Abstract
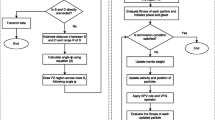
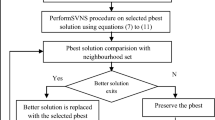
In a Mobile ad hoc network (MANET), scalability, dynamic topology and high mobility are the most significant challenges to perform the routing with improved network lifetime. According to the geographical location, geographic routing termed as position-based routing performs data transmission between source node and destination node in a MANET. But, geographic routing protocols were not able achieve effective routing with enhanced network lifetime by improving the resource optimization and optimal coverage performance. In order to improve the resource optimization and network lifetime, an efficient Particle Swarm based Resource Optimized Geographic Routing (PS-ROGR) technique is introduced in MANET. Initially, each particle (i.e. mobile node) movement in a network is controlled by its local best known position in the search space (i.e. geographic location). The PSO permits all the particles in the network to communicate with the other particles with minimum energy. The particle which has the better global best function is selected for energy efficient routing based on the fitness value. Therefore the entire particles share the similar best position to optimize the network resources. Thereby, the PS-ROGR technique prolong the lifetime of the network with minimum energy utilization. Simulation is carried out on the factors such as packet delivery ratio, average end to end delay, energy consumption and network lifetime. Thus, the proposed PS-ROGR technique improves the network lifetime by 22% and reduces the average end to end delay by 46%. Then, the packet delivery ratio is enhanced up to 11% and energy consumption is minimized to 16% with the help of proposed PS-ROGR technique.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Q, Kanhere SS, Hassan M (2013) Adaptive position update for geographic routing in mobile ad hoc networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 12(3):489–501
Jin X, Zhang R, Sun J, Zhang Y (2014) TIGHT: a geographic routing protocol for cognitive radio mobile ad hoc networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 13(8):4670–4681
Dong P, Qian H, Zhou K, Lu W, Lan S (2015) “a maximally radio-disjoint geographic multipath routing protocol for MANET”, annals of telecommunications - annales des telecommunications. Spring 70(5):207–220
Mouna Rekik, Nathalie Mitton, and Zied Chtourou, “Geographic GReedy routing with ACO recovery strategy GRACO”, Ad-hoc Mobile, and Wireless Networks, Springer, Volume 9143, 2015, Pages 19–32
Devi S, Sarje A (2015) Dir-DREAM: geographical routing protocol for FSO MANET. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Springer, Volume 321:95–106
Manickavelu D, Vaidyanathan RU (2014) Particle swarm optimization (PSO)-based node and link lifetime prediction algorithm for route recovery in MANET. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Net 2014(107):1–10
Zachariah SS, Preetha KG (2013) Shortest Path Geographic Routing for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Int J Comput Sci Eng Technol (IJCSET) 4(08):1177–1180
Xiang X, Wang X, Zhou Z (2012) Self-adaptive on-demand geographic routing for mobile ad hoc networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 11(9):1572–1586
Zongming Feia and Jianjun Yang, Hui Luc, “Improving routing efficiency through intermediate target based geographic routing”, Digital Communications and Networks, Elsevier, Volume 1, 2015, Pages 204–212
Ding Y-z, XuYuan M-z (2016) Tian Hui-ying li, Bing-xiang Liu, “a BER and 2-hop routing information-based stable geographical routing protocol in MANETs for multimedia applications”. Wirel Pers Commun 90(1):3–32
De Rango F, Guerriero F, Fazio P (2012) Link-stability and energy aware routing protocol in distributed wireless networks. IEEE Transact Parallel Distrib Syst 23(4):713–726
Omidvar A, Mohammadi K (2014) Particle swarm optimization in intelligent routing of delay-tolerant network routing. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 2014(147):1–8
Hadi Noureddine, Qiang Ni, Geyong Min, Hamed Al-Raweshidy, “A new link lifetime estimation method for greedy and contention-based routing in mobile ad hoc networks”, Telecommunication Systems, Springer, Volume 55, Issue 3, 2014, Pages 421–433
ALaa E. Abdallah, Emad E. Abdallah, Mohammad Bsoul, Ahmed Fawzi Otoom, “Randomized geographic-based routing with nearly guaranteed delivery for 3D ad hoc network”, International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, hindawi publishing corporation, Volume 2016, 2016, Pages 1–16
Niranjan Kumar Ray and Ashok Kumar Turuk, “A Hybrid Energy Efficient Protocol for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks”, Journal of Computer Networks and Communications, Hindawi Publishing Corporation, Volume 2016, 2016, Pages 1-11
Wen-Zao Li, Feng Lin, Ji-Liu Zhou and Yan Wang, “DTN routing with fixed stations based on the geographic grid approach in an urban environment”, Wireless Personal Communications, Springer, Volume 82, Issue 4, 2015, Pages 2033–2049
Jamali S, Rezaei L, Gudakahriz SJ (2013) An energy-efficient routing protocol for MANETs: a particle swarm optimization approach. Journal of Applied Research and Technology, Elsevier 11(6):803–812
Mahbubur Rahman, Akhtaruzzaman, “An Efficient Position based Power Aware Routing Algorithm in Mobile Ad-hoc Networks”, Int J Comp Network Inf Secur (IJCNIS), Volume 8, Issue 7, 2016, Pages 43–49,
Giagkos A, Wilson MS (2014) “BeeIP – a swarm intelligence based routing for wireless ad hoc networks” information sciences. Elsevier 265:23–35
Sheng-Tzong, Cheng Jian-Pan, Li Gwo-Jiun Horng, “An adaptive cluster-based routing mechanism for energy conservation in mobile ad hoc networks”, Wireless Personal Communications, Springer, Volume 70, Issue 2, 2013, Pages 561–579
Priyanka Jaiswal and Adwitiya Sinha, “Stable geographic forwarding with link lifetime prediction in mobile adhoc networks for battlefield environment”, Human-centric Computing and Information Sciences, Springer, Issue 1, 2016, Pages 1–18
Mishra P, Gandhi C, Singh B (2016) Link quality and energy aware geographical routing in MANETs using fuzzy logics. J Telecommun Inf Technol 6:1–17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nallusamy, C., Sabari, A. Particle Swarm Based Resource Optimized Geographic Routing for Improved Network Lifetime in MANET. Mobile Netw Appl 24, 375–385 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-017-0911-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-017-0911-0