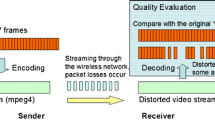
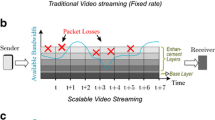
Abstract
In this paper, an adaptive framework for video streaming over the Internet is presented. The framework is a joint design of packet scheduling and rate control with optimal bandwidth resource allocation. The transmission rate is dynamically adjusted to obtain maximal utilization of the client buffer and minimal allocation of the bandwidth. Under the constraint of the transmission rate, a prioritized packet scheduling is designed to provide a better visual quality of video frames. The packet scheduling is a refined bandwidth allocation which takes into account of varying importance of the different packets in a compressed video stream. Moreover, the proposed approach is scalable with increasing multimedia flows in the distributed Internet environment. Comparisons are made with the most current streaming approaches to evaluate the performance of the framework using the H.264 video codec. The extensive simulation results show that the average Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) increases in our proposed approach. It provides a better quality of the decoded frames, and the quality of the decoded frames changes more smoothly. The achieved video quality among different users also has a lower fluctuation, which indicates a fair sharing of network resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajic IV, Tickoo O, Kalyanaraman AS, Woods JW (2003) Integrated end-to-end buffer management and congestion control for scalable video communications. In: IEEE ICIP’03, Barcelona, September 2003, pp 257–260
Balk A, Gerla M, Maggiorini D, Sanadidi MY (2004) Adaptive video streaming: pre-encoded MPEG-4 with bandwidth scaling. Comput Networks 44(4):415–439
Bansal D, Balakrishnan H (2001) Binomial congestion control algorithms. In: Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM’01, Anchorage, pp 631–640
Bouras C, Gkamas A, Karaliotas A, Stamos K (2004) Architecture and performance evaluation for redundant multicast transmission supporting adaptive QoS. J Multimedia Tools Appl 25(1):85–110
Cai L, Shen X, Pan J, Mark JW (2005) Performance analysis of TCP-friendly AIMD algorithms for multimedia applications. IEEE Trans Multimedia 7(2):339–353
Chen I-R, Li S-T, Yen I-L (2005) Adaptive QoS control based on benefit optimization for video servers providing differentiated services. J Multimedia Tools Appl 25(2):167–185
Chen S-C, Shyu M-L, Gray I, Luo H (2005) An adaptive rate-control streaming mechanism with optimal buffer utilization. J Syst Softw 75(3):271–282 (special issue on adaptive multimedia computing)
Chou P, Miao Z (2006) Rate-distortion optimized streaming of packetized media. IEEE Trans Multimedia 8(2):390–404
Cuetos P, Ross K (2003) Optimal streaming of layered video: joint scheduling and error concealment. In: Proceedings of the eleventh ACM international conference on Multimedia, Berkeley, CA, pp 55–64
Dong J, He C, Zheng YF, Ewing RL (2005) AVP: a highly efficient transport protocol for low bit rate multimedia communications. J Multimedia Tools Appl 25(2):187–216
Floyd S, Handley M, Padhye JM, Widmer J (2000) Equation-based congestion control for unicast applications. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM, Stockholm, August 2000, pp 43–56
Jin S, Guo L, Matta I, Bestavros A (2003) A spectrum of TCP-friendly widow-based congestion control algorithms. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 11(3):341–355
Kang SH, Zakhor A (2003) Effective bandwidth based scheduling for streaming multimedia. In: Proceedings of ICIP, Barcelona, September 2003, pp 633–636
Kim Y-G, Kim J, Kuo C-CJ (2004) TCP-friendly internet video with smooth and fast rate adaptation and network-aware error control. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 4(2): 256–268
Krasic C, Walpole J, Feng W (2003) Quality-adaptive media streaming by priority drop. In: NOSSDAV. Monterey, June 2003, pp 112–121
Kusmierek E, Du DHC (2005) Streaming video delivery over internet with adaptive end-to-end QoS. J Syst Softw 75(3):237–252
Luo H, Shyu M-L, Chen S-C (2005) A multi-buffer scheduling scheme for video streaming. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME), Amsterdam, 6–8 July 2005, pp 1218–1221
Luo H, Shyu M-L, Chen S-C (2006) An optimal resource utilization scheme with end-to-end congestion control for continuous media stream transmission. Comput Networks 50(7):921–937
Mielke M, Aygun R, Song Y, Zhang A (2002) Plus: probe-loss utilization streaming mechanism for distributed multimedia presentation systems. IEEE Trans Multimedia 4(4):561–577
Joint Video Team of ISO/IEC MPEG and ITU-T VCEG (2002) Joint model number 1, revision 1 (JM-1R1)
Rejaie R, Handley M, Estrin D (1999) RAP: an end-to-end rate-based congestion control mechanism for realtime streams in the internet. In: Proceedings of INFOCOM 99, New York, March 1999, pp 1337–1345
Rhee I, Xu L (2005) Limitations in equation-based congestion control. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM. Philadelphia, PA, August 2005, pp 49–60
Tunali ET, Kantarci A, Ozbek N (2005) Robust quality adaptation for internet video streaming. J Multimedia Tools Appl 27(3):431–448
Vieron J, Guillemot C (2004) Real-time constrained TCP-compatible rate control for video over the internet. IEEE Trans Multimedia 6(3):634–646
Wang B, Kurose JF, Sheony PJ, Towsley DF (2004) Multimedia streaming via TCP. In: ACM Multimedia, New York City, NY, October 2004, pp 908–915
Widmer J, Denda R, Mauve M (2001) A survey on TCP-friendly congestion control. IEEE Netw 15(3):28–37
Wu D, Hou YT, Zhang Y-Q (2000) Transporting real-time video over the internet: challenges and approaches. Proc IEEE 88(12):1855–1877
Zhang Q, Zhu W, Zhang YQ (2001) Resource allocation for multimedia streaming over the internet. IEEE Trans Multimedia 3(3):339–355
Zhu P, Zeng W, Li C (2007) Joint design of source rate control and QoS aware congestion control for video streaming over the internet. IEEE Trans Multimedia 9(2):366–376
Ziviani A, Wolfinger BE, de Rezende JF, Duarte OCMB, Fdida S (2005) Joint adoption of QoS scheme for MPEG streams. J Multimedia Tools Appl 26(1):59–80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, H., Shyu, ML. & Chen, SC. Video streaming over the internet with optimal bandwidth resource allocation. Multimed Tools Appl 40, 111–134 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-007-0187-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-007-0187-7