Abstract
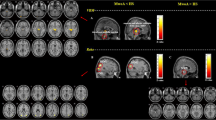
The aim of this study was to investigate the alterations in regional homogeneity assessed by fMRI in patients with migraine without aura (MWoA). Fifty-six eligible MWoA patients and 32 matched healthy volunteers were enrolled in this study. MWoA patients were divided into three groups according to the headache days per month within 3 months: infrequent episodic migraine (IEM) group, frequent episodic migraine (FEM) group, and chronic migraine (CM) group. Data collection and rest-state fMRI examination were performed in all cases. The ReHo method was used to analyze the blood oxygen level dependent (BLOD) signals of the adjacent voxels in the brain regions of each patient, and the consistency of their fluctuations in the sequences of same time. Compared with normal controls, ReHo values of bilateral thalami, right insula and right middle temporal gyrus increased and both precentral gyri decreased in the IEM group; ReHo values of bilateral thalami and the right middle temporal gyrus increased; ReHo values of both anterior cingulate cortex, precentral gyri and putamen decreased in the FEM group. Compared with control group, ReHo values of left olfactory cortex, right hippocampus, parahippocampal gyrus, suboccipital gyrus and precuneus increased, both precentral gyri, precuneus, putamen and anterior cingulate cortex decreased in the CM group. Compared with IEM group, ReHo values of both putamen, left middle frontal gyrus, right superior frontal gyrus increased, and the left precuneus decreased in the FEM group. Compared with FEM group, ReHo values of left olfactory and left precuneus increased, and the right superior frontal gyrus, insula, middle temporal gyrus, thalami, both superior temporal gyri decreased in the CM group. In the IEM group, the changes of function focus on the regions associated with coding, conduction and regulation of pain signals. In the FEM group, functional alterations mainly concentrated on the regions associated with pain regulation and emotion cognition. In the CM group, the changes focus on the regions related to spatial attention and cognition, affective disorders and pain feedback, which may be associated with migraine production, development and chronification.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lanteri-Minet, M., Economic and costs of chronic migraine[J]. Cur pain, headache R 18(1):385, 2014.
Global Burden of Disease Study, Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013[J]. Lancet. 386(9995):743–800, 2015.
Yalın, OIEM Groupan et al., Phenotypic features of chronic migraine[J]. J Headache Pain. 17(1):17–26, 2016.
Goadsby, P. J., Holland, P. R., Martins-Oliveira, M. et al., Pathophysiology of Migraine: A Disorder of Sensory Processing[J]. Physiol Rev. 97(2):553–622, 2017.
Schwedt, T. J., Chiang, C. C., Chong, C. D. et al., Functional MRI of migraine[J]. Lancet Neurol 14(1):81–91, 2015.
Schwedt, T. J., and Dodick, D. W., Advanced neuroimaging of migraine. Lancet Neurol 8(6):560–568, 2009.
Zhang, J., Su, J., Wang, M. et al., The sensorimotor network dysfunction in migraineurs without aura: a resting-state fMRI study. J Neurol. 264(4):654–663, 2017.
Lee, J., Lin, R. L., Garcia, R. G. et al., Reduced insula habituation associated with amplification of trigeminal brainstem input in migraine[J]. Cephalalgia. 37(11):1026–1038, 2017.
Niddam, D. M., Lai, K. L., Tsai, S. Y. et al., Neurochemical changes in the medial wall of the brain in chronic migraine[J]. Brain. 11:1–14, 2017.
Chai, S. C., Kung, J. C., and Shyu, B. C., Roles of the anterior cinglate cortex and medial thalami in short-term and long-term aversive information processing[J]. Mol Pain. 6:42–51, 2010.
Liang, F., Qin, W., Gong, J. et al., Alterations in regional homogeneity assessed by FMRI in patients with migraine without aura stratified by disease duration[J]. J Headache Pain. 14(1):1–9, 2013.
Moulton, E. A., Becerral, L., Maleki, N. et al., Painful heat reveals hyperexcitability of the temporal pole in interictal and inctal migraine states[J]. Cereb Cortex. 21(2):435–448, 2011.
Coppola, G., Renzo, A. D., Tinelli, E. et al., Evidence for brain morphometric changes during the migraine cycle: A magnetic resonance-based morphometry study[J]. Cephalalgia. 35(9):783–791, 2015.
Lorenz, J., Minoshima, S., and Casey, K. L., Keeping pain out of mind: the role of the dorsolateral precentral gyrus in pain modulation[J]. Brain. 126(5):1079–1091, 2003.
