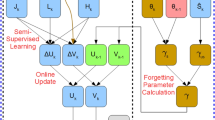
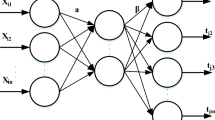
Abstract
Classification is a hotspot in data stream mining and has gained increasing interest from various research fields. Compared with traditional data stream classification methods, Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) has attracted much attention because of its efficiency and simplicity, which inspired the development of many improved ELM algorithms that have been proposed in the past few years. This paper mainly reviews the current state of ELM used to classify data streams and its variants. First, we introduce the principles of ELM and the existing problems of data stream classification. Then we provide an overview of various improvements made to ELM, which further improves its stability, accuracy and generalization ability and present the practical applications of ELM used in data stream classification. Finally, the paper highlights the existing problems of ELM used for data stream mining and development prospects of ELM in the future.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
AI-Behadili H, Grumpet A, Doppt C et al (2015) Extreme Learning Machine based Novelty Detection for Incremental Semi-Supervised Learning. In 2015 Third International Conference on Image Infonnation Processing. IEEE
Alade OA, Selamat A, Sallehuddin R (2017) A review of advances in extreme learning machine techniques and its applications. In International Conference of Reliable Information and Communication Technology:885–895. Springer
Aljawarneh S, Aldwairi M, Yassein MB (2018) Anomaly-based intrusion detection system through feature selection analysis and building hybrid efficient model. Journal of Computational Science 25:152–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2017.03.006
Atli BG, Miche Y, Kalliola A (2018) Anomaly-based intrusion detection using extreme learning machine and aggregation of network traffic statistics in probability space. Cogn Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-018-9564-y
Bloodgood M, Vijay-Shanker K (2009) Taking into account the differences between actively and passively acquired data: The case of active learning with support vector machines for imbalanced datasets. In: Proceedings of Human Language Technologies: The 2009 Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Companion Volume: Short Papers. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 137-140
Bordes A, Ertekin S, Weston J et al (2005) Fast kernel classifiers with online and active learning. J Mach Learn Res 6(Sep):1579–1619
Cao J, Lin Z, Huang G-B (2013) Voting base online sequential extreme learning machine for multi-class classification. In Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 2013 IEEE International Symposium on:2327-2330. IEEE
Cao K, Wang G, Han D et al (2014) Classification of uncertain data streams based on extreme learning machine. Cogn Comput 7(1):150–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-014-9279-7
Cao J, Zhao Y, Lai X et al (2015) Landmark recognition with sparse representation classification and extreme learning machine. Journal of the Franklin Institute 352(10):4528–4545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2015.07.002
Cao K, Wang G, Han D et al (2016) An algorithm for classification over uncertain data based on extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 174:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.05.121
Cavalcante RC, I. Oliveira AL (2015) An Approach to Handle Concept Drift in Financial Time Series Based on Extreme Learning Machines and Explicit Drift Detection. In 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. IEEE
Cucchiara R, Piccard M, Prati A (2003) Detecting moving objects, ghosts and shadows in Vedio streams. IEEE Transaction on Pattern Analysis And Machine Intelligence 25:1337–1342. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1233909
Deng W-Y, Ong Y-S, Tan PS et al (2016) Online sequential reduced kernel extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 174:72–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.06.087
Deng S, Wang B, Huang S et al (2017) Self-adaptive framework for efficient stream data classification on storm. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.2017.2757029
Deo RC, Sahin M (2016) An extreme learning machine model for the simulation of monthly mean streamflow water level in eastern Queensland. Environ Monit Assess 188(2):90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5094-9
Ding S, Zhao H, Zhang Y et al (2013) Extreme learning machine: algorithm, theory and applications. Artif Intell Rev 44(1):103–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-013-9405-z
Ding S, Zhang N, Xu X et al (2015) Deep extreme learning machine and its application in EEG classification. Math Probl Eng 2015:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/129021
Ding S, Mirza B, Lin Z et al (2018) Kernel based online learning for imbalance multiclass classification. Neurocomputing 277:139–148
