automated system for lung nodules classification based on wavelet feature descriptor and support vector machine. Biomed. Eng. Online 14(1):9, 2015.
Li, X. X., Li, B., Tian, L. F., and Zhang, L., Automatic benign and malignant classification of pulmonary nodules in thoracic computed tomography based on RF algorithm. IET Image Process. 12(7):1253–1264, 2018.
Gong, J., Liu, J. Y., Sun, X. W., Zheng, B., and Nie, S. D., Computer-aided diagnosis of lung cancer: the effect of training data sets on classification accuracy of lung nodules. Phys. Med. Biol. 63(3):035036, 2018.
Dhara, A. K., Mukhopadhyay, S., Dutta, A., Garg, M., and Khandelwal, N., A Combination of Shape and Texture Features for Classification of Pulmonary Nodules in Lung CT Images. J. Digit. Imaging 29(4):466–475, 2016.
Xie, Y. T., Zhang, J. P., Xia, Y., Fulham, M., and Zhang, Y. N., Fusing texture, shape and deep model-learned information at decision level for automated classification of lung nodules on chest CT. Inform Fusion 42:102–110, 2018.
Cataldo, S. D., Bottino, A., Islam, I. U., Vieira, T. F., and Ficarra, E., Subclass Discriminant Analysis of morphological and textural features for HEp-2 staining pattern classification. Pattern Recogn. 47(7):2389–2399, 2014.
Shen, W., Zhou, M., Yang, F., Yu, D., Dong, D., Yang, C., Zang, Y., and Tian, J., Multi-crop Convolutional Neural Networks for lung nodule malignancy suspiciousness classification. Pattern Recogn. 61(61):663–673, 2017.
Tajbakhsh, N., and Suzuki, K., Comparing two classes of end-to-end machine-learning models in lung nodule detection and classification MTANNs vs. CNNs. Pattern Recogn. 63:476–486, 2017.
Silva, G. L. F. D., Neto, O. P. D. S., Silva, A. C., Paiva, A. C. D., and Gattass, M., Lung nodules diagnosis based on evolutionary convolutional neural network. Multimed. Tools Appl. (2):1–17, 2017.
Sun, W., Zheng, B., and Wei, Q., Computer aided lung cancer diagnosis with deep learning algorithms. Medical Imaging: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, 2015.
Cheng, J. Z., Ni, D., Chou, Y. H., Qin, J., Tiu, C. M., Chang, Y. C., Huang, C. S., Shen, D., and Chen, C. M., Computer-Aided Diagnosis with Deep Learning Architecture: Applications to Breast Lesions in US Images and Pulmonary Nodules in CT Scans. Sci Rep-UK 6:24454, 2016.
Hua, K. L., Hsu, C. H., Hidayati, S. C., Cheng, W. H., and Chen, Y. J., Computer-aided classification of lung nodules on computed tomography images via deep learning technique. Oncotargets Ther 8:2015, 2015-2022.
Tu, X., Xie, M., Gao, J., Ma, Z., Chen, D., Wang, Q., Finlayson, S. G., Ou, Y., and Cheng, J. Z., Automatic Categorization and Scoring of Solid, Part-Solid and Non-Solid Pulmonary Nodules in CT Images with. Convolutional Neural Network. Sci Rep-UK 7(1):8533, 2017.
Sun, W., Zheng, B., and Qian, W., Automatic Feature Learning Using Multichannel ROI Based on Deep Structured Algorithms for Computerized Lung Cancer Diagnosis. Comput. Biol. Med. 89:530–539, 2017.
Chen, M., Shi, X. B., Zhang, Y., Wu, D., and Mohsen, G., Deep Features Learning for Medical Image Analysis with Convolutional Autoencoder Neural Network. IEEE Transactions on Big Data PP(99):1, 2017.
Yuan, J. J., Liu, X. L., Hou, F., Qin, H., and Hao, A. M., Hybrid-feature-guided lung nodule type classification on CT images. Comput. Graph. 70:288–299, 2017.
