Abstract
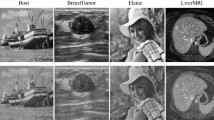
In this article, we propose a mixed-noise removal model which incorporates with a nonsmooth and nonconvex regularizer. To solve this model, a multistage convex relaxation method is used to deal with the optimization problem due to the nonconvex regularizer. Besides, we adopt the number of iteration steps as the termination condition of the proposed algorithm and select the optimal parameters for the model by a genetic algorithm. Several experiments on classic images with different level noises indicate that the robustness, running time, ISNR (Improvement in Signalto-Noise ratio) and PSNR (Peak Signal to Noise Ratio) of our model are better than those of other three models, and the proposed model can retain the local information of the image to obtain the optimal quantitative metrics and visual quality of the restored images.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alliney S (1997) A property of the minimum vectors of a regularizing functional defined by means of the absolute norm. IEEE Trans Signal Process 45(4):913–917
Aubert G, Kornprobst P (2006) Mathematical problems in image processing: partial differential equations and the calculus of variations, vol. 147. Springer Science & Business Media
Aubert G, Aujol J-F (2008) A variational approach to removing multiplicative noise. SIAM J Appl Math 68(4):925–946
Bar L, Chan TF, Chung G, Jung M, Kiryati N, Mohieddine R, Sochen N, Vese LA (2011) Mumford and shah model and its applications to image segmentation andimage restoration. In: Handbook of mathematical methods in imaging. Springer, pp 1095–1157
Blake A, Zisserman A (1987) Visual reconstruction. MIT Press, Cambridge
Bovik AC (2010) Handbook of image and video processing. Academic, New York
Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E, Peleato B, Eckstein J et al (2011) Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found Trends®; Machine Learn 3(1):1– 122
Buades A, Coll B, Morel J-M (2005) A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2005. CVPR 2005, vol 2. IEEE, pp 60–65
Buades A, Coll B, Morel J-M (2005) A review of image denoising algorithms, with a new one. Multiscale Model Simul 4(2):490–530
Burger HC, Schuler CJ, Harmeling S (2012) Image denoising: can plain neural networks compete with bm3d?. In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 2392–2399
Cai J-F, Chan RH, Nikolova M (2008) Two-phase approach for deblurring images corrupted by impulse plus gaussian noise. Inverse Probl Imaging 2(2):187–204
Cai X, Chan R, Zeng T (2013) A two-stage image segmentation method using a convex variant of the mumford–shah model and thresholding. SIAM J Imag Sci 6(1):368–390
Chan TF, Esedoglu S (2005) Aspects of total variation regularized l 1 function approximation. J SIAM Appl Math 65(5):1817–1837
Charbonnier P, Blanc-Féraud L, Aubert G, Barlaud M (1997) Deterministic edge-preserving regularization in computed imaging. IEEE Trans Image Process 6 (2):298–311
Chartrand R, Yin W (2008) Iterative reweighted algorithms for compressive sensing. Tech. Rep.
Chen Y, Pock T (2017) Trainable nonlinear reaction diffusion: a flexible framework for fast and effective image restoration. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39 (6):1256–1272
Chen Y, Yu W, Pock T (2015) On learning optimized reaction diffusion processes for effective image restoration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5261–5269
Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, Egiazarian K (2007) Image denoising by sparse 3-d transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(8):2080–2095
Daubechies I, DeVore R, Fornasier M, Güntürk CS (2010) Iteratively reweighted least squares minimization for sparse recovery. Commun Pure Appl Math: A Journal Issued by the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences 63(1):1–38
Deng L, Zhu H, Li Y, Yang Z (2018) A low-rank tensor model for hyperspectral image sparse noise removal. IEEE Access 6:62120–62127
Dong W, Li X, Zhang L, Shi G (2011) Sparsity-based image denoising via dictionary learning and structural clustering. In: 2011 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 457–464
Dong W, Shi G, Li X (2013) Nonlocal image restoration with bilateral variance estimation: a low-rank approach. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(2):700–711
Dong W, Zhang L, Shi G, Li X (2013) Nonlocally centralized sparse representation for image restoration. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(4):1620–1630
