Abstract
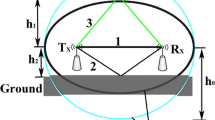
In order to arrange cornfield wireless sensor network nodes rationally, fields of corn were studied in signal loss of 2.4GHZ wireless sensor radio frequency signal, and selecting 3 levels of planting density the field random test were carried out with the transmission distance and antenna height as influencing factors, and then curve fitting and analysis were made by MATLAB simulation. Research shows that different planting density has certain influence on signal attenuation degree, when planting density, intensive plants as well as plant’s scattering, reflection and diffuse will be more serious, leading to the increase of slope signal attenuation; in RF signal propagation model, environmental impact factors and antenna height exist linear relationship, establishing the mathematical model, its correlation between theory value and measurement value is in 0.937 and 0.9888.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyldiz IF, Su W, Sankarasubramaniam Y et al (2002) A survey on sensor networks [J]. IEEE Commun Mag 40(8):102–114
Anderson CR, Dietrich CD, Joshi GG (2005) Near-ground channel measurements over line-of-sight and forested paths. Microw Antennas Propag Iee Proc 152:589–596
Andrade-Sanchez P, Pierce FJ, Elliott TV (2007) Performance assessment of wireless sensor networks in agricultural settings[C]. 2007 ASABE Annual International Meeting
Darr MJ, Zhao L (2008) Modeling path loss in confined animal feeding operations[C]. 2008 ASABE Annual International Meeting
Foran RA, Welch TB, Walker MJ (1999) Verynear ground radio frequency propagation measurements and analysis for military applications [C]. Proceedings of IEEE Military Communications Conference. MILCOM, Atlantic City, USA, p 336–340
Hebel MA, Tate R, Watson DG (2007) Results of wireless sensor network transceiver testing for agricultural applications[C]. 2007 ASABE Annual International Meeting
Joshi GG, Dietrich CB, Anderson CR et al (2005) Near-ground channel measurements over line-of-sight and forested paths[J]. IEE Proc Microw Antennas Propag 152:589–596
Li SY, Gao HJ, Jiang JZ (2009) Impact of antenna height on propagation characteristics of 2. 4 GHz wireless channel in wheat fields [J]. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 25(Supp):184–189, in Chinese
Liu H, Wang MH, Meng ZJ et al (2010) Performance assessment of short-range radio propagation in crop fields[J]. J Jiangsu Univ 31(1):1–5, in Chinese
Lu Q, Luo WS, Hu B (2010) Multi-node cooperative JPEG 2000i mplementation based on neighbor clusters in wireless sensor networks [J]. Opt Precis Eng 18(1):240–247, in Chinese
Luo XW, Zang Y, Zhou ZY (2000) Research progress in farming information acquisition technique for precision agriculture [J]. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 22(1):167–173 (in Chinese)
Martinez SA, Molina GPJM, Egea L et al (2005) An accurate radio channel model for wireless sensor networks simulation [J]. J Commun Netw 7(4):1–6
Meng YS, Lee YH, Ng BC (2009) Empirical near ground path loss modeling in a forest at VHF and UHF bands[J]. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 57(5):1461–1468
Phaebua K, Phongcharoenpanich C, Torrungrueng D et al (2008) Short-distance and near-ground signal measurements in a car park of wireless sensor network system at 433MHz [C]. Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, Krabi, Thailand: ECTI-CON, p 241–244
Roos T, Ki PM, Tirri H (2002) A statistical modeling approach to location estimation[C]// IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, p 59–69
Shen J, Yao DY, Huang HQ et al (2008) Measurement and analysis of radio channel model fornear-ground wireless sensor network [J]. Opt Precis Eng 16(1):141–149, in Chinese
Sikka P, Corke P, Valencia P et al (2006) Wireless ad hoc sensor and actuator networks on the farm[C]//IEEE the Fifth International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks. ACM, New York, pp 492–499
Wang DH, Song LL, Kong XS et al (2012) Path loss modeling for near-ground wireless channel in grassland environment [J]. Opt Precis Eng 20(6):1406–1413 (in Chinese)
Wen T, Hong ST, Li Z et al (2010) Test of wireless sensor network radio frequency signal propagation based on different node deployments in citrus orchards [J]. Trans CSAE 26(6):211–215, in Chinese
Yuan ZQ, Zhang JY (2007) Effect of water stress on growth of maize in the bel-mouthed period. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas [J]. 25(4):235–242
Yue XJ et al (2013) WSN layout experiment based on radio frequency propagation tests in citrus orchard[J]. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 44(5):213–218, in Chinese
Zhao WY, Liu X (2013) Discussion on the direction of maize breeding in northeast china [J]. China Seed Ind 06:12–14
Acknowledgments
Foundation item: he Key Subject of the Twelfth-five Scientific Research in the Education Department of Jilin Province (No.: 201356).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, H., Shi, Y., Wang, X. et al. Modeling wireless sensor networks radio frequency signal loss in corn environment. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 19479–19490 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3150-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3150-z