Ditzler G, Polikar R (2013) Incremental learning of concept drift from streaming imbalanced data. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(10):2283–2301. https://doi.org/10.1109/tkde.2012.136
Domingos P, Hulten G (2000) Mining high-speed data streams. In 6th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, 71-80. ACM
B. Dongre P, Malik. LG (2014a) A review on Real Time Data Stream Classification and Adapting To Various Concept Drift Scenarios. In 2014 IEEE International Advance Computing Conference . IEEE
Dongre PB, Malik LG (2014b) A review on real time data stream classification and adapting to various concept drift scenarios. In Advance Computing Conference (IACC), 2014 IEEE International:533-537. IEEE
Duan L, Xu Y, Cui S (2016) Feature Extraction of Motor Imagery EEG Based on Extreme Learning Machine Auto-encoder. In: Proceedings in Adaptation, Learning and Optimization, vol 6. pp 361-370. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28397-5_28
Duan L, Bao M, Cui S (2017) Motor imagery EEG classification based on kernel hierarchical extreme learning machine. Cogn Comput 9(6):758–765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-017-9494-0
Eirola E, Gritsenko A, Akusok A (2015) Extreme Learning Machines for Multiclass Classification: Refining Predictions with Gaussian Mixture Models. In International Work-Conference on Artificial Neural Networks:153-164. Springer
Fan W, Wang H, Philip SY et al (2003) Is random model better? On its accuracy and efficiency. In Third IEEE International Conference on Data Mining:51. IEEE
Gaber MM, Zaslavsky A, Krishnaswamy S (2007) A survey of classification methods in data streams. In: Data streams. Springer, pp 39-59
Gao J, Ding B, Fan W et al (2008) Classifying data streams with skewed class distributions and concept drifts. IEEE Internet Comput 12(6)
Geoff H, Laurie S, Pedro D (2001) MiningTime-ChangingDataStreams.In 7th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining:97-106. ACM
Ghazikhani A, Monsefi R, Yazdi HS (2013) Ensemble of online neural networks for non-stationary and imbalanced data streams. Neurocomputing 122:535–544
Gomes HM, Barddal JP, Enembreck F et al (2017) A survey on ensemble learning for data stream classification. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 50(2):23
Gu Y, Liu J, Chen Y et al (2014) TOSELM: timeliness online sequential extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 128:119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.02.047
Guang-Bin H, Qin-Yu Z, Chee-Kheong S (2004a) Extreme learning machine: a new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. In: 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. pp 985-990. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ijcnn.2004.1380068
Guang-Bin H, Qin-Yu Z, Chee-Kheong S (2004b) Extreme learning machine: a new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. In 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks 2:985-990. IEEE
Guo W, Xu T, Tang K et al (2018) Online sequential extreme learning machine with generalized regularization and adaptive forgetting factor for time-varying system prediction. Math Probl Eng 2018:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6195387
Han D-H, Zhang X, Wang G-R (2015a) Classifying uncertain and evolving data streams with distributed extreme learning machine. J Comput Sci Technol 30(4):874–887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-015-1566-6
Han D, Giraud-Carrier C, Li S (2015b) Efficient mining of high-speed uncertain data streams. Appl Intell 43(4):773–785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-015-0675-9
Han F, Zhao M-R, Zhang J-M et al (2017) An improved incremental constructive single-hidden-layer feedforward networks for extreme learning machine based on particle swarm optimization. Neurocomputing 228:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.09.092
Han D, Li S, Wei F et al (2018) Two birds with one stone: classifying positive and unlabeled examples on uncertain data streams. Neurocomputing 277:149–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.03.094
Homayoun S, Ahmadzadeh M (2016) A review on data stream classification approaches. Journal of Advanced Computer Science & Technology 5(1):8–13
Huang Y (2015) Dynamic cost-sensitive ensemble classification based on extreme learning machine for mining imbalanced massive data streams. International Journal of u- and e-Service, Science and Technology 8(1):333–346. https://doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2015.8.1.30
Huang G-B, Chen L (2008) Enhanced random search based incremental extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 71(16-18):3460–3468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2007.10.008
Huang GB, Saratchandran P, Sundararajan N (2004) An efficient sequential learning algorithm for growing and pruning RBF (GAP-RBF) networks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics) 34(6):2284–2292. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmcb.2004.834428
