Abstract
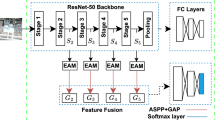
Learning high-level semantic information is important for the task of remote sensing(RS) image scene classification. Due to the great intraclass diversities and the interclass similarities, many researchers have explored the convolutional neural network(CNN) to handle this task recently. However, RS images usually have confusing backgrounds, such as the relevant objects, and features only derived from the whole RS images can not achieve satisfying results. Additionally, the great intraclass diversities also increase the difficulty of recognizing the RS images correctly. To solve the problem, the multi-view feature learning network(MVFLN) is proposed to obtain three domain-specific features for the scene categorization task. FC layers in the VGGNet are replaced by the channel-spatial branch and the other multiple metric branchs. The channel-spatial branch is utilized to localize and learn discriminative regions while the triplet metric branch and the center metric branch are used to enlarge the distance between different classes and reduce the distance of samples belonging to the same class, respectively. In this situation, the proposed MVFLN conducts in a concise way without extra SVM classifiers, achieving better performance. Experiments conducted on the AID, NWPU-RESISC45 and UC Merced datasets evaluate its effectiveness.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaib S, Liu H, Gu Y, Yao H (2017) Deep feature fusion for vhr remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(8):4775–4784
Chen C, Zhang B, Su H, Li W, Wang L (2016) Land-use scene classification using multi-scale completed local binary patterns. Signal Image Video Process 10 (4):745–752
Cheng G, Han J, Guo L, Liu T (2015) Learning coarse-to-fine sparselets for efficient object detection and scene classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1173–1181
Cheng G, Han J, Guo L, Liu Z, Bu S, Ren J (2015) Effective and efficient midlevel visual elements-oriented land-use classification using vhr remote sensing images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(8):4238–4249
Cheng G, Han J, Zhou P, Guo L (2014) Multi-class geospatial object detection and geographic image classification based on collection of part detectors. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 98:119–132
Cheng G, Li Z, Yao X, Guo L, Wei Z (2017) Remote sensing image scene classification using bag of convolutional features. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 14(10):1735–1739
Cheng G, Yang C, Yao X, Guo L, Han J (2018) When deep learning meets metric learning: remote sensing image scene classification via learning discriminative cnns. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(5):2811–2821
Cheng G, Zhou P, Han J (2016) Learning rotation-invariant convolutional neural networks for object detection in vhr optical remote sensing images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(12):7405–7415
Cheng G, Zhou P, Han J, Guo L, Han J (2015) Auto-encoder-based shared mid-level visual dictionary learning for scene classification using very high resolution remote sensing images. IET Comput Vis 9(5):639–647
Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J (2016) Region-based convolutional networks for accurate object detection and segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(1):142–158
Guo Y, Ji J, Lu X, Huo H, Fang T, Li D (2019) Global-local attention network for aerial scene classification. IEEE Access
He N, Fang L, Li S, Plaza A, Plaza J (2018) Remote sensing scene classification using multilayer stacked covariance pooling. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(12):6899–6910
Hu F, Xia GS, Hu J, Zhang L (2015) Transferring deep convolutional neural networks for the scene classification of high-resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens 7(11):14680–14707
Huang L, Chen C, Li W, Du Q (2016) Remote sensing image scene classification using multi-scale completed local binary patterns and fisher vectors. Remote Sens 8(6):483
Ji J, Jiang L, Lei C, Zhong W, Xiong H (2018) Learning two-level features for fine-grained image classification. In: 2018 14th IEEE international conference on signal processing (ICSP). IEEE, pp 544–549
Jia Y, Huang C, Darrell T (2012) Beyond spatial pyramids: receptive field learning for pooled image features. In: CVPR. IEEE, pp 3370–3377
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1097–1105
Li E, Xia J, Du P, Lin C, Samat A (2017) Integrating multilayer features of convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(10):5653–5665
Lin M, Chen Q, Yan S (2013) Network in network. arXiv:1312.4400
Liu Y, Liu Y, Ding L (2018) Scene classification based on two-stage deep feature fusion. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 15(2):183–186
