Abstract
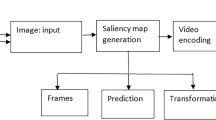
Despite the great evolution in the field of quality metrics, classical tools such as the PSNR remain useful in the field of evolution of video coding research. Our idea is to improve the limited performance of these tools using simple and well known techniques. In the quality measurement of images and video sequences, the use of the characteristics of human visual systems becomes a priority in order to have a better correlation between the objective measurement and the judgment of the observers. For this, we try to improve the performance of the two existing metrics (PSNR “Peak Signal / Noise Ratio”, DVQ “Digital Video Quality”) for the H.264 / MPEG-4 (Motion Picture Expert Group) AVC (Advanced Video Coding). This improvement is carried out by extracting the zones of interest using a saliency map and using a filtering by the contrast sensitivity function CSF. We did a study using two types of saliency map SURF (Speeded Up Robust Features) and HARRIS saliency map. We use the subjective video database “LIVE” to test the performance of our proposed idea. Performance indicators, namely Pearson (PLCC), the Spearman coefficient (SROCC) and mean squared prediction error (RMSE) indicate that SURF give best results for the distortion produced by H264 video encoding then HARRIS. Our idea is proven especially in short distances of observation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F, Susstrunk S (2009) Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition, 2009. cvpr 2009. IEEE Conference on. IEEE, p 1597–1604
Bay H, Ess A, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L (2008) Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Comput Vis Image Underst 110(3):346–359
Ben Amor M, Samet A, Kammoun F, Masmoudi N (2010) Exploitation des caractéristiques du système visuel humain dans les métriques de qualité. Cinquième workshop AMINA, In, pp 123–130
Ben Amor M, Kammoun F, Masmoudi N (2012) A new quality metric based on FFT transform. Int J Comput Appl IJCA 40(2):41–46
Ben Amor M, Larabi MC, Kammoun F, Masmoudi N (2014) A block artifact distortion measure for no reference video quality evaluation. In: Image Processing, Applications and Systems Conference (IPAS), 2014 First International. IEEE, p 1–5
Ben Amor M, Larabi MC, Kammoun F, Masmoudi N (2016) A no reference quality metric to measure the blocking artefacts for video sequences. Imaging Sci J 64(7):408–417
Ben Amor M, Kammoun F, Masmoudi N (2016) A pretreatment to improve the quality metrics performance for encoding H264/AVC. J Soc Inf Disp 24(3):187–197
Ben AM, Larabi MC, Kammoun F, Masmoudi N (2014) A perceptual measure of blocking artifact for no-reference video quality evaluation of H. 264 codec. J Test Eval 43(6):1247–1257
Chandler DM, Hemami SS (2007) VSNR: a wavelet-based visual signal-to-noise ratio for natural images. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(9):2284–2298
Chen J, Zhang Y, Liang L, Ma S, Wang R, Gao W (2008) A no-reference blocking artifacts metric using selective gradient and plainness measures. In: Advances in Multimedia Information Processing-PCM 2008, p 894–897
Cui J, Liu Y, Xu Y, Zhao H, Zha H (2013) Tracking generic human motion via fusion of low-and high-dimensional approaches. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 43(4):996–1002
Derpanis KG (2004) The harris corner detector. York University, Toronto
Frintrop S, Rome E, Christensen HI (2010) Computational visual attention systems and their cognitive foundations: a survey. ACM Trans Appl Percept (TAP) 7(1):6
Geng Y, Deng H (2013) Modeling the effect of human body on TOA ranging for indoor human tracking with wrist mounted sensor. Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications (WPMC), 2013 16th International Symposium on IEEE:1–6
Girod B (1993) What’s wrong with mean-squared error. In: Digital images and human vision. MIT press, Cambridge, pp 207–220
Harel J, Koch C, Perona P (2007) Graph based visual saliency. In: Proceedings of the advances in neural information and processing systems. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 545–552
Harris C, Stephens M (1988) A combined corner and edge detector. In: Alvey vision conference, Vol. 15, No. 50. p 10–5244
Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E (1998) A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20(11):1254–1259
Itti L, Rees G, Tsotsos JK (eds) (2005) Neurobiology of attention. Academic Press, Cambridge
Judd T, Ehinger K, Durand F, Torralba A (2009) Learning to predict where humans look. In: Computer Vision, 2009 I.E. 12th international conference on IEEE, p 2106–2113
Koch C, Ullman S (1987) Shifts in selective visual attention: towards the underlying neural circuitry. In: Matters of intelligence. Springer, Netherlands, pp 115–141
Leutenegger S, Chli M, Siegwart RY (2011) BRISK: binary robust invariant scalable keypoints. Computer Vision (ICCV), 2011 I.E. International Conference on IEEE:2548–2555
Liu Y, Xie H (2009) Constructing SURF visual-words for pornographic images detection. In: Computers and information technology, 2009. ICCIT'09. 12th international conference on. IEEE, pp 404–407
Liu Y, Zhang X, Cui J, Wu C, Aghajan H, Zha H (2010) Visual analysis of child-adult interactive behaviors in video sequences. In: Virtual Systems and Multimedia (VSMM), 2010 16th International Conference on. IEEE, p 26–33
Liu Y, Cui J, Zhao H, Zha H (2012) Fusion of low-and high-dimensional approaches by trackers sampling for generic human motion tracking. In: Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2012 21st International Conference on. IEEE, p 898–901