Ciompi, F., Chung, K., Riel, S. J. V., Setio, A. A. A., Gerke, P. K., Jacobs, C., Scholten, E. T., Schaeferprokop, C., Wille, M. M. W., and Marchianò, A., Towards automatic pulmonary nodule management in lung cancer screening with deep learning. Sci Rep-UK 7:46479, 2016.
Zhu, W., DeepLung: 3D Deep Convolutional Nets for Automated Pulmonary Nodule Detection and Classification, 2017.
Zhu, W., Liu, C., Wei, F., and Xie, X., DeepLung: Deep 3D Dual Path Nets for Automated Pulmonary Nodule Detection and Classification. In: IEEE Winter Conf. on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV2018). pp 673–681, 2018.
Liao, F., Ming, L., Zhe, L., Hu, X., and Song, S., Evaluate the Malignancy of Pulmonary Nodules Using the 3D Deep Leaky Noisy-or Network, 2017.
Wang, H. F., Zhao, T. T., Li, L. C., Pan, H. X., Liu, W. Q., Gao, H. Q., Han, F. F., Wang, Y. H., Qi, Y. F., and Liang, Z. R., A hybrid CNN feature model for pulmonary nodule malignancy risk differentiation. J X-Ray Sci Technol 26(2):171–187, 2018.
Zhao, X., Liu, L., Qi, S., Teng, Y., Li, J., and Wei, Q., Agile convolutional neural network for pulmonary nodule classification using CT images. Int J Comput Ass Rad 13(4):585–595, 2018.
Kaya, A., Cascaded Classifiers and Stacking Methods for Classification of Pulmonary Nodule Characteristics. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 166:77–89, 2018.
Liu, Y., Hao, P., Zhang, P., Xu, X., Wu, J., and Chen, W., Dense Convolutional Binary-Tree Networks for Lung Nodule Classification. IEEE Access 6:49080–49088, 2018.
Wang, Z., Xin, J., Sun, P., Lin, Z., Yao, Y., and Gao, X., Improved Lung Nodule Diagnosis Accuracy Using Lung CT Images With Uncertain Class. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 162:197–209, 2018.
Nibali, A., He, Z., and Wollersheim, D., Pulmonary nodule classification with deep residual networks. Int J Comput Ass Rad 12(10):1799–1808, 2017.
Liu, K., and Kang, G., 3D multi-view convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification. PLoS One 12(1):12–22, 2017.
Zhang, G., 3D Spatial Pyramid Dilated Network for Pulmonary Nodule Classification. Symmetry-Basel. 10(9), 2018.
Yan, Q., Lei, G., Xin, Z., Zhang, X., and Tang, X., Pulmonary nodule diagnosis using dual-modal supervised autoencoder based on extreme learning machine. Expert. Syst. 34(6):e12224, 2017.
Jung, H., Kim, B., Lee, I., Lee, J., and Kang, J., Classification of lung nodules in CT scans using three-dimensional deep convolutional neural networks with a checkpoint ensemble method. BMC Med. Imaging 18, 2018.
Nishio, M., Sugiyama, O., Yakami, M., Ueno, S., Kubo, T., Kuroda, T., and Togashi, K., Computer-aided diagnosis of lung nodule classification between benign nodule, primary lung cancer, and metastatic lung cancer at different image size using deep convolutional neural network with transfer learning. PLoS One 13(7):e0200721, 2018.
Liu, S., Xie, Y., Jirapatnakul, A., and Reeves, A. P., Pulmonary nodule classification in lung cancer screening with three-dimensional convolutional neural networks. Journal of Medical Imaging 4(4):041308, 2017.
Wei, G. H., Ma, H., Qian, W., Han, F. F., Jiang, H. Y., Qi, S. L., and Qiu, M., Lung nodule classification using local kernel regression models with out-of-sample extension. Biomed Signal Proces 40:1–9, 2018.
Farag, A. A., Ali, A., Elshazly, S., and Farag, A. A., Feature fusion for lung nodule classification. Int J Comput Ass Rad 12(10):1809–1818, 2017.
Dilger, S. K., Judisch, A., Uthoff, J., Hammond, E., Newell, J. D., and Sieren, J. C., Improved pulmonary nodule classification utilizing lung parenchyma texture features. Medical Imaging: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, 2015.
