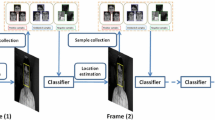
Abstract
Visual tracking estimates the trajectory of an object of interest in non-stationary image streams that change over time. Recently, approaches for model-free tracking have received increased interest since manually annotating sufficient examples of all objects in the world is prohibitively expensive. By definition, a model-free tracker has only one labeled instance in the form of an identified object in the first frame. In the subsequent frames, it has to learn variations of the tracked object with only unlabeled data available. There exists a dilemma for model-free trackers, i.e., whether the tracker would shift the focus to clutters (i.e., adaptivity) or result in very short tracks (i.e., stability) largely depends on how sensitive the appearance model is. In contrast to recent survey efforts with data-driven approaches focusing on the performance on benchmarks, this article aims to provide an in-depth survey on solutions to the dilemma between adaptivity and stability in model-free tracking focusing on the ability of achieving situation awareness, i.e., learning the object appearance adaptively in a non-stationary environment. The survey results show that, regardless of visual representations and statistical models involved, the way of exploiting unlabeled data in the changing environment and the extent of how rapidly the appearance model need be updated accordingly with selected example(s) of estimated labels are the key to many, if not all, evaluation measures for tracking. Such conceptual consensuses, despite the diversity of approaches in this field, for the first time capture the essence of model-free tracking and facilitate the design of visual tracking systems.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam A, Rivlin E, Shimshoni I (2006) Robust fragments-based tracking using the integral histogram. In: 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol 1. IEEE, pp 798–805
Avidan S (2004) Support vector tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26(8):1064–1072
Avidan S (2007) Ensemble tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29 (2):261–271
Babenko B, Yang M, Belongie S (2009) Visual tracking with online multiple instance learning. In: 2009. CVPR 2009. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, pp 983–990
Bai Q, Wu Z, Sclaroff S, Betke M, Monnier C (2013) Randomized ensemble tracking. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE, pp 2040–2047
Bao C, Wu Y, Ling H., Ji H (2012) Real time robust L1 tracker using accelerated proximal gradient approach. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1830–1837
Black MJ, Jepson AD (1998) Eigentracking: Robust matching and tracking of articulated objects using a view-based representation. Int J Comput Vis 26(1):63–84
Black MJ, Jepson AD (1998) Eigentracking: Robust matching and tracking of articulated objects using a view-based representation. Int J Comput Vis 26(1):63–84
Bolme DS, Beveridge JR, Draper B, Lui YM (2010) Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 2544–2550
Boykov Y, Kolmogorov V (2004) An experimental comparison of min-cut/max-flow algorithms for energy minimization in vision. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26 (9):1124–1137
Cai Z, Wen L, Lei Z, Vasconcelos N, Li S (2014) Robust deformable and occluded object tracking with dynamic graph. IEEE Trans Image Process 23 (12):5497–5509
Cehovin L, Leonardis A, Kristan M (2015) Visual object tracking performance measures revisited. arXiv:1502.05803
Cehovin L, Kristan M, Leonardis A (2013) Robust visual tracking using an adaptive coupled-layer visual model. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(4):941–953
Chapelle, O, Zien, A, Scholkopf, B (Eds.) (2006). Semi-supervised learning. MIT Press
Chapelle, O, Zien, A, Scholkopf, B (Eds.). (2006c) Semi-supervised learning. MIT Press
Chapelle O (2007) Training a support vector machine in the primal. Neural Comput 19(5):1155–1178
Chen W, Cao L, Zhang J, Huang K (2013) An adaptive combination of multiple features for robust tracking in real scene. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW). IEEE, pp 129–136
Collins RT (2003) Mean-shift blob tracking through scale space. In: 2003. Proceedings. 2003 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol 2. IEEE, pp II–234
Comaniciu D, Meer P (2002) Mean shift: A robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(5):603–619
Comaniciu D, Ramesh V, Meer P (2003) Kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(5):564–577
Danelljan M, Häger G, Khan F, Felsberg M (2014) Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking. In: British Machine Vision Conference. BMVA Press, Nottingham, pp 1–5
