Abstract
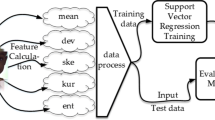
Image quality assessment is very crucial for certain image processing applications. Images can be distorted from multiple sources like a fault in sensors, camera shake, poor lighting, over-exposure etc. All these distortions reduce the visual quality of images. Assessing the quality of images can be done with the use of a reference image of the same scene or without it. Without the use of reference image, quality assessment is a very difficult task. Machine learning approaches are very common in no-reference image quality assessment. No reference strategies are very useful if the type of distortion is known. Contrast assessment is a very important application in image processing as poor contrast images are difficult for automated image processing. In this paper, we propose a no-reference image quality measure for images with respect to contrast using random forest regression and validate the results using standard datasets. Experimental results on standard datasets show that the proposed method demonstrates promising results when compared to existing no-reference techniques and the proposed method shows high correlation values with human opinion scores.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahumada A, Beard BL (1998) 43.1: a simple vision model for inhomogeneous image-quality assessment. In: SID Symposium digest of technical papers, vol 29. Wiley Online Library, pp 1109–1111
Arici T, Dikbas S, Altunbasak Y (2009) A histogram modification framework and its application for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans Image Process 18 (9):1921–1935
Boccignone G, Ferraro M, Caelli T (2001) Encoding visual information using anisotropic transformations. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(2):207–211
Bong D B L, Khoo B E (2014) Blind image blur assessment by using valid reblur range and histogram shape difference. Signal Process Image Commun 29(6):699–710
Bong D B L, Khoo B E (2015) Objective blur assessment based on contraction errors of local contrast maps. Multimed Tools Appl 74(17):7355–7378
Breiman L (1996) Bagging predictors. Mach Learn 24(2):123–140
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32
Deng C, Ma L, Lin W, Ngan KN Visual signal quality assessment
Du S, Yan Y, Ma Y (2016) Blind image quality assessment with the histogram sequences of high-order local derivative patterns. Digit Signal Process 55:1–12
Eskicioglu A M, Fisher P S (1995) Image quality measures and their performance. IEEE Trans Commun 43(12):2959–2965
Fang Y, Ma K, Wang Z, Lin W, Fang Z, Zhai G (2015) No-reference quality assessment of contrast-distorted images based on natural scene statistics. IEEE Signal Process Lett 22(7):838–842
Ferraro M, Boccignone G (2004) Image contrast enhancement via entropy production. Real-Time Imag 10(4):229–238
Flach P (2012) Machine learning: the art and science of algorithms that make sense of data. Cambridge University Press
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2001) The elements of statistical learning, vol 1. Springer Series in Statistics Springer, Berlin
Golestaneh S A, Chandler D M (2014) No-reference quality assessment of jpeg images via a quality relevance map. IEEE Signal Process Lett 21(2):155–158
Gonzalez R C, Woods R E (2008) Digital image processing. Nueva Jersey
Group VQE et al (2000) Vqeg, final report from the video quality experts group on the validation of objective models of video quality assessment (mar. 2000). [Online]. Available: http://www.vqeg.org/
Group VQE et al (2003) Final report from the video quality experts group on the validation of objective models of video quality assessment. [Online]. Available: http://www.vqeg.org/
Gu K, Zhai G, Lin W, Liu M (2016) The analysis of image contrast: from quality assessment to automatic enhancement. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(1):284–297
Gu K, Zhai G, Lin W, Yang X, Zhang W (2015) No-reference image sharpness assessment in autoregressive parameter space. IEEE Trans Image Process 24 (10):3218–3231
Hassen R, Wang Z, Salama M M et al (2013) Image sharpness assessment based on local phase coherence. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(7):2798–2810
Hastie T J, Tibshirani R J, Friedman J H (2011) The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction. Springer
Hess R, Bradley A, Piotrowski L (1983) Contrast-coding in amblyopia i. differences in the neural basis of human amblyopia. Proc R Soc London B: Biol Sci 217 (1208):309–330
Hosking J (1992) Moments or l moments? An example comparing two measures of distributional shape. Amer Stat 46(3):186–189
Hosking J (2006) On the characterization of distributions by their l-moments. J Stat Plan Infer 136(1):193–198
Jaiantilal A (2009) Classification and regression by randomforest-matlab. http://code.google.com/p/randomforest-matlab
Kim Y T (1997) Contrast enhancement using brightness preserving bi-histogram equalization. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 43(1):1–8
Larson E C, Chandler D M (2010) Most apparent distortion: full-reference image quality assessment and the role of strategy. J Electron Imag 19(1):011,006–011,006
Leszczuk M, Hanusiak M, Blanco I, Dziech A, Derkacz J, Wyckens E, Borer S (2014) Key indicators for monitoring of audiovisual quality. In: 2014 22nd Signal processing and communications applications conference (SIU). IEEE, pp 2301–2305
