Abstract
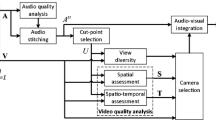
A video remix is generally created by arranging selected video clips and combining them with other media streams such as audio clips and video transition effects. This paper proposes a system for semi-automatically creating video remixes of good expressive quality. Given multiple original video clips, audio clips, and transition effects as the input, the proposed system generates a video remix by five processes: I) video clip sequence generation, II) audio clip selection, III) audio boundary extraction, IV) video segment extraction, and V) transition effect selection, based on the spatial and temporal structural patterns automatically learned from professionally created video remix examples. Experiments using movie trailers of action genre as video remix examples not only demonstrate that video remixing by professionals can be imitated based on examples but also reveal that the video clip sequence generation and audio clip selection are the most important processes to improve the perceived expressive quality of video remixes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyanagi S, Kourai K, Sato K, Takada T, Sugawara T (2003) Evaluation of new video skimming method using audio and video information. In: Proc. DEWS, 2-A-01
Blairwitch.de, Horror Movie Entertainment. http://www.blairwitch.de/index.php?seitenid=1. Accessed 2008
Bouguet J-Y (2000) Pyramidal implementation of the Lucas Kanade feature tracker. OpenCV Documentation, Microprocessor Research Labs, Intel Corporation
Chen H-W, Kuo J-H, Chu W-T, Wu J-L (2004) Action movies segmentation and summarization based on tempo analysis. In: Proc. ACM SIGMM international workshop on multimedia information retrieval, pp 251–258
Duda RO, Hart PE, Stork DG (2006) Pattern classification, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, 2001. p 7307
Dunker P, Nowak S, Begau A, Lanz C (2008) Content-based mood classification for photos and music: a generic multi-modal classification framework and evaluation approach. In: Proc. international conference on multimedia information retrieval, pp 97–104
Foote J, Cooper M, Girgensohn A (2002) Creating music videos using automatic media analysis. In: Proc. ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 553–560
Hua X-S, Lu L, Zhang H-J (2004) Automatic music video generation based on temporal pattern analysis. In: Proc. ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 472–475
Hua X-S, Lu L, Zhang H-J (2004) Optimization-based automated home video editing system. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 14(5):572–583
Jung B, Song J, Lee Y (2007) A narrative-based abstraction framework for story-oriented video. In: ACM transactions on multimedia computing, communications and applications, vol 3, no 2
Kim J-G, Chang HS, Kim J, Kim H-M (2004) Threshold-based camera motion characterization of MPEG video. ETRI J 26(3):269–272
Kumano M, Ariki Y, Shunto K, Tsukada K (2002) Video editing support system based on video content analysis. In: Proc. Asian conference on computer vision, pp 628–633
Kurihara Y, Nitta N, Babaguchi N (2009) Automatic appropriate segment extraction from shots based on learning from example videos. In: Proc. Pacific-Rim symposium on image and video technology, pp 1082–1093
Lee S-H, Yeh CH, Kuo C-CJ (2004) Video skimming based on story units via general tempo analysis. In: Proc. IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo, vol 2, pp 1099– 1102
Li B, Pan H, Sezan I (2003) A general framework for sports video summarization with its application to soccer. In: Proc. IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, pp 169–172
Li T, Ogihara M, Li Q (2003) A comparative study on content-based music classification. In: Proc. international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, pp 282–289
Lienhart R (1999) Abstracting home video automatically. In: Proc. ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 37–40
Liu Z, Wang Y, Chen T (1998) Audio feature extraction and analysis for scene segmentation and classification. J VLSI Signal Process Syst 20(1–2):pp 61–79
Mckinney M, Breebaart J (2003) Features for audio and music classification. In: Proc. international symposium on music information retrieval, pp 151–158
MixMeister BPM Analyzer. http://www.mixmeister.com/download_freestuff.html. Accessed 2008
Mulhem P, Kankanhalli MS, Yi J, Hassan H (2003) Pivot vector space approach for audio-video mixing. IEEE Multimed 10(2):28–40
Nitta N, Takahashi Y, Babaguchi N (2009) Automatic personalized video abstraction for sports videos using metadata. Multimed Tools Appl 41(1):1–25
Rabiner LR (1989) A tutorial on Hidden Markov Models and selected applications in speech recognition. In: Proc. IEEE, vol 77, pp 257–285
Rasheed Z, Sheikh Y, Shah M (2005) On the use of computable features for film classification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 15(1):52–64
Smeaton AF, Lehane B, O’Connor NE, Brady C, Craig G (2006) Automatically selecting shots for action movie trailers. In: Proc. ACM international workshop on multimedia information retrieval, pp 231–238
Soundtracknet, The Art of Film and Television Music. http://www.soundtrack.net/. Accessed 2008
Sundaram H, Chang S-F (2001) Condensing computable scenes using visual complexity and film syntax analysis. In: Proc. IEEE international conference on mutimedia and expo, pp 389–392
Takemoto R, Yoshitaka A, Hirashima T (2006) Video editing based on movie effects by shot length transition. Technical Report of IEICE PRMU2005-149-183, pp 19–24
Taskiran CM, Pizlo Z, Amir A, Poncelelon D, Delp EJ (2006) Automated video program summarization using speech transcripts. IEEE Trans Multimedia 8(4):775–791
The International Movie Database. http://www.imdb.com/. Accessed 2005
Tjondronegoro D, Chen Y-PP, Pham B (2003) Sports video summarization using highlights and play-breaks. In: Proc. ACM international workshop on multimedia information retrieval, pp 201–208
Viola P, Jones M (2001) Rapid object detection using a boosting cascade of simple features. In: Proc. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol 1, pp 511–518
Wang J, Xu C, Chung E, Duan L, Wan K, Tian Q (2005) Automatic generation of personalized music sports video. In: Proc. ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 735–744
Yoon J-C, Lee I-K, Byun S (2009) Automated music video generation using multi-level feature-based segmentation. Multimed Tools Appl 41(2):197–214
Zettl H (1999) Sight sound motion: applied media aesthetics, 3rd edn. Wadsworth Publishing
Acknowledgement
This research was partially supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) 20700087 from JSPS and by Core Project from Microsoft Institute for Japanese Academic Research Collaboration. The authors especially thank Jang-il Kim, Yosuke Kurihara, and Guozhen Jiang for their contributions to the development of the system.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nitta, N., Babaguchi, N. Example-based video remixing. Multimed Tools Appl 51, 649–673 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-010-0633-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-010-0633-9