Danelljan M, Khan F, Felsberg M, Weijer J (2014) Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1090–1097
Danelljan M, Hager G, Khan F, Felsberg M (2015) Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking.. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 4310–4318
Danelljan M, Hager G, Shahbaz Khan F, Felsberg M (2015) Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 4310–4318
Dinh TB, Vo N, Medioni G (2011) Context tracker: Exploring supporters and distracters in unconstrained environments. In: 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1177–1184
Du W, Piater J (2008) A probabilistic approach to integrating multiple cues in visual tracking. In: Computer Vision ECCV 2008. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 225–238
Duffner S, Garcia C (2014) Exploiting contextual motion cues for visual object tracking. In: Computer Vision-ECCV 2014 Workshops. Springer International Publishing, pp 232–243
Duffner S, Garcia C (2014) Exploiting contextual motion cues for visual object tracking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer International Publishing, pp 232–243
Duffner S, Garcia C (2013) PixelTrack: a fast adaptive algorithm for tracking non-rigid objects. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE, pp 2480–2487
Fan Z, Wu Y, Yang M (2005) Multiple collaborative kernel tracking. In: 2005. CVPR 2005. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol 2. IEEE, pp 502–509
Felsberg M (2013) Enhanced distribution field tracking using channel representations. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW). IEEE, pp 121–128
Freund Y, Schapire RE (1997) A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. J Comput Syst Sci 55(1):119–139
Gavrila DM (1999) The visual analysis of human movement: A survey. Comput Vis Image Understand 73(1):82–98
Gabriel PF, Verly JG, Piater J, Genon A (2003, September) The state of the art in multiple object tracking under occlusion in video sequences. In: Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, pp 166– 173
Grabner H, Grabner M, Bischof H (2006, September) Real-time tracking via on-line boosting. In: BMVC, vol 1, p 6
Grabner H, Leistner C, Bischof H (2008) Semi-supervised on-line boosting for robust tracking. In: Computer Vision ECCV 2008. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp 234–247
Grabner H, Matas J, Van Gool L, Cattin P (2010) Tracking the invisible: Learning where the object might be. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1285–1292
Godec M, Roth PM, Bischof H (2013) Hough-based tracking of non-rigid objects. Comput Vis Image Understand 117(10):1245–1256
Hare S, Saffari A, Torr P (2011) Struck: Structured output tracking with kernels. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE, pp 263–270
Henriques JF, Caseiro R, Martins P, Batista J (2012) Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. In: Computer Vision ECCV 2012. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 702–715
Henriques JF, Caseiro R, Martins P, Batista J (2015) High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):583–596
Hua Y, Alahari K, Schmid C (2015) Online object tracking with proposal selection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 3092–3100
Hu W, Tan T, Wang L, Maybank S (2004) A survey on visual surveillance of object motion and behaviors. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybern, Part C: Appl Rev 34 (3):334–352
Isard M, Blake A (1998) Condensation conditional density propagation for visual tracking. Int J Comput Vis 29(1):5–28
Jia X, Lu H, Yang M (2012) Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1822–1829
Joachims T, Finley T, Yu CNJ (2009) Cutting-plane training of structural SVMs. Mach Learn 77(1):27–59
Kalal Z, Matas J, Mikolajczyk K (2010) Pn learning: Bootstrapping binary classifiers by structural constraints. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 49–56
Kalal Z, Mikolajczyk K, Matas J (2010) Forward-backward error: Automatic detection of tracking failures. In: 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). IEEE, pp 2756–2759
Kalal Z, Mikolajczyk K, Matas J (2012) Tracking-learning-detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(7):1409–1422
Kim SJ, Koh K, Lustig M, Boyd S, Gorinevsky D (2007) An interior-point method for large-scale L1-regularized least squares. IEEE J Select Top Signal Process 1(4):606–617
Kristan M, Pflugfelder R, Leonardis A, Matas J, Porikli F, Cehovin L, Vojir T (2013) The Visual Object Tracking VOT2013 challenge results. ICCV2013 Workshops. In: Workshop on Visual Object Tracking Challenge
Kristan M, Pflugfelder R, Leonardis A, Matas J, Cehovin L, Nebehay G, Golodetz S (2014) The visual object tracking vot2014 challenge results. In: Computer Vision-ECCV 2014 Workshops. Springer International Publishing, pp 191–217
