Abstract
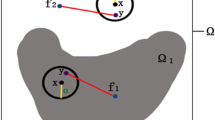
Image segmentation is an important processing in many applications such as image retrieval and computer vision. One of the most successful models for image segmentation is the level set methods which are based on local context. The methods, though comparatively effective in segmenting images with inhomogeneous intensity, are considerably computation-intensive and at the risk of falling into local minima in the convergence of the active contour energy function. To address the issues, we propose a region-based level set method, called KL-MLBF, which is based on the multi-scale local binary fitting (MLBF) and the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence. We first apply the multi-scale theory to the local binary fitting model to build MLBF. Then the energy term measured by KL divergence between regions to be segmented is incorporated into the energy function of MLBF. KL-MLBF utilizes the between-cluster distance and the adaptive kernel function selection strategy to formulate the energy function. Being more robust to the initial location of the contour than the classical segmentation models, KL-MLBF can deal with blurry boundaries and noise problems. The results of experiments on synthetic and real images have shown that KL-MLBF can improve the effectiveness of segmentation while ensuring the accuracy by accelerating the minimization of the energy function.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balla-Arabé S, Gao X, Wang B (2013) A fast and robust level set method for image segmentation using fuzzy clustering and lattice boltzmann method. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 43(3):910– 920
Candès E J, Li X, Ma Y, Wright J (2011) Robust principal component analysis?. J ACM (JACM) 58(3):11
Casselles F C V, Dibos F (1993) A geometric model for active contours in image processing. Numer Math 66(1):1–31
Cheng D, Huang J, Yu Z, Tang X, Yang J (2007) Medical image enhancement based on fuzzy techniques. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology 39 (3):435–437
Cheng D, Liu X, Tang X, Liu J, Huang J (2007) An image segmentation method based on an improved pcnn [j]. Chinese High Technology Letters 12:24–29
Cohen L, Cohen I (1993) “Finite-element methods for active contour models and balloons for 2-d and 3-d images”. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 15(11):1131–1147
Gong M, Liang Y, Shi J, Ma W, Ma J (2013) Fuzzy c-means clustering with local information and kernel metric for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(2):573–584
Islam M J, Basalamah S, Ahmadi M, Sid-Ahmed M A (2011) “Capsule image segmentation in pharmaceutical applications using edge-based techniques”. In: Electro/Information Technology (EIT), 2011 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, pp 1–5
Kass M, Witkin A, Terzopoulos D (1988) Snakes: Active contour models. Int J Comput Vis 1(4):321–331
Kullback S, Leibler R A (1951) On information and sufficiency. Ann Math Stat:79–86
Lankton S, Tannenbaum A (2008) Localizing region-based active contours. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(11):2029–2039
Leung T, Malik J (1998) “Contour continuity in region based image segmentation”. In: Computer VisionłECCV’98. Springer, pp 544–559
Li C, Huang R, Ding Z, Gatenby J, Metaxas D N, Gore J C (2011) A level set method for image segmentation in the presence of intensity inhomogeneities with application to mri. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(7):2007–2016
Li C, Kao C. -Y., Gore J C, Ding Z (2007) “Implicit active contours driven by local binary fitting energy”. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2007. CVPR’07 IEEE Conference on. IEEE , pp 1–7
Li C, Xu C, Gui C, Fox M D (2005) “Level set evolution without re-initialization: a new variational formulation”. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2005. CVPR 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on, vol. 1. IEEE, pp 430–436
Li C, Xu C, Gui C, Fox M D (2010) Distance regularized level set evolution and its application to image segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(12):3243–3254
Liu S, Peng Y (2012) A local region-based chan–vese model for image segmentation. Pattern Recogn 45(7):2769–2779
Liu T, Yuan Z, Sun J, Wang J, Zheng N, Tang X, Shum H -Y (2011) Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33 (2):353–367
Mansouri A -R, Konrad J (2003) Multiple motion segmentation with level sets. IEEE Trans Image Process 12(2):201–220
Malladi R, Sethian J A, Vemuri B C (1995) Shape modeling with front propagation: a level set approach. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 17(2):158–175
Martin D, Fowlkes C, Tal D, Malik J (2001) “A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics”. In: Computer Vision, 2001. ICCV 2001 Proceedings. Eighth IEEE International Conference on, vol. 2. IEEE, pp 416–423
Monteiro F C, Campilho A (2008) “Watershed framework to region-based image segmentation”. In: in Pattern Recognition, 2008. ICPR 2008 19th International Conference on. IEEE, pp 1–4
Mumford D, Shah J (1989) Optimal approximations by piecewise smooth functions and associated variational problems. Commun Pure Appl Math 42(5):577–685
Osher S, Sethian J A (1998) Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: Algorithms based on hamilton-jacobi formulations. J Comput Phys 79(1):12–49
Paragios N, Deriche R (2000) Geodesic active contours and level sets for the detection and tracking of moving objects. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22 (3):266–280
Reddi S, Rudin S, Keshavan H (1984) An optimal multiple threshold scheme for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 4:661–665
Sapna Varshney S, Rajpa N, Purwar R (2009) “Comparative study of image segmentation techniques and object matching using segmentation”. In: in Methods and Models in Computer Science, 2009. ICM2CS 2009 Proceeding of International Conference on. IEEE, pp 1–6
Sofou A, Maragos P (2008) Generalized flooding and multicue pde-based image segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(3):364–376
Tsai A, Yezzi JrA., Willsky A S (2001) Curve evolution implementation of the mumford-shah functional for image segmentation, denoising, interpolation, and magnification. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(8):1169–1186
Vese L A, Chan T F (2002) A multiphase level set framework for image segmentation using the mumford and shah model. Int J Comput Vis 50(3):271–293
Wang X -F, Huang D -S, Xu H (2010) An efficient local chan–vese model for image segmentation. Pattern Recogn 43(3):603–618
Wang L, Li C, Sun Q, Xia D, Kao C -Y (2009) Active contours driven by local and global intensity fitting energy with application to brain mr image segmentation. Comput Med Imaging Graph 33(7):520– 531
Wang L, Pan C (2014) Robust level set image segmentation via a local correntropy-based k-means clustering. Pattern Recogn 47(5):1917–1925
Wang L, Yu Z, Pan C (2011) “Medical image segmentation based on novel local order energy”. In: Computer Vision–ACCV 2010. Springer, pp 148–159
Xu C, Prince J (1998) Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans Image Process 7(3):359– 369
Yasmin M, Sharif M, Mohsin S (2013) Neural networks in medical imaging applications: a survey. World Applied Sciences Journal 22(1):85–96
Zhang K, Song H, Zhang L (2010) Active contours driven by local image fitting energy. Pattern Recogn 43(4):1199–1206
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61440025 , 61402133) and the National Postdoctoral Science Foundation(Grant No. 20100480998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Cheng, D., Tian, F. et al. Active contour driven by multi-scale local binary fitting and Kullback-Leibler divergence for image segmentation. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 10149–10168 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3603-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3603-z