Huang GB, Saratchandran P, Sundararajan N (2005) A generalized growing and pruning RBF (GGAP-RBF) neural network for function approximation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 16(1):57–67. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2004.836241
Huang G-B, Zhu Q-Y, Siew C-K (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1-3):489–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126
Huang G-B, Zhou H, Ding X et al (2012) Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics) 42(2):513–529
Huang G, Huang GB, Song S et al (2015) Trends in extreme learning machines: a review. Neural Netw 61:32–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.10.001
Janardan MS (2017) Concept drift in streaming data classification :Algorithms,Platforms and issues. Procedia Computer Science 122:804–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.11.440
Junhai Z, Jinggeng W, Xizhao W (2014) Ensemble online sequential extreme learning machine for large data set classification In 2014 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC). IEEE
Kasun LLC, Zhou H, Huang G-B (2013) Representational learning with extreme learning with extreme learning machine for big data. IEEE Intell Syst
Kegelmeyer WP, Hall LO, Bowyer KW et al (2002) SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Intell Res 16:321–357. https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.953
Khan I, Huang JZ, Ivanov K (2016) Incremental density-based ensemble clustering over evolving data streams. Neurocomputing 191:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.01.009
Kim Y, Toh K-A, Teoh ABJ et al (2013) An online learning network for biometric scores fusion. Neurocomputing 102:65–77
Krawczyk B (2016a) GPU-accelerated extreme learning Machines for Imbalanced Data Streams with concept drift. Procedia Computer Science 80:1692–1701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2016.05.509
Krawczyk B (2016b) Learning from imbalanced data: open challenges and future directions. Progress in Artificial Intelligence 5(4):221–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13748-016-0094-0
Krawczyk B, Stefanowski J, Wozniak M (2015) Data stream classification and big data analytics. Neurocomputing 150:238–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2014.10.025
Kuang Y, Wu Q, Shao J et al (2017) Extreme learning machine classification method for lower limb movement recognition. Clust Comput 20(4):3051–3059. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-0985-2
Kumar S, Pal SK, Singh RP (2018) A novel method based on extreme learning machine to predict heating and cooling load through design and structural attributes. Energy and Buildings 176:275–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2018.06.056
Lan Y, Soh YC, Huang G-B (2009) Ensemble of online sequential extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 72(13-15):3391–3395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2009.02.013
Li P, Wu X, Liang Q et al (2011) Random ensemble decision trees for learning concept-drifting data streams. In Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining:313-325. Springer
Li P, Wu X, Hu X et al (2015) Learning concept-drifting data streams with random ensemble decision trees. Neurocomputing 166:68–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.04.024
Li M, Xiao P, Zhang J (2018a) Text classification based on ensemble extreme learning machine. arXiv preprint arXiv:180506525
Li Y, Qiu R, Jing S (2018b) Intrusion detection system using online sequence extreme learning machine (OS-ELM) in advanced metering infrastructure of smart grid. PLoS One 13(2):e0192216. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0192216
Liang NY, Huang GB, Saratchandran P et al (2006) A fast and accurate online sequential learning algorithm for feedforward networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17(6):1411–1423. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2006.880583
Lindenbaum M, Markovitch S, Rusakov D (2004) Selective sampling for nearest neighbor classifiers. Mach Learn 54(2):125–152
Liu N, Wang H (2010) Ensemble based extreme learning machine. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 17(7):754
Lu Y, N S PS (1997) A sequential learning scheme for function approximation using minimal radial basis function neural networks. Neural Comput:461–478
Luo X, Chang X (2015) A novel data fusion scheme using grey model and extreme learning machine in wireless sensor networks. Int J Control Autom Syst 13(3):539–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-014-0309-8
Mao W, Wang J, Wang L (2015) Online Sequential Classification of Imbalanced Data by Combining Extreme Learning Machine and improved SMOTE Algorithm. In 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks 1-8. IEEE
Mirza B, Lin Z (2016) Meta-cognitive online sequential extreme learning machine for imbalanced and concept-drifting data classification. Neural Netw 80:79–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2016.04.008
