Abstract
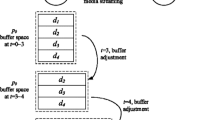
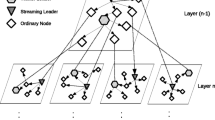
In peer-to-peer video-on-demand streaming networks, the alleviation of server load depends on reciprocal stream sharing among peers. In general, on-demand video services enable clients to watch videos from beginning to the end in a pipeline fashion. As long as a client still caches the initial part of the video, it can provide on-demand service to the subsequent clients without intervention of a server. Therefore, the key challenge is how to maximize the availability of a video for stream relay by keeping the initial part of a video in a peer’s buffer as long as possible. In addition, to address the issues of delivering data on lossy network and providing scalable video quality of services for clients, the adoption of multiple description coding has been proven as a feasible resolution by much research work. In this paper, we propose a novel caching scheme for P2P on-demand streaming called Balanced Dynamic Buffering with multiple description coding. The proposed balanced dynamic buffering gradually reduces the number of buffered descriptions once the buffer of a peer gets full. In addition, peers are grouped based on the number of descriptions cached in their buffer. The intra-group balancing and inter-group balancing are applied for well distributing descriptions and balancing their forwarding bandwidth on peer-to-peer on-demand streaming networks. In the paper, we also propose the failure recovery for the balanced dynamic buffering scheme. Simulation results showed that the balanced dynamic buffering significantly outperformed other dynamic buffering schemes and the CoopNet in server bandwidth utilization, and a longer buffer in a peer did favor the failure recovery on peer-to-peer on-demand streaming networks.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyol E, Tekalp A, Civanlar M (2007) A flexible multiple description coding framework for adaptive peer-to-peer video streaming. IEEE J Sel Topics Signal Process 1(2):231–245
Androutsellis-Theotokis S, Spinellis D (2004) A survey of peer-to-peer content distribution technologies. ACM Comput Surv 36(4):335–371. doi:10.1145/1041680.1041681
Apostolopoulos J (2001) Reliable video communication over lossy packet networks using multiple state encoding and path diversity. In: Proc. of visual communications: image processing, pp 392–409
Apostolopoulos J, Trott M (2004) Path diversity for enhanced media streaming. IEEE Commun Mag 42(8):80–87. doi:10.1109/MCOM.2004.1321395
Ardestani M, Shirazi A, Hashemi M (2010) An improved low-complexity multiple description coding for peer-to-peer video streaming. In: 2010 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME), pp 255–260. doi:10.1109/ICME.2010.5583053
Bernardini R, Durigon M, Rinaldo R, Celetto L, Vitali A (2004) Polyphase spatial subsampling multiple description coding of video streams with h264. In: Proc. of IEEE international conference on image processing, vol 5, pp 3213–3216
Campana O, Milani S (2004) A multiple description coding scheme for the h.264/avc coder. In: Proc. of the international conf. on telecommunication and computer networks, pp 191–195
Castro M, Druschel P, Kermarrec A, Nandi A, Rowstron A, Singh A (2003) Splitstream: high-bandwidth multicast in cooperative environments. In: ACM conference on SOSP, pp 298–313
Cui Y, Nahrstedt K (2003) Layered peer-to-peer streaming. In: ACM conference on NOSSDAV, pp 162–171
Cui Y, Li B, Nahrstedt K (2004) Ostream: asynchronous streaming multicast in application-layer overlay networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 22(1):91–106
De P, Banerjee N, De S (2011) Exploiting multiple description coding for intermediate recovery in wireless mesh networks. J Netw Comput Appl (in press). doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2011.03.032
Do TT, Hua KA, Tantaoui MA (2004) P2vod: providing fault tolerant video-on-demand streaming in peer-to-peer environment. In: IEEE conference on communications, pp 1467–1472
Frossard P, de Martin J, Reha Civanlar M (2008) Media streaming with network diversity. Proc IEEE 96(1):39–53
Goyal VK (2001) Multiple description coding: compression meets the network. IEEE Signal Process Mag 18:74–93
Guo Y, Suh K, Kurose J, Towsley D (2003) P2cast: peer-to-peer patching scheme for vod service. In: ACM conference on WWW, pp 301–309
Jin S, Bestavros A (2002) Cache and relay streaming media delivery for asynchronous clients. In: Proc. international workshop on networked group communication (NGC’02), Boston, MA, USA. citeseer.ist.psu.edu/jin02cacherelay.html
Kusmierek E, Dong Y, Du DH (2006) Loopback: exploiting collaborative caches for large-scale streaming. IEEE Trans Multimedia 8(2):233–242
Lin CS (2010) Improving the availability of scalable on-demand streams by dynamic buffering on p2p networks. KSII Trans Int Inf Syst (TIIS) 4(4):491–508
Lin CS (2011) Enhancing p2p live streaming performance by balancing description distribution and available forwarding bandwidth in p2p streaming network. Int J Commun Syst 24(4):568–585
Lin CS, Lee IT (2011) Applying multiple description coding to enhance the streaming scalability on cdn-p2p network. Int J Commun Syst 23(5):553–568
Lin CS, Syu WT (2010) A fine-grained balancing scheme for improved scalability in p2p streaming. Multimed Tools Appl 46(1):71–90
Padmanabhan VN, Wang HJ, Chou PA, Sripanidkulchai K (2002) Distributing streaming media content using cooperative networking. In: ACM conference on NOSSDAV, pp 177–186
Schollmeier R (2001) A definition of peer-to-peer networking for the classification of peer-to-peer architectures and applications. In: Proceedings. First international conference on peer-to-peer computing, 2001, pp 101–102. doi:10.1109/P2P.2001.990434
Wand Y, Reibman AR, Lin S (2005) Multiple description coding for video delivery. In: Proc. of the IEEE, pp 57–70
Zandon‘a N, Milani S, Giusti AD (2005) Motion-compensated multiple description video coding for the h.264/avc standard. In: Proc. of IADAT international conf. on multimedia, image processing and computer vision, pp 290–294
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by National Science Council under contract NSC 100-2221-E-024-006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, CS. Balanced dynamic buffering for scalable video-on-demand streaming on peer-to-peer networks. Multimed Tools Appl 62, 701–718 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-011-0872-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-011-0872-4