Leszczuk M, Hanusiak M, Farias M C, Wyckens E, Heston G (2014) Recent developments in visual quality monitoring by key performance indicators. Multimed Tools Appl:1–23
Li C, Bovik A C, Wu X (2011) Blind image quality assessment using a general regression neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(5):793–799
Li L, Lin W, Wang X, Yang G, Bahrami K, Kot A C (2016) No-reference image blur assessment based on discrete orthogonal moments. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(1):39–50
Li L, Zhu H, Yang G, Qian J (2014) Referenceless measure of blocking artifacts by tchebichef kernel analysis. IEEE Signal Process Lett 21(1):122–125
Liu A, Lin W, Narwaria M (2012) Image quality assessment based on gradient similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(4):1500–1512
Liu X, Tanaka M, Okutomi M (2013) Single-image noise level estimation for blind denoising. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(12):5226–5237
Liu T J, Liu K H, Lin J Y, Lin W, Kuo CCJ (2015) A paraboost method to image quality assessment
Michelson A A (1995) Studies in optics. Courier Corporation
Mittal A, Moorthy A K, Bovik A C (2012) No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(12):4695–4708
Moorthy A K, Bovik A C (2011) Blind image quality assessment: from natural scene statistics to perceptual quality. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(12):3350–3364
Narwaria M, Lin W (2010) Objective image quality assessment based on support vector regression. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 21(3):515–519
Pei S C, Chen L H (2015) Image quality assessment using human visual dog model fused with random forest. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(11):3282–3292
Peli E (1990) Contrast in complex images. JOSA A 7(10):2032–2040
Ponomarenko N, Ieremeiev O, Lukin V, Egiazarian K, Jin L, Astola J, Vozel B, Chehdi K, Carli M, Battisti F et al (2013) Color image database tid2013: peculiarities and preliminary results. In: 2013 4th European Workshop on visual information processing (EUVIP). IEEE, , pp 106– 111
Pyatykh S, Hesser J, Zheng L (2013) Image noise level estimation by principal component analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(2):687–699
Rizzi A, Algeri T, Medeghini G, Marini D (2004) A proposal for contrast measure in digital images. In: Conference on colour in graphics, imaging, and vision, vol 2004. Society for Imaging Science and Technology, pp 187–192
Rizzi A, Simone G, Cordone R (2008) A modified algorithm for perceived contrast in digital images. In: CGIV 2008-Fourth European conference on color in graphics, imaging and vision, pp 249– 252
Saad M A, Bovik A C, Charrier C (2012) Blind image quality assessment: a natural scene statistics approach in the dct domain. IEEE Trans Image Process 21 (8):3339–3352
Sheskin D J (2003) Handbook of parametric and nonparametric statistical procedures. CRC Press
Sheikh H R, Bovik A C, Cormack L (2005) No-reference quality assessment using natural scene statistics: Jpeg2000. IEEE Trans Image Process 14(11):1918–1927
Sheikh H R, Sabir M F, Bovik A C (2006) A statistical evaluation of recent full reference image quality assessment algorithms. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(11):3440–3451
Simone G, Pedersen M, Hardeberg J Y (2012) Measuring perceptual contrast in digital images. J Vis Commun Image Represent 23(3):491–506
Simone G, Pedersen M, Hardeberg J Y, Rizzi A (2009) Measuring perceptual contrast in a multi-level framework. In: IS&T/SPIE electronic imaging, pp 72,400Q–72,400Q. International Society for Optics and Photonics
Tadmor Y, Tolhurst D (2000) Calculating the contrasts that retinal ganglion cells and lgn neurones encounter in natural scenes. Vis Res 40(22):3145–3157
Tremeau A (2000) Color contrast parameters for analysing image differences. In: CIS proceedings, pp 11–23
Wang S, Ma K, Yeganeh H, Wang Z, Lin W (2015) A patch-structure representation method for quality assessment of contrast changed images. IEEE Signal Process Lett 22(12):2387–2390
Wang Y, Chen Q, Zhang B (1999) Image enhancement based on equal area dualistic sub-image histogram equalization method. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 45 (1):68–75
Wang Z, Bovik A C (2006) Modern image quality assessment. Synthesis Lect Image Video Multimed Process 2(1):1–15
Wang Z, Bovik A C, Sheikh H R, Simoncelli E P (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13 (4):600–612
Wu J, Lin W, Shi G, Liu A (2013) Perceptual quality metric with internal generative mechanism. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(1):43–54
Xu L, Lin W, Kuo C C J (2015) Visual quality assessment by machine learning. Springer
Xue W, Zhang L, Mou X, Bovik A C (2014) Gradient magnitude similarity deviation: a highly efficient perceptual image quality index. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(2):684–695
Zhang L, Zhang L, Mou X, Zhang D (2011) Fsim: a feature similarity index for image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(8):2378–2386
Zuiderveld K (1994) Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization. In: Graphics gems IV, pp 474–485. Academic Press Professional, Inc
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De, K., Masilamani, V. No-reference image contrast measure using image statistics and random forest. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 18641–18656 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4335-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4335-9