Mirza B, Lin Z, Toh K-A (2013) Weighted online sequential extreme learning machine for class imbalance learning. Neural Process Lett 38(3):465–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-013-9286-9
Mirza B, Lin Z, Cao J et al (2015a) Voting based weighted online sequential extreme learning machine for imbalance multi-class classification. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits & Systems:565–568. https://doi.org/10.1109/iscas.2015.7168696
Mirza B, Lin Z, Liu N (2015b) Ensemble of subset online sequential extreme learning machine for class imbalance and concept drift. Neurocomputing 149:316–329
Mohammadi K, Shamshirband S, Motamedi S et al (2015) Extreme learning machine based prediction of daily dew point temperature. Comput Electron Agric 117:214–225
Nguyen H-L, Woon Y-K, Ng W-K (2014) A survey on data stream clustering and classification. Knowl Inf Syst 45(3):535–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-014-0808-1
Ouyang Z, Zhou M, Wang T et al (2009) Mining Concept-Drifting and Noisy Data Streams Using Ensemble Classifiers.360-364. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/aici.2009.153
Pan S, Wu K, Zhang Y et al (2010a) Classifier Ensemble for Uncertain Data Stream Classification. In: Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. pp 488-495. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13657-3_52
Pan S, Wu K, Zhang Y et al (2010b) Classifier Ensemble for Uncertain Data Stream Classification. In Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining 6118:488-495. Springer
Platt J (1991) A resource-allocating network for function interpolation. Neural Comput 3(2):213–225. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1991.3.2.213
Polikar R, DePasquale J, Syed Mohammed H et al (2010) Learn++.MF: a random subspace approach for the missing feature problem. Pattern Recogn 43(11):3817–3832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2010.05.028
Qiu J, Wu Q, Ding G et al (2016) A survey of machine learning for big data processing. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing 2016(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13634-016-0355-x
Ramírez-Gallego S, Krawczyk B, García S et al (2017) A survey on data preprocessing for data stream mining: current status and future directions. Neurocomputing 239:39–57
Roshan S, Miche Y, Akusok A et al (2018) Adaptive and online network intrusion detection system using clustering and extreme learning machines. Journal of the Franklin Institute 355(4):1752–1779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2017.06.006
Samat A, Du P, Liu S et al (2014) ${{\text E}^{2}}{\text LMs}$: ensemble extreme learning Machines for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 7(4):1060–1069. https://doi.org/10.1109/jstars.2014.2301775
Savitha R, Suresh S, Kim HJ (2013) A meta-cognitive learning algorithm for an extreme learning machine classifier. Cogn Comput 6(2):253–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-013-9223-2
Scardapane S, Comminiello D, Scarpiniti M et al (2015) Online sequential extreme learning machine with kernels. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems 26(9):2214–2220
Seliya N, Khoshgoftaar TM (2010) Active learning with neural networks for intrusion detection. In: Information Reuse and Integration (IRI), 2010 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, pp 49-54
Shamshirband S, Mohammadi K, Tong CW (2015) Application of extreme learning machine for estimation of wind speed distribution. Clim Dyn 46(5-6):1893–1907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2682-2
Shao Z, Er MJ (2016) An online sequential learning algorithm for regularized extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 173:778–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.08.029
Shukla S, Yadav R (2015) Voting based Extreme learning machine with entropy based ensemble pruning. In Cognitive Computing and Information Processing (CCIP), 2015 International Conference on:1-6. IEEE
Shukla A, Bhandari V, Shrivastava A (2017) Stay one Forget Multiple Extreme Learning Machine with deep Network using time interval process: A review. In 2017 7th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT). IEEE
Sun J, Fu Y, Li S (2018) Sequential Human Activity Recognition based on Deep Convolutional Network and Extreme Learning Machine using Wearable Sensors
Tennant M, Stahl F, Rana O et al (2017) Scalable real-time classification of data streams with concept drift. Futur Gener Comput Syst 75:187–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2017.03.026
Tian H-X, Mao Z-Z (2010) An ensemble ELM based on modified AdaBoost. RT algorithm for predicting the temperature of molten steel in ladle furnace. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 7(1):73–80
Tong S, Koller D (2001) Support vector machine active learning with applications to text classification. J Mach Learn Res 2(Nov):45–66
Wang Z, Crammer K, Vucetic S (2012) Breaking the curse of kernelization: budgeted stochastic gradient descent for large-scale svm training. J Mach Learn Res 13:3103–3131