Kaya, A., and Can, A. B., A weighted rule based method for predicting malignancy of pulmonary nodules by nodule characteristics. J. Biomed. Inform. 56(C):69–79, 2015.
Chen, C. H., Chang, C. K., Tu, C. Y., Liao, W. C., Wu, B. R., Chou, K. T., Chiou, Y. R., Yang, S. N., Zhang, G., and Huang, T. C., Radiomic features analysis in computed tomography images of lung nodule classification. PLoS One 13(2):e0192002, 2018.
Reeves, A. P., Xie, Y., and Jirapatnakul, A., Automated pulmonary nodule CT image characterization in lung cancer screening. Int J Comput Ass Rad 11(1):1–16, 2015.
Sun, W., Xia, H., Tseng, T. L., Zhang, J., and Wei, Q., Computerized lung cancer malignancy level analysis using 3D texture features. Medical Imaging: Computer-aided Diagnosis, 2016.
Ferreira, J. R., and Oliveira, M. C., Characterization of Pulmonary Nodules Based on Features of Margin Sharpness and Texture. J. Digit. Imaging:1–13, 2017.
Nishio, M., Nishizawa, M., Sugiyama, O., Kojima, R., Yakami, M., Kuroda, T., and Togashi, K., Computer-aided diagnosis of lung nodule using gradient tree boosting and Bayesian optimization. PLoS One 13(4):e0195875, 2017.
Hancock, M. C., and Magnan, J. F., Lung nodule malignancy classification using only radiologist-quantified image features as inputs to statistical learning algorithms: probing the Lung Image Database Consortium dataset with two statistical learning methods. J Med Imaging 3(4):044504, 2016.
Mao, K. M., and Deng, Z. F., Lung Nodule Image Classification Based on Local Difference Pattern and Combined Classifier. Comput Math Method M, 2016.
Hawkins, S. H., Korecki, J. N., Balagurunathan, Y., Gu, Y., Kumar, V., Basu, S., Hall, L. O., Goldgof, D. B., Gatenby, R. A., and Gillies, R. J., Predicting Outcomes of Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Using CT Image Features. IEEE Access 2:1418–1426, 2014.
Li, Q., and Doi, K., Reduction of bias and variance for evaluation of computer-aided diagnostic schemes. Med. Phys. 33(4):868–875, 2006.
He, K. M., Zhang, X. Y., Ren S. Q., Sun, J., Deep residual learning for image recognition. In CVPR: 770–778, 2016.
Huang, G., Liu, Z., van der Maaten, L., and Weinberger, K. Q., Densely connected convolutional networks. In CVPR 2261–2269, 2017.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E., ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012.
Padma, A., and Giridharan, N., Performance comparison of texture feature analysis methods using PNN classifier for segmentation and classification of brain CT images: Performance Comparison of Texture Feature Analysis Methods Using PNN Classifier for Segmentation and Classification of B. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 26(2):97–105, 2016.
Amato, F., Mazzocca, N., Moscato, F., and Vivenzio, E., Multilayer Perceptron: An Intelligent Model for Classification and Intrusion Detection. International Conference on Advanced Information Networking & Applications Workshops, 2017.
Sindhumol, S., Kumar, A., and Balakrishnan, K., Spectral clustering independent component analysis for tissue classification from brain MRI. Biomed Signal Proces 8(6):667–674, 2013.
Feiping, N., Zinan, Z., Tsang, I. W., Dong, X., and Changshui, Z., Spectral embedded clustering: a framework for in-sample and out-of-sample spectral clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 22(11):1796–1808, 2011.
de Carvalho, A. O., de Sampaio, W. B., Silva, A. C., de Paivaa, A. C., Nunes, R. A., and Gattass, M., Automatic detection of solitary lung nodules using quality threshold clustering, genetic algorithm and diversity index. Artif. Intell. Med. 60(3):165–177, 2014.
Ohtsu, N., A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE T Syst Man Cy-S 9(1):62–66, 2007.