Dong W, Shi G, Li X, Ma Y, Huang F (2014) Compressive sensing via nonlocal low-rank regularization. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(8):3618–3632
Elad M, Aharon M (2006) Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(12):3736–3745
Esser E (2009) Applications of lagrangian-based alternating direction methods and connections to split bregman. CAM Report 9:31
Feng W, Qiao P, Chen Y (2018) Fast and accurate poisson denoising with trainable nonlinear diffusion. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(6):1708–1719
Figueiredo MA, Bioucas-Dias JM (2010) Restoration of poissonian images using alternating direction optimization. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(12):3133–3145
Garnett R, Huegerich T, Chui C, He W (2005) A universal noise removal algorithm with an impulse detector. IEEE Trans Image Process 14(11):1747–1754
Geman S, Geman D (1984) Stochastic relaxation, gibbs distributions, and the bayesian restoration of images. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 6:721–741
Geman D, Reynolds G (1992) Constrained restoration and the recovery of discontinuities. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 3:367–383
Geman D, Yang C (1995) Nonlinear image recovery with half-quadratic regularization. IEEE Trans Image Process 4(7):932–946
Goldstein T, Osher S (2009) The split bregman method for l1-regularized problems. SIAM J Imag Sci 2(2):323–343
Gu S, Zhang L, Zuo W, Feng X (2014) Weighted nuclear norm minimization with application to image denoising. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2862–2869
Han Y, Feng X-C, Baciu G, Wang W-W (2013) Nonconvex sparse regularizer based speckle noise removal. Pattern Recognit 46(3):989–1001
He B, Liao L-Z, Han D, Yang H (2002) A new inexact alternating directions method for monotone variational inequalities. Math Program 92(1):103–118
He K, Wang R, Tao D, Cheng J, Liu W (2018) Color transfer pulse-coupled neural networks for underwater robotic visual systems. IEEE Access 6:32850–32860
Hintermüller M, Langer A (2012) Subspace correction methods for a class of non-smooth and non-additive convex variational problems in image processing
Huang T, Dong W, Xie X, Shi G, Bai X (2017) Mixed noise removal via laplacian scale mixture modeling and nonlocal low-rank approximation. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(7):3171–3186
Jain V, Seung S (2009) Natural image denoising with convolutional networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 769–776
Ji H, Huang S, Shen Z, Xu Y (2011) Robust video restoration by joint sparse and low rank matrix approximation. SIAM J Imag Sci 4(4):1122–1142
Ji H, Liu C, Shen Z, Xu Y (2010) Robust video denoising using low rank matrix completion
Jia T, Shi Y, Zhu Y, Wang L (2016) An image restoration model combining mixed L1/L2 fidelity terms. J Vis Commun Image Represent 38:461–473
Jiang J, Zhang L, Yang J (2014) Mixed noise removal by weighted encoding with sparse nonlocal regularization. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(6):2651–2662
Jung M, Kang M (2015) Efficient nonsmooth nonconvex optimization for image restoration and segmentation. J Sci Comput 62(2):336–370
Li SZ (1994) Markov random field models in computer vision. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 361–370
Liu L, Chen L, Chen CP, Tang YY et al (2017) Weighted joint sparse representation for removing mixed noise in image. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(3):600–611
Mairal J, Bach F, Ponce J, Sapiro G, Zisserman A (2009) Non-local sparse models for image restoration. In: 2009 IEEE 12th international conference on computer vision. IEEE, pp 2272–2279
Mumford D, Shah J (1989) Optimal approximations by piecewise smooth functions and associated variational problems. Commun Pure Appl Math 42(5):577–685
Nikolova M (1999) Markovian reconstruction using a gnc approach. IEEE Trans Image Process 8(9):1204–1220
Nikolova M (2002) Minimizers of cost-functions involving nonsmooth data-fidelity terms. application to the processing of outliers. SIAM J Numer Anal 40(3):965–994
Nikolova M (2004) A variational approach to remove outliers and impulse noise. J Math Imaging Vision 20(1–2):99–120
Nikolova M (2005) Analysis of the recovery of edges in images and signals by minimizing nonconvex regularized least-squares. Multiscale Model Simul 4(3):960–991
Nikolova M, Chan RH (2007) The equivalence of half-quadratic minimization and the gradient linearization iteration. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(6):1623–1627
Nikolova M, Ng MK, Zhang S, Ching W-K (2008) Efficient reconstruction of piecewise constant images using nonsmooth nonconvex minimization. SIAM J Imag Sci 1(1):2–25
