Abstract
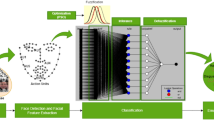
Facial Emotion Recognition (FER) is an important research domain which allows us to provide a better interactive environment between humans and computers. Some standard and popular features extracted from facial expression images include Uniform Local Binary Pattern (uLBP), Horizontal-Vertical Neighborhood Local Binary Pattern (hvnLBP), Gabor filters, Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) and Pyramidal HOG (PHOG). However, these feature vectors may contain some features that are irrelevant or redundant in nature, thereby increasing the overall computational time as well as recognition error of a classification system. To counter this problem, we have proposed a new feature selection (FS) algorithm based on Late Hill Climbing and Memetic Algorithm (MA). A novel local search technique called Late Acceptance Hill Climbing through Redundancy and Relevancy (LAHCRR) has been used in this regard. It combines the concepts of Local Hill-Climbing and minimal-Redundancy Maximal-Relevance (mRMR) to form a more effective local search mechanism in MA. The algorithm is then evaluated on the said feature vectors extracted from the facial images of two popular FER datasets, namely RaFD and JAFFE. LAHCRR is used as local search in MA to form Late Hill Climbing based Memetic Algorithm (LHCMA). LHCMA is compared with state-of-the-art methods. The experimental outcomes show that the proposed FS algorithm reduces the feature dimension to a significant amount as well as increases the recognition accuracy as compared to other methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agada R, Yan J (2015) Edge based mean LBP for valence facial expression detection. Proc 2015 IEEE Int Conf Electr Comput Commun Technol ICECCT 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECCT.2015.7226014
Ahmed F, Hossain E (2013) Automated Facial Expression Recognition Using Gradient-Based Ternary Texture Patterns. Faisal Chinese J Eng 2013:8
Appleby JS, Blake DV, Newman EA (1961) Techniques for producing school timetables on a computer and their application to other scheduling problems. Comput J 3:237–245
Barman A, Dutta P (2019) Facial expression recognition using distance and texture signature relevant features. Appl Soft Comput
Belanche LA, González FF (2011) Review and Evaluation of Feature Selection Algorithms in Synthetic Problems
Bosch A, Zisserman A, Munoz X (2007) Representing shape with a spatial pyramid kernel. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM international conference on Image and video retrieval. ACM, pp 401–408
Burke EK, Bykov Y (2017) The late acceptance Hill-Climbing heuristic. Eur J Oper Res 258:70–78
Carcagnì P, Del Coco M, Leo M, Distante C (2015) Facial expression recognition and histograms of oriented gradients: a comprehensive study. Springerplus 4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-015-1427-3
Dalai N, Triggs B, Rhone-Alps I, Montbonnot F (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognition, 2005 CVPR 2005 1:886–893. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2005.177
Daugman JG (1985) Uncertainty relation for resolution in space, spatial frequency, and orientation optimized by two-dimensional visual cortical filters. J Opt Soc Am A 2:1160. https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.2.001160
Dhall A, Asthana A, Goecke R, Gedeon T (2011) Emotion recognition using PHOG and LPQ features. 2011 IEEE Int Conf Autom Face Gesture Recognit Work FG 2011 878–883. https://doi.org/10.1109/FG.2011.5771366
Ding C, Peng H (2005) Minimum redundancy feature selection from microarray gene expression data. J Bioinforma Comput Biol 3:185–205
Dyer CR (2003) Simultaneous feature selection and classifier training via linear programming: a case study for face expression recognition. 2003 IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognition, 2003 Proceedings 1:I-346-I-352. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2003.1211374
Ekman P, Rosenberg EL (1997) What the face reveals: Basic and applied studies of spontaneous expression using the Facial Action Coding System (FACS)
Gharsalli S, Emile B, Laurent H, Desquesnes X (2016) Feature Selection for Emotion Recognition based on Random Forest. pp 511–517
Ghimatgar H, Kazemi K, Helfroush MS, Aarabi A (2018) An improved feature selection algorithm based on graph clustering and ant colony optimization. Knowledge-Based Syst 159:270–285
Ghimire D, Jeong S, Lee J, Park SH (2016) Facial expression recognition based on local region specific features and support vector machines. Multimed Tools Appl:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3418-y
Ghosh M, Adhikary S, Ghosh KK et al (2019) Genetic algorithm based cancerous gene identification from microarray data using ensemble of filter methods. Med Biol Eng Comput 57:159–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-1874-4