Liu X, Song M, Tao D, Liu Z, Zhang L, Chen C, Bu J (2013) Semi-supervised node splitting for random forest construction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 492–499
Liu Y, Nie L, Han L, Zhang L, Rosenblum DS (2015) Action2Activity: recognizing complex activities from sensor data. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on artificial intelligence. Buenos Aires, Argentina pp 1617–1623
Liu Y, Nie L, Liu L, Rosenblum DS (2016) From action to activity: sensor-based activity recognition. Neurocomputing 181:108–115
Liu L, Cheng L, Liu Y, Jia Y, Rosenblum DS (2016) Recognizing complex activities by a probabilistic interval-based model. In AAAI, vol 30. p 1266–1272
Liu Y, Zhang L, Nie L et al (2016) Fortune teller: predicting your career path. In: AAAI. Phoenix, pp 201–207
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Liang Y, Liu S, Rosenblum S (2016) Urban water quality prediction based on multi-task multi-view learning. Proceedings of the international joint conference on artificial intelligence. New York, pp 2576–2581
Liu Y, Liang Y, Liu S, Rosenblum DS, Zheng Y (2016) Predicting urban water quality with ubiquitous data. CoRR arXiv:1610.09462
Lowe DG (1999) Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In: computer vision, 1999. The proceedings of the seventh IEEE international conference on, vol 2. IEEE:1150–1157
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Lu Y, Wei Y, Liu L, Zhong J, Sun L, Liu Y (2017) Towards unsupervised physical activity recognition using smartphone accelerometers. Multimed Tools Applications 76(8):10701–10719
Ma L, Li S, Ngan KN (2013) Reduced-reference image quality assessment in reorganized DCT domain. Signal Process Image Commun 28(8):884–902
Mannos J, Sakrison D (1974) The effects of a visual fidelity criterion of the encoding of images. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 20(4):525–536
Matas J, Chum O, Urban M, Pajdla T (2004) Robust wide-baseline stereo from maximally stable extremal regions. Image Vis Comput 22(10):761–767
Moravec HP (1977) Towards automatic visual bbstacle avoidance. In: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (5th: 1977: Massachusetts Institute of Technology)
Moravec HP (1979) Visual mapping by a robot rover. Proceedings of the 6th international joint conference on Artificial intelligence-Volume 1 Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc:598–600
Nauge M, Larabi MC, Fernandez-Maloigne C (2012) A statistical study of the correlation between interest points and gaze points, Human Vision and Electronic Imaging, p 829111
Ngan KN, Leong KS, Singh H (1986) Cosine transform coding incorporating human visual system model. In: Cambridge symposium-fiber/LASE'86. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 165–171
Nill N (1985) A visual model weighted cosine transform for image compression and quality assessment. IEEE Trans Commun 33(6):551–557
Pinson MH, Wolf S (2004) A new standardized method for objectively measuring video quality. IEEE Trans Broadcast 50(3):312–322
Preoţiuc-Pietro D, Liu Y, Hopkins D, Ungar L (2017) Beyond binary labels: political ideology prediction of Twitter users. In: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), vol 1. p 729–740
Redi JA, Gastaldo P, Heynderickx I, Zunino R (2010) Color distribution information for the reduced-reference assessment of perceived image quality. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 20(12):1757–1769
Rosselli V, Larabi MC, Fernandez-Maloigne C (2007) Métrique de différence couleur basée sur le seuil de perception on COROSA COmpression et REprésentation des Signaux Audiovisuels. Montpellier, pp 8–9
Rosten E, Porter R, Drummond T (2010) Faster and better: a machine learning approach to corner detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(1):105–119
Rublee E, Rabaud V, Konolige K, Bradski G (2011) ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. Computer Vision (ICCV), 2011 I.E. international conference on IEEE:2564–2571
Sadaka NG, Karam LJ, Ferzli R, Abousleman GP (2008) A no-reference perceptual image sharpness metric based on saliency-weighted foveal pooling. In: Image Processing, 2008. ICIP 2008. 15th IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, p 369–372
Seshadrinathan K, Bovik AC (2010) Motion tuned spatio-temporal quality assessment of natural videos. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(2):335–350
Seshadrinathan K, Soundararajan R, Bovik AC, Cormack LK (2010) Study of subjective and objective quality assessment of video. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(6):1427–1441
Seshadrinathan K, Soundararajan R, Bovik AC, Cormack LK (2010) A subjective study to evaluate video quality assessment algorithms. In: Human Vision and Electronic Imaging, vol 7527:75270
Sheikh HR, Bovik AC (2006) Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(2):430–444
Sheikh HR, Bovik AC, Cormack L (2005) No-reference quality assessment using natural scene statistics: JPEG2000. IEEE Trans Image Process 14(11):1918–1927
Sheikh HR, Sabir MF, Bovik AC (2006) A statistical evaluation of recent full reference image quality assessment algorithms. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(11):3440–3451
Stoica A, LARABI MC, Fernandez-Maloigne C (2004) 6-Amélioration de la qualité visuelle d'images couleur dans le cadre du standard de compression JPEG2000. Traitement du Signal, Lavoisier 21(6):661–677.