Wang G-G, Lu M, Dong Y-Q et al (2015a) Self-adaptive extreme learning machine. Neural Comput & Applic 27(2):291–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1874-3
Wang Y, Li D, Du Y et al (2015b) Anomaly detection in traffic using L1-norm minimization extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 149:415–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2014.04.073
Wang L, Liu H, Sun F (2016) Dynamic texture video classification using extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 174:278–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.03.114
Wenhua X, Zheng Q, Yang C (2011) A framework for classifying uncertain and evolving data stream. Inf Technol J:1926–1933
Wu D, Wang Z, Chen Y et al (2016) Mixed-kernel based weighted extreme learning machine for inertial sensor based human activity recognition with imbalanced dataset. Neurocomputing 190:35–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.11.095
Xiao W, Zhang J, Li Y et al (2017) Class-specific cost regulation extreme learning machine for imbalanced classification. Neurocomputing 261:70–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.09.120
Xin Y, Fei L, Jingshuai W (2017) Signal Detection of MIMO-OFDM System Based on Auto Encoder and Extreme Learning Machine. In 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). IEEE
Xu Z, Murch RD (2002) Performance analysis of maximum likelihood detection in a MIMO antenna system. IEEE Trans Commun 50(2):187–191. https://doi.org/10.1109/26.983313
Xu S, Wang J (2016) A fast incremental extreme learning machine algorithm for data streams classification. Expert Syst Appl 65:332–344
Xu S, Wang J (2017) Dynamic extreme learning machine for data stream classification. Neurocomputing 238:433–449
Xue X, Yao M, Wu Z et al (2014) Genetic ensemble of extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 129:175–184
Yadav B, Ch S, Mathur S et al (2016) Discharge forecasting using an online sequential extreme learning machine (OS-ELM) model: a case study in Neckar River, Germany. Measurement 92:433–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.06.042
Yang R, Xu S, Feng L (2018) An ensemble extreme learning machine for data stream classification. Algorithms 11(7):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11070107
Yu CH, Choi JW (2014) Interacting multiple model filter-based distributed target tracking algorithm in underwater wireless sensor networks. Int J Control Autom Syst 12(3):618–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-013-0238-y
Yu H, Sun C, Yang W et al (2015) AL-ELM: one uncertainty-based active learning algorithm using extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 166:140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.04.019
Yu H, Yang X, Zheng S et al (2018) Active learning from imbalanced data: a solution of online weighted extreme learning machine. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2855446
Zhai J-h, H-y X, X-z W (2012) Dynamic ensemble extreme learning machine based on sample entropy. Soft Comput 16(9):1493–1502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-012-0824-6
Zhang P, Zhu X, Shi Y et al (2009) An aggregate ensemble for mining concept drifting data streams with noise. In Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining:1021-1029. Springer
Zhang Y, Liu W, Ren X et al (2017) Dual weighted extreme learning machine for imbalanced data stream classification. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 33(2):1143–1154
Zhao J, Wang Z, Park DS (2012) Online sequential extreme learning machine with forgetting mechanism. Neurocomputing 87:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2012.02.003
Zhenyu C, Shuangquan W, Zhiqi S (2013) Online Sequential ELM based Transfer Learning for Transportation Mode Recognition. In 2013 IEEE Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems (CIS). IEEE
Zhiyuan M, Guangchun L, Huang D (2016) Short Term Traffic Flow Prediction Based on Online Sequential Extreme Learning Machine. In 2016 Eighth International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI). IEEE
Zhou W, Ji C, Mou J et al (2013) Adaptive target synchronization for wireless sensor networks with Markov delays and noise perturbation. Int J Control Autom Syst 11(5):919–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-012-9511-8
Zhu J, Hovy E (2007) Active learning for word sense disambiguation with methods for addressing the class imbalance problem. In: Proceedings of the 2007 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning (EMNLP-CoNLL)
Zong W, Huang G-B, Chen Y (2013) Weighted extreme learning machine for imbalance learning. Neurocomputing 101:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2012.08.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Sun, R., Cai, S. et al. A review of improved extreme learning machine methods for data stream classification. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 33375–33400 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7543-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7543-2