Kristan M, Matas J, Leonardis A, Vojir T, Pflugfelder R, Fernandez G (2015) A Novel Performance Evaluation Methodology for Single-Target Trackers. arXiv:1503.01313
Kristan M, Matas J, Leonardis A, Felsberg M, Cehovin L, Fernandez G, Vojir T, Hager G, Nebehay G, Pflugfelder R (2015) The visual object tracking VOT2015 challenge results. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pp 1–23
Kwon J, Lee KM (2010) Visual tracking decomposition. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1269–1276
L Bertinetto MO, J Valmadre GS, Torr P The importance of estimating object extent when tracking with correlation filters. Preprint, 2015
Lebeda K, Hadfield S, Matas J, Bowden R (2013) Long-term tracking through failure cases. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pp 153–160
Lee JY, Yu W (2011) Visual tracking by partition-based histogram backprojection and maximum support criteria. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). IEEE, pp 2860–2865
Li Y, Zhu J (2014) A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration. In: Computer Vision-ECCV 2014 Workshops. Springer International Publishing, pp 254–265
Liu B, Huang J, Yang L, Kulikowsk C (2011) Robust tracking using local sparse appearance model and k-selection. In: 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1313–1320
Li X, Hu W, Shen C, Zhang Z, Dick A, Hengel AVD (2013) A survey of appearance models in visual object tracking. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol (TIST) 4(4):58
Louppe G (2014) Understanding Random Forests: From Theory to Practice. arXiv:1407.7502
Mallapragada PK, Jin R, Jain AK, Liu Y (2009) Semiboost: Boosting for semi-supervised learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(11):2000–2014
Maresca ME, Petrosino A (2014) Clustering local motion estimates for robust and efficient object tracking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer International Publishing, pp 244–253
Mei X, Ling H (2009) Robust visual tracking using L1 minimization. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, pp 1436–1443
Mei X, Ling H (2011) Robust visual tracking and vehicle classification via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(11):2259–2272
Moeslund TB, ranum E (2001) A survey of computer vision-based human motion capture. Comput Vis Image Understand 81(3):231–268
Moeslund TB, Hilton A, Krger V (2006) A survey of advances in vision-based human motion capture and analysis. Comput Vis Image Understand 104(2):90–126
Nam H, Han B (2015) Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. arXiv:1510.07945
Nam H, Hong S, Han B (2014) Online graph-based tracking. In: Computer Vision ECCV 2014. Springer International Publishing, pp 112–126
Nebehay G, Pflugfelder R (2014) Consensus-based matching and tracking of keypoints for object tracking. In: 2014 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). IEEE, pp 862–869
Nebehay G, Pflugfelder R (2014) Consensus-based matching and tracking of keypoints for object tracking. In: IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. IEEE, pp 862–869
Ofjall K, Felsberg M (2014) Weighted update and comparison for channel-based distribution field tracking. In: Computer Vision-ECCV 2014 Workshops. Springer International Publishing, pp 218–231
Okuma K, Taleghani A, De Freitas N, Little JJ, Lowe DG (2004) A boosted particle filter: Multitarget detection and tracking. In: Computer Vision-ECCV 2004. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 28–39
Oron S, Bar-Hillel A, Levi D, Avidan S (2012) Locally orderless tracking. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1940–1947
Pérez P, Hue C, Vermaak J, Gangnet M (2002) Color-based probabilistic tracking. In: Computer Vision ECCV 2002. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 661–675
Platt J (1999) Fast training of support vector machines using sequential minimal optimization, Advances in kernel methodssupport vector learning, 3
Ross DA, Lim J, Lin RS, Yang M (2008) Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int J Comput Vis 77(1-3):125–141
Sevilla-Lara L, Learned-Miller E (2012) Distribution fields for tracking. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1910–1917
Shi J, Tomasi C (1994) Good features to track. In: 1994. Proceedings CVPR’94., 1994 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, pp 593–600
Sinha SN (2004) Graph Cut Algorithms in Vision, Graphics and Machine Learning An Integrative Paper. UNC Chapel Hill
Smeulders AW, Chu DM, Cucchiara R, Calderara S, Dehghan A, Shah M (2014) Visual tracking: an experimental survey. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(7):1442–1468