Suthaharan S (2009) No-reference visually significant blocking artifact metric for natural scene images. Signal Process 89(8):1647–1652
Tagliasacchi M, Valenzise G, Naccari M, Tubaro S (2010) A reduced-reference structural similarity approximation for videos corrupted by channel errors. Multimed Tools Appl 48(3):471–492
Haglund L (2001) “SVT video test sequence,” SVT sveriges television AB. [Online]. Available: ftp://ftp.ldv.e-technik.tu-muenchen.de/pub/test sequences/
Veeraswamy K, Srinivaskumar S, Chatterji BN (2007) Designing quantization table for hadamard transform based on human visual system for image compression. ICGST-GVIP Journal 7(3):31–38
Wang Z, Simoncelli EP, Bovik AC (2003) Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. Signals, Systems and Computers, 2004 Conference Record of the Thirty-Seventh Asilomar Conference on, vol 2 IEEE:1398–1402
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Wang W, Yan Y, Zhang L, Hong R, Sebe N (2016) Collaborative sparse coding for multiview action recognition. IEEE MultiMedia 23(4):80–87
Watson AB (1998) Toward a perceptual video-quality metric. In: Photonics west’98 electronic imaging, international society for optics and photonics. San Jose, pp 139–147
Watson AB, Hu J, McGowan JF (2001) Digital video quality metric based on human vision. Journal of Electronic imaging 10(1):20–29
Wolf S, Pinson MH (2005) Low bandwidth reduced reference video quality monitoring system. In: Proceedings of the international workshop video processing and quality metrics for consumer electronics. Scottsdale, p 23–25
Xiao F (2000) DCT-based video quality evaluation. Technical report, MSU graphics and media lab (video group). http://compression.ru/video/quality_measure/vqm
Zhang L, Zhang L, Mou X, Zhang D (2011) FSIM: a feature similarity index for image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(8):2378–2386
Zhang L, Song M, Liu Z, Liu X, Bu J, Chen C (2013) Probabilistic graphlet cut: exploiting spatial structure cue for weakly supervised image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. p 1908–1915
Zhang L, Han Y, Yang Y, Song M, Yan S, Tian Q (2013) Discovering discriminative graphlets for aerial image categories recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(12):5071–5084
Zhang X, Feng X, Wang W, Xue W (2013) Edge strength similarity for image quality assessment. IEEE Signal processing letters 20(4):319–322
Zhang L, Yang Y, Gao Y, Yu Y, Wang C, Li X (2014) A probabilistic associative model for segmenting weakly supervised images. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(9):4150–4159
Zhang L, Gao Y, Xia Y, Lu K, Shen J, Ji R (2014) Representative discovery of structure cues for weakly-supervised image segmentation. IEEE Trans Multimedia 16(2):470–479
Zhang L, Song M, Yang Y, Zhao Q, Zhao C, Sebe N (2014) Weakly supervised photo cropping. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 16(1):94–107
Zhang L, Gao Y, Ji R, Xia Y, Dai Q, Li X (2014) Actively learning human gaze shifting paths for semantics-aware photo cropping. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(5):2235–2245
Zhang L, Gao Y, Zimmermann R, Tian Q, Li X (2014) Fusion of multichannel local and global structural cues for photo aesthetics evaluation. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(3):1419–1429
Zhang L, Gao Y, Hong C, Feng Y, Zhu J, Cai D (2014) Feature correlation hypergraph: exploiting high-order potentials for multimodal recognition. IEEE transactions on cybernetics 44(8):1408–1419
Zhang L, Gao Y, Xia Y, Dai Q, Li X (2015) A fine-grained image categorization system by cellet-encoded spatial pyramid modeling. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(1):564–571
Zhang X, Wang S, Ma S, Gao W (2015) A study on interest point guided visual saliency. In picture coding symposium (PCS), 2015. IEEE:307–311
Zhang, L., Li, X., Nie, L., Yan, Y., & Zimmermann, R. (2016). Semantic photo retargeting under noisy image labels. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl (TOMM), 12(3): 37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Amor, M., Kammoun, F. & Masmoudi, N. Improved performance of quality metrics using saliency map and CSF filter for standard coding H264/AVC. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 19377–19397 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5393-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5393-3