Abstract
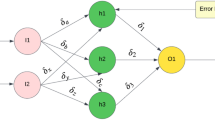
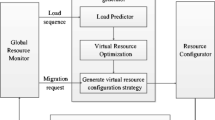
The utilization of cloud services has significantly increased due to the easiness in accessibility, better performance, and decrease in the high initial cost. In general, cloud users anticipate completing their tasks without any delay, whereas cloud providers yearn for reducing the energy cost, which is one of the major costs in the cloud service environment. However, reducing energy consumption increases the makespan and leads to customer dissatisfaction. So, it is essential to obtain a set of non-domination solutions for these multiple and conflicting objectives (makespan and energy consumption). In order to control the energy consumption efficaciously, the Dynamic Voltage Frequency Scaling system is incorporated in the optimization procedure and a set of non-domination solutions are obtained using Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm (NSGA-II). Further, the Artificial Neural Network (ANN), which is one of the most successful machine learning algorithms, is used to predict the virtual machines based on the characteristics of tasks and features of the resources. The optimum solutions obtained using the optimization process with the support of ANN and without the support of ANN are presented and discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calheiros, R.N., Ranjan, R., Beloglazov, A., De Rose, C.A., Buyya, R.: CloudSim: a toolkit for modeling and simulation of cloud computing environments and evaluation of resource provisioning algorithms. Softw. Pract. Exp. 41(1), 23–50 (2011)
Wu, C.M., Chang, R.S., Chan, H.Y.: A green energy-efficient scheduling algorithm using the DVFS technique for cloud datacenters. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 37, 141–147 (2014)
Kliazovich, D., Bouvry, P., Khan, S.U.: GreenCloud: a packet-level simulator of energy-aware cloud computing data centers. J. Supercomput. 62(3), 1263–1283 (2012)
Jin, X., Zhang, F., Fan, L., Song, Y., Liu, Z.: Scheduling for energy minimization on restricted parallel processors. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 81, 36–46 (2015)
Piątek, W., Oleksiak, A., Da Costa, G.: Energy and thermal models for simulation of workload and resource management in computing systems. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 58, 40–54 (2015)
Ding, Y., Qin, X., Liu, L., Wang, T.: Energy efficient scheduling of virtual machines in cloud with deadline constraint. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 50, 62–74 (2015)
Mustafa, S., Nazir, B., Hayat, A., Madani, S.A.: Resource management in cloud computing: taxonomy, prospects, and challenges. Comput. Electr. Eng. 47, 186–203 (2015)
Lei, H., Zhang, T., Liu, Y., Zha, Y., Zhu, X.: SGEESS: smart green energy-efficient scheduling strategy with dynamic electricity price for data center. J. Syst. Softw. 108, 23–38 (2015)
Pedram, M.: Energy-efficient datacenters. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 31(10), 1465–1484 (2012)
Beloglazov, A., Buyya, R., Lee, Y.C., Zomaya, A.: A taxonomy and survey of energy-efficient data centers and cloud computing systems. Adv. Comput. 82(2), 47–111 (2011)
Quan, D.M., Mezza, F., Sannenli, D., Giafreda, R.: T-Alloc: a practical energy efficient resource allocation algorithm for traditional data centers. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 28(5), 791–800 (2012)
Castane, G.G., Nunez, A., Llopis, P., Carretero, J.: E-mc 2: a formal framework for energy modelling in cloud computing. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 39, 56–75 (2013)
Zheng, X., Cai, Y.: Energy-aware load dispatching in geographically located internet data centers. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 1(4), 275–285 (2013)
Wang, L., Zhang, F., Arjona Aroca, J., Vasilakos, A.V., Zheng, K., Hou, C., Li, D., Liu, Z.: GreenDCN: a general framework for achieving energy efficiency in data center networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 32(1), 4–15 (2014)
Kim, N., Cho, J., Seo, E.: Energy-credit scheduler: an energy-aware virtual machine scheduler for cloud systems. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 32, 128–137 (2014)
Luo, L., Wu, W., Tsai, W.T., Di, D., Zhang, F.: Simulation of power consumption of cloud data centers. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 39, 152–171 (2013)
Hammadi, A., Mhamdi, L.: A survey on architectures and energy efficiency in data center networks. Comput. Commun. 40, 1–21 (2014)
Rodero, I., Jaramillo, J., Quiroz, A., Parashar, M., Guim, F., Poole, S.: Energy-efficient application-aware online provisioning for virtualized clouds and data centers. In: Presented at the IEEE International Conference on Green Computing, pp. 31–45 (2010)
Kessaci, Y., Melab, N., Talbi, E.G.: A multi-start local search heuristic for an energy efficient VMs assignment on top of the OpenNebula cloud manager. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 36, 237–256 (2014)