Tessitore, A., Russo, A., Giordano, A. et al., Disrupted default mode network connectivity in migraine without aura[J]. J Headache Pain. 14:89, 2013.
Yu, D., Yuan, K., Zhao, L. et al., Regional homogeneity abnormalities in patients with interictal migraine without aura[J]: a resting-state study. NMR Biomed. 25(5):806–812, 2012.
Nicole, S., Faiza, A. B., Arkink, E. B. et al., Attack Frequency and Disease Duration as Indicators for Brain Damage in Migraine[J]. Headache. 48(7):1044–1055, 2008.
Zhao, L., Liu, J., Dong, X. et al., Alterations in regional homogeneity assessed by FMRI in patients with migraine without aura stratified by disease duration[J]. J Headache Pain. 14:85, 2013.
Kuchinad, A., Schweinhardt, P., Seminowicz, D. A. et al., Accelerated brain gray matter loss in fibromyalgia patients: premature aging of the brain[J]. J Neurosci. 27(15):4004–4007, 2007.
Davis, K. D., Pope, G., Chen, J. et al., Corticalthinning in IBS: implications for homeostatic, attention, and pain processing[J]. Neurology. 70(2):153–154, 2008.
Schmidt, W. T., Leinisch, E., Straube, A. et al., Gray matter decrease in patients with chronic tension type headache[J]. Neurology. 65(9):1483–1486, 2005.
Valfre, W., Rainero, I., Bergui, M. et al., Voxel-based morphometry reveals gray matter abnormalities in migraine[J]. Headache. 48(1):109–117, 2008.
Kim, J. H., Kim, S., Suh, S. I. et al., Interictal meta bolicchanges in episodic migraine: a voxel-based FDG-PET study[J]. Cephalalgia. 30(1):53–61, 2010.
Prescot, A., Becerra, L., Pendse, G. et al., Excitatory neurotranIEM Groupitters in brain regions ininterictal migraine patients[J]. Mol Pain. 5:34, 2009.
Burstein, R., Noseda, R., Fulton, A. B. et al., Neurobiology of Photophobia. J Neuroophthalmol[J]. 39(1):94–102, 2019.
Géraud, G., Trotter, Y., Fabre, N. et al., Photophobia in migraine: an interictal PET study of cortical hyperexcitability and its modulation by pain[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:978–984, 2010.
Matsutani, K., Tsuruoka, M., Shinya, A. et al., Stimulation of the locus coeruleus suppresses trigeminal sensorimotor function in the rat[J]. Brain Res Bull. 53:827–832, 2000.
Tsuruoka, M., Matsutani, K., Maeda, M. et al., Coeruleotrigeminal inhibition of nociceptive processing in the rat trigeminal subnucleus caudalis[J]. Brain Res. 993(1–2):146–153, 2003.
Rocha-Filho, P., Marques, K. S., Torres, R. et al., Osmophobia and Headaches in Primary Care: Prevalence, Associated Factors, and Importance in Diagnosing Migraine[J]. J Headache Pain. 55(6):840–845, 2015.
Jingjing, Q., Gang, Y., Xijing, M. et al., Non-headache symptoms in migraine attack[J]. Chinese Journal of Neuromedicine 11(2):173–176, 2012.
Maleki, N., Becerra, L., Brawn, J. et al., Common hippocampal structural and functional changes in migraine[J]. Brain Struct Funct. 218(4):903–912, 2013.
Wilcox, S. L., Veggeberg, R., Lemme, J. et al., Increased functional activation of limbic brain regions during negative emotional processing in migraine[J]. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 10:1–10, 2016.
Maizels, M., Aurora, S., and Heinricher, M., Beyond neurovascular: migraine as a dysfunctional neurolimbic pain matrix[J]. Headache. 52:1553–1565, 2012.
IEM Groupitherman, T. A., Rains, J. C., and Penzien, D. B., Psychiatric comorbidities and migraine chronification. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 13(4):326–331, 2009.
Zhang, Q., Shao, A., Jiang, Z. et al., The exploration of mechanisms of comorbidity between migraine and depression. J. Cell. Mol. Med[J]. 00:1–9, 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Patient Facing Systems
Can Chen and Manyun Yan are co-first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen*, C., Yan*, M., Yu, Y. et al. Alterations in Regional Homogeneity Assessed by fMRI in Patients with Migraine Without Aura. J Med Syst 43, 298 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1425-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1425-z