Nikolova M, Ng MK, Tam C-P (2010) Fast nonconvex nonsmooth minimization methods for image restoration and reconstruction. IEEE Trans Image Process 19 (12):3073–3088
Ochs P, Dosovitskiy A, Brox T, Pock T (2013) An iterated l1 algorithm for non-smooth non-convex optimization in computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1759–1766
Osher S, Shi Z, Zhu W (2017) Low dimensional manifold model for image processing. SIAM J Imag Sci 10(4):1669–1690
Robini MC, Lachal A, Magnin IE (2007) A stochastic continuation approach to piecewise constant reconstruction. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(10):2576–2589
Rockafellar R (1997) Convex analysis, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1970. MATH Google Scholar
Roth S, Black MJ (2009) Fields of experts. Int J Comput Vis 82(2):205–229
Rudin LI, Osher S, Fatemi E (1992) Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena 60(1–4):259–268
Shao L, Yan R, Li X, Liu Y (2014) From heuristic optimization to dictionary learning: a review and comprehensive comparison of image denoising algorithms. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(7):1001–1013
Tao D, Cheng J, Song M, Lin X (2016) Manifold ranking-based matrix factorization for saliency detection. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(6):1122–1134
Teboul S, Blanc-Feraud L, Aubert G, Barlaud M (1998) Variational approach for edge-preserving regularization using coupled pdes. IEEE Trans Image Process 7(3):387–397
Vogel CR, Oman ME (1998) Fast, robust total variation-based reconstruction of noisy, blurred images. IEEE Trans Image Process 7(6):813–824
Wang Y, Yang J, Yin W, Zhang Y (2008) A new alternating minimization algorithm for total variation image reconstruction. SIAM J Imag Sci 1(3):248–272
Xiao Y, Zeng T, Yu J, Ng MK (2011) Restoration of images corrupted by mixed gaussian-impulse noise via l1–l0 minimization. Pattern Recognit 44(8):1708–1720
Xie J, Xu L, Chen E (2012) Image denoising and inpainting with deep neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 341–349
Yan M (2013) Restoration of images corrupted by impulse noise and mixed gaussian impulse noise using blind inpainting. SIAM J Imag Sci 6(3):1227–1245
Yan R, Shao L, Liu Y (2013) Nonlocal hierarchical dictionary learning using wavelets for image denoising. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(12):4689–4698
Zhang T (2010) Analysis of multi-stage convex relaxation for sparse regularization. J Mach Learn Res 11:1081–1107
Zhang X, Lu Y, Chan T (2012) A novel sparsity reconstruction method from poisson data for 3d bioluminescence tomography. J Sci Comput 50(3):519–535
Zhang H, Yang J, Zhang Y, Huang TS (2013) Image and video restorations via nonlocal kernel regression. IEEE Trans Cybern 43(3):1035–1046
Zhang K, Zuo W, Chen Y, Meng D, Zhang L (2017) Beyond a gaussian denoiser: residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(7):3142–3155
Acknowledgments
Funding were provided by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant NO.61361126011, No. 90912006; the Special Project of Informatization of Chinese Academy of Sciences in “the Twelfth Five-Year Plan” under Grant No. XXH12504-1-06, Science and Technology Service Network Initiative, CAS, (STS Plan); he IT integrated service platform of Sichuan Wolong Natural Reserve, under Grant No. Y82E01; The National R&D Infrastructure and Facility Development Program of China, “Fundamental Science Data Sharing Platform” (DKA2018-12-02-XX); Supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Grant No. XDA19060205; the Special Project of Informatization of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XXH13505-03-205); the Special Project of Informatization of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XXH13506-305); the Special Project of Informatization of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XXH13506-303); Supported by Around Five Top Priorities of “One-Three-Five” Strategic Planning, CNIC(Grant No. CNIC_PY-1408); Supported by Around Five Top Priorities of “One-Three-Five” Strategic Planning, CNIC(Grant No. CNIC_PY-1409) The authors wish to gratefully thank all anoymous reriewers who provided insightful and helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Li, Y., Zhao, Z. et al. A mixed noise removal algorithm based on multi-fidelity modeling with nonsmooth and nonconvex regularization. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 23117–23140 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7625-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7625-1