Eberhart R, Kennedy J, A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Proceedings of the sixth international symposium on micro machine and human science, vol. 1, pp. 39–43. New York, 1995. https://doi.org/10.1109/MHS.1995.494215
Lecun, Y., Boser, B., Denker, J. S., Henderson, D., Howard, R. E., Hubbard, W., and Jackel, L. D., Backpropagation Applied to Handwritten Zip Code Recognition. Neural Comput. 1(4):541–551, 2014.
Lecun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., and Haffner, P., Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. P IEEE 86(11):2278–2324, 1998.
Bengio, Y., Lamblin, P., Popovici, D., Larochelle, H., and Montreal, U., Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Proces. Syst. 19:153–160, 2007.
Coates A, Lee H, and Ng, A. Y., An analysis of single-layer networks in unsupervised feature learning. In Aistats, 2011.
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., and Brox, T., U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention 9351:234–241, 2015.
Heckerman, D., A tractable inference algorithm for diagnosing multiple diseases. Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. North-Holland Publishing Co:163–172, 1990.
Dalal, N., and Triggs, B., Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection 886–893, 2005.
Ojala, T., Pietikainen, M., and Harwood, D., A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on featured distributions. Pattern Recogn. 29(1):51–59, 1996.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E., ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: NIPS: 1097–1105, 2012.
Bengio, Y., Louradour, J., Collobert, R., and Weston, J., Curriculum learning. Procintconfon Machine Learning 60(60):6, 2009.
Mcnittgray, M. F., Armato, S. G., Iii, M. C. R., Reeves, A. P., Mclennan, G., Pais, R., Freymann, J., Brown, M. S., Engelmann, R. M., and Bland, P. H., The Lung Image Database Consortium (LIDC) Data Collection Process for Nodule Detection and Annotation. Acad. Radiol. 14(12):1464–1474, 2007.
Dhara, A. K., Mukhopadhyay, S., Gupta, R. D., Garg, M., and Khandelwal, N., Erratum to: A Segmentation Framework of Pulmonary Nodules in Lung CT Images. J. Digit. Imaging 29(1):86–103, 2016.
Vincent, P., Larochelle, H., Lajoie, I., Bengio, Y., and Manzagol, P. A., Stacked Denoising Autoencoders: Learning Useful Representations in a Deep Network with a Local Denoising Criterion. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11(12):3371–3408, 2010.
Jing-Jing, W., Hai-Feng, W., Tao, S., Xia, L., Wei, W., Li-Xin, T., Da, H., Ping-Xin, L., Wen, H., and Xiu-Hua, G., Prediction models for solitary pulmonary nodules based on curvelet textural features and clinical parameters. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention Apjcp 14(10):6019–6023, 2013.
Haifeng, W., Tao, S., Jingjing, W., Xia, L., Wei, W., Da, H., Pingxin, L., Wen, H., Keyang, W., and Xiuhua, G., Combination of radiological and gray level co-occurrence matrix textural features used to distinguish solitary pulmonary nodules by computed tomography. J. Digit. Imaging 26(4):797–802, 2013.
Farag, A. A., Farag, A. A., Falk, R., Ali, A. M., Graham, J., Elshazly, S., Evaluation of geometric feature descriptors for detection and classification of lung nodules in low dose CT scans of the chest, 2011.
Farag, A., Elhabian, S., Graham, J., Farag, A., and Falk, R., Toward Precise Pulmonary Nodule Descriptors for Nodule Type Classification. International Conference on Medical Image Computing & Computer-assisted Intervention, 2010.
Lin, P. L., Huang, P. W., Lee, C. H., and Wu, M. T., Automatic classification for solitary pulmonary nodule in CT image by fractal analysis based on fractional Brownian motion model. Pattern Recogn. 46(12):3279–3287, 2013.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81871457), National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 51811530310), National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 51775368) and Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (grant number 2017B020210004) and the Science and Technology Project of Tianjin (grant number 18YFZCSY01300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Image & Signal Processing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Yang, Z., Gong, L. et al. An Appraisal of Nodule Diagnosis for Lung Cancer in CT Images. J Med Syst 43, 181 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1327-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1327-0