Abstract
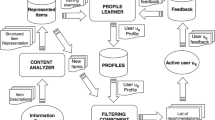
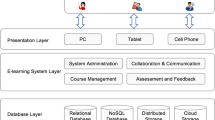
As the latest stage of learning and training evolution, e-Learning is supposed to provide intelligent functionalities not only in processing multi-media education resources but also in supporting context-sensitive pedagogical education processes. Towards providing an integrated solution for intelligent multimedia e-Learning, this paper presents a context-aware knowledge management framework named ConKMeL. Proposed framework features a semantic context-based approach for representing and integrating information and knowledge in e-Learning. Requirement analysis in university e-Learning environments shows that knowledge communications are usually in a hybrid mode across different conceptual levels. Based on the fact, a multi-layer contextual knowledge representation model called KG (knowledge graph) is presented. Corresponding key issues in development such as context-based knowledge retrieval and logical knowledge interpretation are discussed. On the application side, a scenario-based learning case study is shown to demonstrate the concepts and techniques developed in the ConKMeL framework.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akman V (2002) Context in artificial intelligence: a fleeting overview. McGraw-Hill, Milano
Akman V, Bouquet P, Thomason R, Young RA (eds) (2001) Modeling and using context. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Bailey C, El-Beltagy SR, Hall W (2001) Link augmentation: a context-based approach to support adaptive hypermedia. In: Proc. of Hypertext'01. Arhus, Denmark, pp 239–251
Berners-Lee T, Hendler J, Lassila O (2001) The semantic web. Scientific American
Brezillon P, Pomerol J (2001) Is context a kind of collective tacit knowledge? In: Proceedings of European CSCW 2001 workshop on managing tacit knowledge. Bonn, Germany, pp 23–29
Champin PA (2001) A model to represent design episodes for reuse assistance with interactive case-based reasoning. In: Proc. of GWCBR 2001. Baden-Baden, Germany, pp 189–197
DAML (2000) DARPA Agent Markup Language. http://www.daml.org/
DC (2003) Dublin core metadata element set. Version 1.1. http://dublincore.org/documents/dces/
Delteil A, Faron-Zucker C, Dieng R (2001) Extension of RDF(S) with contextual and definitional knowledge. In: Proc. of SWWS 2001. California, USA
Dorai C, Venkatesh S (2002) Media computing: computational media aesthetics. Kluwer
Egyed-Zs E, Prie Y, Mille A, Pinon J (2002) un modele de traces d'utilisation. In: Proc. of Ingenierie de Connaissances (IC). Rouen, France, pp 39–50
Fan J, Zhu X, Elmagarmid AK, Aref WG (2003) ClusterView: a hierarchical video shot classification system. IEEE Trans on Multimedia 5(3)
Graves AP, Lalmas M (2002) Video retrieval using an MPEG-7 based inference network. In: Proc. of ACM SIGIR2002. Tampere, Finland, pp 339–346
Huang W, Hacid MS (2003) Contextual knowledge representation, retrieval and interpretation in multimedia e-Learning. In: Proceedings of the fourth IEEE international conference on information reuse and integration. Las Vegas, USA
Huang W, Tao T (2004) Adding context-awareness to knowledge management in modern enterprises. In: Proc. of IEEE international conference on intelligent systems. Varna, Bulgaria
Huang W, Shi J, Zhang F (2000) An RDF-based approach of heterogeneous resources description in an educational digital video library. In: Proc. of IMSA 2000. Las Vegas, USA, pp 245–250
Huang W, Prie Y, Champin PA, Mille A (2002) Semantic context representation of resources using annotation graph. In: Proceedings of the eighth international workshop on multimedia information systems. Tempe, USA
Huang W, Tao T, Hacid MS, Mille A (2003) Facilitate knowledge communications in multimedia e-Learning environments. In: Proceedings of the first ACM international workshop on multimedia databases. New Orleans, USA
Ioannidis Y, LY (1994) Incomplete path expressions and their disambiguation. In: Proc. of SIGMOD 1994. Minneapolis, USA, pp 138–149
Kalfoglou Y, Schorlemmer M (2002) Information flow based ontology mapping. In: Proc. of ODBASE'02. Irvine, USA
Katz B, Lin J (2002) Annotating the semantic web using natural language. In: Proc. of NLPXML-2002. Taipei, China
Kindley R (2002) Scenario-based e-Learning: a step beyond traditional e-Learning. ASDT online magazine-learning circuits 3(5)
Lave J, Wenger E (1990) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
LOM (1999) IEEE P1484.12 learning object metadata working group, learning object metadata. http://ltsc.ieee.org/wg12/
Martin P (2003) Knowledge representation, sharing and retrieval on the web
RDF (2004) Resource description framework. http://www.w3.org/RDF/
SCORM (2003) Advanced distributed learning initiative, sharable content object reference model (SCORM). http://www.adlnet.org/
Sowa J (1992) Conceptual graphs summary. pp 3–52
Theodorakis M, Analyti A, Constantopoulos P, Spyratos N (2002) A theory of context in information bases. Inf Syst 27:151–191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, W., Mille, A. ConKMeL: a contextual knowledge management framework to support multimedia e-Learning. Multimed Tools Appl 30, 205–219 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-006-0024-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-006-0024-4