Stalder S, Grabner H, Van Gool L (2009) Beyond semi-supervised tracking: Tracking should be as simple as detection, but not simpler than recognition. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops). IEEE, pp 1409–1416
Tang M, Feng J (2015) Multi-kernel correlation filter for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 3038–3046
Tang F, Brennan S, Zhao Q, Tao H (2007) Co-tracking using semi-supervised support vector machines. In: ICCV 2007. IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, 2007. IEEE, pp 1–8
Tian M, Zhang W, Liu F (2007) On-line ensemble SVM for robust object tracking. In: Computer VisionACCV 2007. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 355–364
Vermaak J, Doucet A, Pérez P (2003) Maintaining multimodality through mixture tracking. In: 2003. Proceedings. Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, pp 1110–1116
Viola P, Jones M (2001) Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In: 2001. CVPR 2001. Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol 1. IEEE, pp I–511
Vojír T, Matas J (2014) The enhanced flock of trackers. In: Registration and Recognition in Images and Videos. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 113–136
Vojir T, Noskova J, Matas J (2013) Robust scale-adaptive mean-shift for tracking. In: Image Analysis. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 652–663
Wang N, Yeung DY (2013) Learning a deep compact image representation for visual tracking. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp 809–817
Wang N, Li S, Gupta A, Yeung DY (2015) Transferring rich feature hierarchies for robust visual tracking. arXiv:1501.04587
Wang X, Valstar M, Martinez B, Haris Khan M, Pridmore T (2015) Tric-track: Tracking by regression with incrementally learned cascades. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 4337–4345
Wendel A, Sternig S, Godec M (2011) Robustifying the flock of trackers. Citeseer, p 91
Williams O, Blake A, Cipolla R (2005) Sparse bayesian learning for efficient visual tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(8):1292–1304
Wright J, Ma Y, Mairal J, Sapiro G, Huang TS, Yan S (2010) Sparse representation for computer vision and pattern recognition. Proc IEEE 98(6):1031–1044
Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M (2013) Online object tracking: A benchmark. In: 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 2411–2418
Wu Y, Shen B, Ling H (2012) Online robust image alignment via iterative convex optimization. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1808–1814
Xiao J, Stolkin R, Leonardis A (2013) An enhanced adaptive coupled-layer LGTracker++. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW). IEEE, pp 137–144
Yang M, Wu Y, Hua G (2009) Context-aware visual tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(7):1195–1209
Yilmaz A, Javed O, Shah M (2006) Object tracking: A survey. Acm Comput Surv (CSUR) 38(4):13
Yu Q, Dinh TB, Medioni G (2008) Online tracking and reacquisition using co-trained generative and discriminative trackers. In: Computer Vision ECCV 2008. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 678–691
Zeisl B, Leistner C, Saffari A, Bischof H (2010) On-line semi-supervised multiple-instance boosting. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1879–1879
Zeisl B, Leistner C, Saffari A, Bischof H (2010) On-line semi-supervised multiple-instance boosting. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1879–1879
Zhang L, Van der Maaten LJ (2014) Preserving structure in model-free tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(4):756–769
Zhang K, Zhang L, Yang M (2012) Real-time compressive tracking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 864–877
Zhang K, Zhang L, Liu Q, Zhang D, Yang M (2014) Fast visual tracking via dense spatio-temporal context learning. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer International Publishing, pp 127–141
Zhang T, Ghanem B, Liu S, Ahuja N (2012) Low-rank sparse learning for robust visual tracking. In: Computer Vision ECCV 2012. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 470–484
Zhong W, Lu H, Yang M (2012) Robust object tracking via sparsity-based collaborative model. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1838–1845
Zhu G, Porikli F, Li H Tracking randomly moving objects on edge box proposals. arXiv:1507.08085.2015
Zhu G, Porikli F, Li H (2015) Tracking randomly moving objects on edge box proposals. arXiv:1507.08085
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, X.L., Zhang, C. Toward situation awareness: a survey on adaptive learning for model-free tracking. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 21073–21115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4001-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4001-2