Abstract
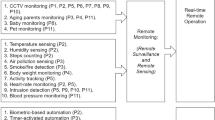
We’re currently shifting from the Information Age to the Intelligence Age. The Intelligence Age will be characterized by autonomous communication between intelligent devices that are sensitive to a person’s presence and respond by performing a specific task that enhances that person’s lifestyle. In this perspective, the Internet of Things envisages a plethora of heterogeneous objects interacting with people and the physical environment. Things are able to sense a user’s presence, movement and behaviour, analyse that data in order to learn about that user, and then make an intelligent decision to perform a task based on the data. Context-aware computing has proven to be successful in understanding data captured by sensors. In this paper, we present a Internet of Things (IoT) context-aware system and its application in the Cultural Heritage domain. Cultural Heritage is a domain where the widespread diffusion of ICT technology and sensors, within its spaces like museums, art exhibition, etc., can strongly enhance the quality of the offered services and subsequently create a Smart Cultural Environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Weiser M (1991) The computer for the 21st century. Sci Am 265(3):66–75. doi:10.1145/329124.329126
Bolchini C, Curino CA, Orsi G, Quintarelli E, Rossato R, Schreiber FA, Tanca L (2009) And what can context do for data? ACM Commun 52(11):136–140
Dey A, Abowd GD (2000) Towards a better understanding of context and context-awareness. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on The What, Who, Where, When, and How of Context-Awareness, pp 1–12
Jones Q, Grandhi SA (2005) P3 Systems: Putting the place back into social networks. IEEE Internet Comput 9(5):38–46
Schilit BN, Adams N, Want R (1994) Context-aware computing applications. In: Proceedings of the workshop on mobile computing systems and applications, pp 85–90
Strang T, Linnhoff-Popien C (2004) A context modeling survey. In: Workshop on advanced context modelling, reasoning and management as part of ubicomp
Vinh PC (2014) Information and service integration based on Agent-Oriented ubiquitous computing. Mobile Netw Appl 19:227–243
Furno A, Zimeo E (2014) Context-aware composition of semantic web services. Mobile Netw Appl 19:235–248
Lee C-H, Huang C-M, Chen W-S (2016) A POI-aware power saving scheme for ubiquitous touring service using mobile devices over the cellular and Wi-Fi hybrid network. Mobile Netw Appl 21:299–312
Bettini C, ea Brdiczka O (2010) A survey of context modeling and reasoning techniques. Pervasive Mob Comput 6:161–180
Schafer JB, Frankowski D, Herlocker J, Sen S (2007) Collaborative filtering recommender systems. In: The adaptive web: methods and strategies of web personalization. Lecture Notes in Computer Science Series 4321, pp 291–324
Park AH, Park SH, Youn HY (2007) A flexible and scalable agent platform for Multi-Agent systems. Proceedings of WASET, pp 1–6
Song SK, Han SW, Youn HY (2008) A new agent platform architecture supporting the agent group paradigm for multi-agent systems. In: IEEE/WIC/ACM international conference on Intelligent agent technology, 2007, IAT07, pp 399–402. IEEE
Dragoi O, Black JP (2004) Discovering services is not enough. IEEE Distrib Syst 5(8):3–13
Schilit BN, Adams N, Want R (1994) Context-aware computing applications. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, pp 85–90
Abowd GD, Dey A, Brown PJ, Davies N, Smith M, Steggles P (1999) Towards a better understanding of context and context-awareness. In: Proceedings 1st international symposium on Handheld and Ubiquitous Computing, ser. HUC ’99. London, UK: Springer-Verlag, pp 304–307
Dey A (2001) Understanding and using context. Pers Ubiquit Comput 5(1):4–7
Chianese A, Marulli F, Piccialli F, Benedusi P, Jung JE (2016) An associative engines based approach supporting collaborative analytics in the internet of cultural things, future generation computing systems. Elsevier. doi:10.1016/j.future.2016.04.015
Chianese A, Marulli F, Moscato V, Piccialli F (2013) Smartweet: a location-based smart application for exhibits and museums, International Conference on Signal Image Technology and Internet Based Systems, pp 408–415
Chianese A, Piccialli F, Valente I (2015) Smart environments and Cultural Heritage: a novel approach to create intelligent cultural spaces Journal of Location Based Services, pp 209–334
Chianese A, Piccialli F (2016) A smart system to manage the context evolution in the Cultural Heritage domain. Computers & Electrical Engineering. doi:10.1016/j.compeleceng.2016.02.008
Becker C, Duurr F (2005) On location models for ubiquitous computing. Pers Ubiquit Comput 9(1):20–31
Nicklas D, Grossmann M, Minguez J, Wieland M (2004) Adding high-level reasoning to efficient low-level context management: A hybrid approach. In: Proceedings of the 6th IEEE annual conference on pervasive computing and communications workshops, IEEE Computer Society
Schaffers H, Komninos N, Pallot M, Trousse B, Nilsson M, Oliveira A (2011) Smart cities and the future internet: Towards cooperation frameworks for open innovation. Lect Notes Comput Sci 6656:431–446
Albanese M, d’Acierno A, Moscato V, Persia F, Picariello A (2011) A multimedia semantic recommender system for cultural heritage applications. In: Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference on Semantic Computing, pp 403–410
Hart S, Staveland LE (1988) Development of nasa-tlx (task load index): Results of empirical and theoretical research. In: Human mental workload, pp 139–183
Kuflik T, Boger Z, Zancanaro M (2012) Analysis and prediction of museum visitors behavioral pattern types, ubiquitous display environments. Cogn Tech 161–176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piccialli, F., Chianese, A. The Internet of Things Supporting Context-Aware Computing: A Cultural Heritage Case Study. Mobile Netw Appl 22, 332–343 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-017-0810-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-017-0810-4