Luo, Y., Zhou, S.: Power consumption optimization strategy of cloud workflow scheduling based on SLA. WSEAS Trans. Syst. 13, 368–377 (2014)
Guo-ning, G., Ting-Lei, H., Shuai, G.: Genetic simulated annealing algorithm for task scheduling based on cloud computing environment. In: Presented at the International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Integrated Systems (2010)
Priyanto, A.A., Adiwijaya, W.: Implementation of ant colony optimization algorithm on the project resource scheduling problem. Faculty of informatics, Institute of Technology Telkom, Bandung (2008)
Preve, N.: Balanced job scheduling based on ant algorithm for grid network. Int. J. Grid High Perform. Comput. 2(1), 34–50 (2010)
Banerjee, S., Mukherjee, I., Mahanti, P.K.: Cloud computing initiative using modified ant colony framework. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 56, 221–224 (2009)
Feller, E., Rilling, L., Morin, C.: Energy-aware ant colony based workload placement in clouds. In: Presented at the IEEE/ACM 12th International Conference on Grid Computing, pp. 26–33 (2011)
Pandey, S., Wu, L., Guru, S.M., Buyya, R.: A particle swarm optimization-based heuristic for scheduling workflow applications in cloud computing environments. In: Presented at the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA), pp. 400–407 (2010)
Tayal, S.: Tasks scheduling optimization for the cloud computing systems. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Sci. Technol. 5(2), 111–115 (2011)
Ajila, S.A., Bankole, A.A.: Using machine learning algorithms for cloud client prediction models in a web VM resource provisioning environment. Trans. Mach. Learn. Artif. Intell. 4(1), 28–51 (2016)
Bala, A., Chana, I.: Prediction-based proactive load balancing approach through VM migration. Eng. Comput. 32(4), 1–12 (2016)
Kumar, N., Patel, P.: Resource management using feed forward ANN-PSO in cloud computing environment. In: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Competitive Strategies, p. 57 (2016)
Islam, S., Keung, J., Lee, K., Liu, A.: Empirical prediction models for adaptive resource provisioning in the cloud. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 28(1), 155–162 (2012)
Suresh, S., Sujit, P.B., Rao, A.K.: Particle swarm optimization approach for multi-objective composite box-beam design. Compos. Struct. 81(4), 598–605 (2007)
Omkar, S.N., Khandelwal, R., Ananth, T.V.S., Naik, G.N., Gopalakrishnan, S.: Quantum behaved Particle Swarm Optimization (QPSO) for multi-objective design optimization of composite structures. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(8), 11312–11322 (2009)
Omkar, S.N., Mudigere, D., Naik, G.N., Gopalakrishnan, S.: Vector evaluated particle swarm optimization (VEPSO) for multi-objective design optimization of composite structures. Comput. Struct. 86(1), 1–14 (2008)
Deb, K.: Multi-objective Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithms. Wiley, Hoboken (2001)
Nicholas, P.E., Padmanaban, K.P., Babu, M.C.: Multi-objective optimization of laminated composite plate with diffused layer angles using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II). Adv. Compos. Lett. 23(4), 96–105 (2014)
Bolanos, R., Echeverry, M., Escobar, J.: A multiobjective non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) for the Multiple Traveling Salesman Problem. Decis. Sci. Lett. 4(4), 559–568 (2015)
Hsu, C.H., Kremer, U.: The design, implementation, and evaluation of a compiler algorithm for CPU energy reduction. ACM SIGPLAN Not. 38(5), 38–48 (2003)
Tao, F., LaiLi, Y., Xu, L., Zhang, L.: FC-PACO-RM: a parallel method for service composition optimal-selection in cloud manufacturing system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 9(4), 2023–2033 (2013)
Demuth, H., Beale, M.: Neural Network Toolbox User’s Guide. The Mathworks, Natick (2000)
Yuen, K.V., Lam, H.F.: On the complexity of artificial neural networks for smart structures monitoring. Eng. Struct. 28(7), 977–984 (2006)
Bolanca, T., Ukic, S., Peternel, I., Kusic, H., Bozic, A.L.: Artificial neural network models for advanced oxidation of organics in water matrix-comparison of applied methodologies. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 21(1), 21–29 (2014)
Kermanshahi, B., Iwamiya, H.: Up to year 2020 load forecasting using neural nets. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 24(9), 789–797 (2002)
Chakraborty, D.: Artificial neural network based delamination prediction in laminated composites. Mater. Des. 26(1), 1–7 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sathya Sofia, A., GaneshKumar, P. Multi-objective Task Scheduling to Minimize Energy Consumption and Makespan of Cloud Computing Using NSGA-II. J Netw Syst Manage 26, 463–485 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-017-9425-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-017-9425-0