Abstract
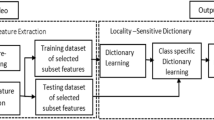
In recent years, sparse representation has attracted a blooming interest in the areas of pattern recognition, image processing, and computer vision. In video semantic analysis, the diversity of scene for the same semantic content in video always exists. Using dictionary learning in sparse representation can capture the latent relationship among the original diverse video semantic features. To enhance the discriminative ability of diverse video semantic features, the method of discriminative self-adapted locality-sensitive sparse representation for video semantic analysis is proposed. In the proposed method, a discriminative self-adaptive locality-sensitive dictionary learning method (DSALSDL) is designed. In DSALSDL, a self-adaptive local adapter is built to join in the process of dictionary learning for sparse representation, so as to obtain the potential information of the video data. Furthermore, in the self-adaptive locality-sensitive sparse representation, a discriminant loss function based on class-specific representation coefficients is imposed to further learn appropriate dictionary for video semantic analysis. Using the self-adaptive local adapter and discriminant loss function in dictionary learning, the sparse representation is exploited for video semantic concept detection. The proposed method is evaluated on the related video databases in comparison with existing relative sparse representation methods. Experimental results show that our method can improve the power of discrimination of video features and improve the accuracy of video semantic concept detection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharon M, Elad M, Bruckstein A (2006) R m k-svd: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 54(11):4311–4322
Chang X, Yang Y (2017) Semisupervised feature analysis by mining correlations among multiple tasks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(10):2294–2305
Chang X, Nie F, Wang S, Yang Y, Zhou X, Zhang C (2016) Compound rank-k projections for bilinear analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(7):1502–1513
Chang X, Ma Z, Lin M, Yang Y, Hauptmann A (2017) Feature interaction augmented sparse learning for fast kinect motion detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(8):3911–3920
Chang X, Ma Z, Yang Y, Zeng Z, Hauptmann AG (2017) Bi-level semantic representation analysis for multimedia event detection. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(5):1180–1197
Chang X, Yu YL, Yang Y, Xing EP (2017) Semantic pooling for complex event analysis in untrimmed videos. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(8):1617–1632
Cui J, Liu Y, Xu Y, Zhao H, Zha H (2013) Tracking generic human motion via fusion of low- and high-dimensional approaches. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 43(4):996–1002
Dai S, Zhan Y, Mao Q, Zhang S (2013) A video semantic analysis method based on kernel discriminative sparse representation and weighted knn. In: Green Computing and Communications, pp 879–886
Fergus R, Perona P, Zisserman A (2007) Weakly supervised scale-invariant learning of models for visual recognition. Int J Comput Vis 71(3):273–303
Geisler G, Song YX The Open Video Project. https://open-video.org/index.php
Khan HA, Helal AA, Ahmed KI (2014) Handwritten bangla digit recognition using sparse representation classifier. In: International Conference on Informatics, Electronics and Vision, pp 1–6
Kreutzdelgado K, Murray JF, Rao BD, Engan K, Lee TW, Sejnowski TJ (2014) Dictionary learning algorithms for sparse representation. Neural Comput 15(2):349–396
Li H, Liu F (2010) Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries in wavelet domain. In: International Conference on Image and Graphics, pp 754–758
Li Z, Tang J (2015) Unsupervised feature selection via nonnegative spectral analysis and redundancy control. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5343–5355
Li Z, Tang J (2015) Weakly supervised deep metric learning for community-contributed image retrieval. IEEE Trans Multimed 17(11):1989–1999
Li Z, Tang J (2017) Weakly supervised deep matrix factorization for social image understanding. IEEE Press, Piscataway
Li N, Zhan Y, Gou J (2014) A dictionary learning method based on self-adaptive locality-sensitive sparse representation. In: International Conference on Human Centered Computing, pp 115–126
Li T, Tang J, Xu J (2015) A predictive scheduling framework for fast and distributed stream data processing. In: IEEE International Conference on Big Data, pp 333–338
