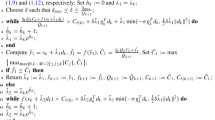Abstract
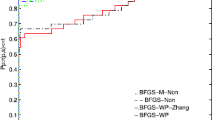
This paper mainly aims to study a new nonmonotone line search slackness technique for unconstrained optimization problems and show that it possesses the global convergence without needing condition of convexity. We establish the corresponding algorithm and illustrate its effectiveness by virtue of some numerical tests. Simulation results indicate that the proposed method is very effective for non-convex functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ni, Q.: Optimization Methods and Programming. Science Press, Beijing (2009)
Grippo, L., Lampariello, F., Lucidi, S.: A nonmonotone line search technique for Newton’s methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 23, 707–716 (1986)
Sun, W., Han, J., Sun, J.: Global convergence of non-monotone descent methods for unconstrained optimization problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 146, 89–98 (2002)
Yu, Z., Pu, D.: A new nonmonotone line search technique for unconstrained optimization. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 219, 134–144 (2008)
Grippo, L., Lampariello, F., Lucidi, S.: A truncated Newton method with nonmonotone line search for unconstrained optimization. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 60, 401–419 (1989)
Nocedal, J., Wright, S.J.: Numerical Optimization, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2006)
Shi, Z., Shen, J.: Convergence of PRP method with new nonmonotone line search. Appl. Math. Comput. 181, 423–431 (2006)
Shi, Z., Shen, J.: Convergence of nonmonotone line search method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 193, 397–412 (2006)
Sun, W., Zhou, Q.: An unconstrained optimization method using nonmonotone second order Goldstein’s line search. Sci. China Ser. A 50, 1389–1400 (2007)
Yu, Y., Gao, L.: Nonmonotone line search algorithm for constrained minimax problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 115, 419–446 (2002)
Zhou, Q., Sun, W.: Adaptive nonmonotone line search method for unconstrained optimization. Front. Math. China 3, 133–148 (2008)
Andrei, N.: An unconstrained optimizaition test functions collection. Adv. Model. Optim. 10, 147–161 (2008)
Shi, Z.J., Shen, J.: New inexact line search method for unconstrained optimization. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 127, 425–446 (2005)
Acknowledgements
Research supported by Grant HGA0905 and the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (Grant No.: 11KJB110001). The second author is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.: 51205151). The authors are very grateful to the referees for valuable comments and constructive suggestions which result in the present version of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Alexander S. Strekalovsky.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, P., Liu, XQ. A Nonmonotone Line Search Slackness Technique for Unconstrained Optimization. J Optim Theory Appl 158, 773–786 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-012-0247-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-012-0247-7