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Lu X, Guo Y, Liu N, Wan L, Fang T (2018) Non-convex joint bilateral guided depth upsampling. Multimed Tools Appl 77(12):15521–15544
Lu X, Li X, Mou L (2014) Semi-supervised multitask learning for scene recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 45(9):1967–1976
Lu X, Ma C, Ni B, Yang X (2019) Adaptive region proposal with channel regularization for robust object tracking. IEEE Trans Circ Sys Video Technol 10(19):1–15
Lu X, Ma C, Ni B, Yang X, Reid I, Yang MH (2018) Deep regression tracking with shrinkage loss. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 353–369
Lu X, Ni B, Ma C, Yang X (2019) Learning transform-aware attentive network for object tracking. Neurocomputing 349:133–144
Lu X, Wang W, Ma C, Shen J, Shao L, Porikli F (2019) See more, know more: unsupervised video object segmentation with co-attention siamese networks. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Lu X, Wang W, Ma C, Shen J, Shao L, Porikli F (2019) See more, know more: unsupervised video object segmentation with co-attention siamese networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3623–3632
Luus FP, Salmon BP, Van den Bergh F, Maharaj BTJ (2015) Multiview deep learning for land-use classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 12(12):2448–2452
Nogueira K, Penatti OA, dos Santos JA (2017) Towards better exploiting convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification. Pattern Recogn 61:539–556
Othman E, Bazi Y, Melgani F, Alhichri H, Alajlan N, Zuair M (2017) Domain adaptation network for cross-scene classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(8):4441–4456
Penatti OA, Nogueira K, dos Santos JA (2015) Do deep features generalize from everyday objects to remote sensing and aerial scenes domains?. In: CVPR workshops, pp 44–51
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. Int Conf Learn Represent
Wang G, Fan B, Xiang S, Pan C (2017) Aggregating rich hierarchical features for scene classification in remote sensing imagery. IEEE J Select Topics Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 10(9):4104–4115
Wang Q, Liu S, Chanussot J, Li X (2018) Scene classification with recurrent attention of vhr remote sensing images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens (99):1–13
Wang W, Lu X, Shen J, Crandall DJ, Shao L (2019) Zero-shot video object segmentation via attentive graph neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 9236–9245
Wen Y, Zhang K, Li Z, Qiao Y (2016) A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 499–515
Woo S, Park J, Lee JY, So Kweon I (2018) Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 3–19
Xia GS, Hu J, Hu F, Shi B, Bai X, Zhong Y, Zhang L, Lu X (2017) Aid: a benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(7):3965–3981
Yang Y, Newsam S (2010) Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification. In: Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL international conference on advances in geographic information systems. ACM, pp 270–279
Yao X, Han J, Cheng G, Qian X, Guo L (2016) Semantic annotation of high-resolution satellite images via weakly supervised learning. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(6):3660–3671
Zhang F, Du B, Zhang L (2015) Scene classification via a gradient boosting random convolutional network framework. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(3):1793–1802
Zhao B, Wu X, Feng J, Peng Q, Yan S (2017) Diversified visual attention networks for fine-grained object classification. IEEE Trans Multimed 19(6):1245–1256
Zhao B, Zhong Y, Xia GS, Zhang L (2016) Dirichlet-derived multiple topic scene classification model for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(4):2108–2123
Zhao W, Du S (2016) Scene classification using multi-scale deeply described visual words. Int J Remote Sens 37(17):4119–4131
Zou J, Li W, Chen C, Du Q (2016) Scene classification using local and global features with collaborative representation fusion. Inf Sci 348:209–226
Acknowledgements
This paper was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under grant 2018YFB0505400, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grants 41822106, the Dawn Scholar of Shanghai Program under grant 18SG22, the State Key Laboratory of Disaster Reduction in Civil Engineering under grant SLDRCE19-B-35, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Ji, J., Shi, D. et al. Multi-view feature learning for VHR remote sensing image classification. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 23009–23021 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08713-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08713-z