Li Z, Liu J, Tang J, Lu H (2015) Robust structured subspace learning for data representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(10):2085–2098
Li T, Tang J, Xu J (2016) Performance modeling and predictive scheduling for distributed stream data processing. IEEE Trans Big Data PP(99):1–1
Li Z, Tang J, He X (2017) Robust structured nonnegative matrix factorization for image representation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst PP(99):1–14
Liu Y, Cui J, Zhao H, Zha H (2012) Fusion of low-and high-dimensional approaches by trackers sampling for generic human motion tracking. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp 898–901
Liu W, Yu Z, Lu L, Wen Y, Li H, Zou Y (2015) Kcrc-lcd: discriminative kernel collaborative representation with locality constrained dictionary for visual categorization. Pattern Recogn 48(10):3076–3092
Liu Y, Nie L, Han L, Zhang L, Rosenblum DS (2015) Action2activity: recognizing complex activities from sensor data. In: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 1617–1623
Liu L, Cheng L, Liu Y, Jia Y, Rosenblum DS (2016) Recognizing complex activities by a probabilistic interval-based model. In: Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 1266–1272
Liu Y, Nie L, Liu L, Rosenblum DS (2016) From action to activity: sensor-based activity recognition. Neurocomputing 181:108–115
Liu Y, Zhang L, Nie L, Yan Y, Rosenblum DS (2016) Fortune teller: predicting your career path. In: Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 201–207
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Liang Y, Liu S, Rosenblum DS (2016) Urban water quality prediction based on multi-task multi-view learning. In: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Mukundan R (2007) Radial tchebichef invariants for pattern recognition. In: Tencon 2005 IEEE Region, pp 1–6
Tosic I, Frossard P (2011) Dictionary learning. IEEE Signal Proc Mag 28(2):27–38
TREVID[EB/OL]: http://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/tv2012/tv2012.html
Wang J, Yang J, Yu K, Lv F, Huang T, Gong Y (2010) Locality-constrained linear coding for image classification. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3360–3367
Wang YD, Yan QY, Li KF (2011) Hand vein recognition based on multi-scale lbp and wavelet. In: International Conference on Wavelet Analysis and Pattern Recognition, pp 214–218
Wang B, Wang Y, Xiao W, Wang W, Zhang M (2012) Human action recognition based on discriminative sparse coding video representation. Robot 34(6):745
Wang JGM, Zhan Y, Mao Q (2015) Locality-sensitive discriminant sparse representation for video semantic analysis. Comput Sci 42:313–318
Wei CP, Chao YW, Yeh YR, Wang YCF (2013) Locality-sensitive dictionary learning for sparse representation based classification. Pattern Recogn 46(5):1277–1287
Wright J, Yang AY, Ganesh A, Sastry SS, Ma Y (2009) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31 (2):210–227
Xu Y, Zuo W, Fan Z (2012) Supervised sparse representation method with a heuristic strategy and face recognition experiments. Neurocomputing 79(1):125–131
Yang J, Yu K, Gong Y, Huang T (2009) Linear spatial pyramid matching using sparse coding for image classification, pp 1794–1801
Yang M, Zhang L, Feng X, Zhang D (2012) Fisher discrimination dictionary learning for sparse representation. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 543–550
YouTube[EB/OL]: http://crcv.ucf.edu/data/UCF_YouTube_Action.php
Zhan Y, Wang M, Ke J (2012) Video key-frame extraction using ordered samples clustering based on artificial immune. J Jiangsu University 33(2):199–204
Zhan Y, Liu J, Gou J, Wang M (2016) A video semantic detection method based on locality-sensitive discriminant sparse representation and weighted knn. J Visual Commun Image Representation 41:65–73
Zhang H, Zhang Y, Huang T (2013) Pose-robust face recognition via sparse representation. Pattern Recogn 46(5):1511–1521
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61672268, Grant Nos. 61502208), Primary Research & Development Plan of Jiangsu Province of China (Grant No. BE2015137) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (Grant No. BK20150522).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Gou, J., Zhan, Y. et al. Discriminative self-adapted locality-sensitive sparse representation for video semantic analysis. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 29143–29162 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6090-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6090-6