Ghosh M, Begum S, Sarkar R et al (2019) Recursive Memetic Algorithm for gene selection in microarray data. Expert Syst Appl 116:172–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.06.057
Ghosh M, Malakar S, Bhowmik S, et al (2019) Feature Selection for Handwritten Word Recognition Using Memetic Algorithm. In: Advances in Intelligent Computing. Springer, pp 103–124
Haghighat M, Zonouz S, Abdel-Mottaleb M (2015) CloudID: Trustworthy cloud-based and cross-enterprise biometric identification. Expert Syst Appl 42:7905–7916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.06.025
Hamamoto Y, Uchimura S, Watanabe M et al (1998) A Gabor filter-based method for recognizing handwritten numerals. Pattern Recogn 31:395–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(97)00057-5
Happy SL, George A, Routray A (2012) A real time facial expression classification system using Local Binary Patterns. Intell Hum Comput Interact (IHCI), 2012 4th Int Conf 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/IHCI.2012.6481802
Hsu H-H, Hsieh C-W, Lu M-D (2011) Hybrid feature selection by combining filters and wrappers. Expert Syst Appl 38:8144–8150
Huang J, Cai Y, Xu X (2007) A hybrid genetic algorithm for feature selection wrapper based on mutual information. Pattern Recogn Lett 28:1825–1844
Huang D, Shan C, Ardabilian M et al (2011) Facial image analysis based on local binary patterns : A survey. IEEE Trans Syst Man, Cybern Part C (Applications Rev) 41:765–781
Jain AK, Farrokhnia F (1991) Unsupervised texture segmentation using Gabor filters. Pattern Recogn 24:1167–1186. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-3203(91)90143-S
Kamarainen JK, Kyrki V, Kälviäinen H (2006) Invariance properties of Gabor filter-based features - Overview and applications. IEEE Trans Image Process 15:1088–1099
Kashef S, Nezamabadi-pour H (2015) An advanced ACO algorithm for feature subset selection. Neurocomputing 147:271–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2014.06.067
Kong WK, Zhang D, Li W (2003) Palmprint feature extraction using 2-D Gabor filters. Pattern Recogn 36:2339–2347. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(03)00121-3
Kononenko I (1994) Estimating attributes: analysis and extensions of RELIEF. In: European conference on machine learning. Springer, pp 171–182
Lajevardi S, Hussain Z (2009) Feature selection for facial expression recognition based on optimization algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn:182–185
Lajevardi SM, Hussain ZM (2012) Automatic facial expression recognition: Feature extraction and selection. Signal, Image Video Process 6:159–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-010-0177-5
Langner O, Dotsch R, Bijlstra G et al (2010) Presentation and validation of the radboud faces database. Cognit Emot 24:1377–1388. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699930903485076
Li Z, Imai J, Kaneko M (2009) Facial-component-based bag of words and phog descriptor for facial expression recognition. In: 2009 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. IEEE, pp 1353–1358
Li P, Phung SL, Bouzerdom A, Tivive FHC (2010) Feature selection for facial expression recognition. 2010 2nd Eur Work Vis Inf Process 35–40. https://doi.org/10.1109/EUVIP.2010.5699141
Liu C, Wechsler H (2002) Gabor feature based classification using the enhanced fisher linear discriminant model for face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 11:467–476. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2002.999679
Lyons M, Akamatsu S, Kamachi M, Gyoba J (1998) Coding facial expressions with Gabor wavelets. In: Proceedings - 3rd IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, FG 1998. pp 200–205
Mafarja M, Mirjalili S (2018) Whale optimization approaches for wrapper feature selection. Appl Soft Comput 62:441–453
Makhmudkhujaev F, Abdullah-Al-Wadud M, Bin IMT et al (2019) Facial expression recognition with local prominent directional pattern. Signal Process Image Commun
Malakar S, Ghosh M, Bhowmik S et al (2019) A GA based hierarchical feature selection approach for handwritten word recognition. Neural Comput & Applic:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3937-8
Meshgini S, Aghagolzadeh A, Seyedarabi H (2013) Face recognition using Gabor-based direct linear discriminant analysis and support vector machine. Comput Electr Eng 39:727–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2012.12.011
Mistry K, Zhang L, Neoh SC et al (2017) A micro-GA embedded PSO feature selection approach to intelligent facial emotion recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 47:1496–1509
Mohamed NS, Zainudin S, Othman ZA (2017) Metaheuristic approach for an enhanced mRMR filter method for classification using drug response microarray data. Expert Syst Appl 90:224–231
Nava R, Cristóbal G, Escalante-Ramírez B (2011) Invariant texture analysis through Local Binary Patterns. Comput Vis pattern Recognit
Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Maenpaa T (2002) Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24:971–987. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2002.1017623
Ou J, Bai X-B, Pei Y et al (2010) Automatic Facial Expression Recognition Using Gabor Filter and Expression Analysis. Second Int Conf Comput Model Simul 2010:215–218. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCMS.2010.45
Pantic M, Rothkrantz LJM (2000) Automatic analysis of facial expressions: the state of the art. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22:1424–1445. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.895976
Peng H, Long F, Ding C (2005) Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27:1226–1238
Priya RV (2019) Emotion recognition from geometric fuzzy membership functions. Multimed Tools Appl:1–32
Radovic M, Ghalwash M, Filipovic N, Obradovic Z (2017) Minimum redundancy maximum relevance feature selection approach for temporal gene expression data. BMC Bioinformatics 18:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-016-1423-9
Sakar CO, Kursun O, Gurgen F (2012) A feature selection method based on kernel canonical correlation analysis and the minimum Redundancy–Maximum Relevance filter method. Expert Syst Appl 39:3432–3437
Senawi A, Wei H-L, Billings SA (2017) A new maximum relevance-minimum multicollinearity (MRmMC) method for feature selection and ranking. Pattern Recogn 67:47–61
Shan C, Gong S, McOwan PW (2009) Facial expression recognition based on Local Binary Patterns: A comprehensive study. Image Vis Comput 27:803–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2008.08.005
Shan C, Gritti T (2008) Learning Discriminative LBP-Histogram Bins for Facial Expression Recognition. Procedings Br Mach Vis Conf 2008:27.1–27.10. https://doi.org/10.5244/C.22.27
Shen L, Bai L, Fairhurst M (2007) Gabor wavelets and General Discriminant Analysis for face identification and verification. Image Vis Comput 25:553–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2006.05.002
Sreedharan NPN, Ganesan B, Raveendran R et al (2018) Grey Wolf optimisation-based feature selection and classification for facial emotion recognition. IET Biometrics 7:490–499
Viola P, Jones MMJ (2004) Robust Real-Time Face Detection. Int J Comput Vis 57:137–154. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:VISI.0000013087.49260.fb
Wang X, Jin C, Liu W, et al (2013) Feature Fusion of HOG and WLD for Facial Expression Recognition. Syst Integr (SII), 2013 IEEE/SICE Int Symp 227–232. https://doi.org/10.1109/SII.2013.6776664
Wang F, Lv J, Ying G et al (2019) Facial expression recognition from image based on hybrid features understanding. J Vis Commun Image Represent 59:84–88
Wang S-H, Phillips P, Dong Z-C, Zhang Y-D (2018) Intelligent facial emotion recognition based on stationary wavelet entropy and Jaya algorithm. Neurocomputing 272:668–676
Wang G, Yang Y, Kong H (2009) Self-Learning facial emotional feature selection based on rough set theory. Math Probl Eng 2009. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/802932
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Chen Z, et al (2016) Application of ReliefF algorithm to selecting feature sets for classification of high resolution remote sensing image. In: Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), 2016 IEEE International. IEEE, pp 755–758
Wei J, Zhang R, Yu Z et al (2017) A BPSO-SVM algorithm based on memory renewal and enhanced mutation mechanisms for feature selection. Appl Soft Comput J 58:176–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.04.061
Yu J, Bhanu B (2006) Evolutionary feature synthesis for facial expression recognition. Pattern Recogn Lett 27:1289–1298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2005.07.026
Zhang S, Zhao X, Lei B (2012) Facial expression recognition based on local binary patterns and local fisher discriminant analysis. WSEAS Trans Signal Process 8:21–31
Zhao L, Wang Z, Zhang G (2017) Facial Expression Recognition from Video Sequences Based on Spatial-Temporal Motion Local Binary Pattern and Gabor Multiorientation Fusion Histogram. Math Probl Eng 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7206041
Zhu Z, Ong Y-S, Dash M (2007) Wrapper–filter feature selection algorithm using a memetic framework. IEEE Trans Syst Man, Cybern Part B 37:70–76
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Code
https://github.com/ManosijGhosh/Late-Hill-Climbing-based-Memetic-Algorithm-LHCMA
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, M., Kundu, T., Ghosh, D. et al. Feature selection for facial emotion recognition using late hill-climbing based memetic algorithm. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 25753–25779 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-07811-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-07811-x