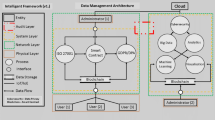
Abstract
Chaotic image encryption has been greatly investigated in recent years. However, a considerable number of the encryption schemes had been cracked by chosen plaintext attack (CPA). Although the new proposed plaintext-related chaotic image encryption schemes can resist CPA effectively, the emerged key management problem is a hot potato. In this paper, a novel fingerprint-related chaotic image encryption scheme is proposed. The generation of key streams is affected by the fingerprints of distributors rather than the plaintexts of images. In addition, the blockchain framework is adopted to ensure that the encrypted image was sent correctly form the distributor. Moreover, the distributors’ fingerprints embedded in the encrypted images are encoded by the anti-collusion code in order to record multiple fingerprints with fixed length of data. The proposed method has the following superiorities: 1) Security. CPA is invalid because the attacker does not have the fingerprint of the legal receiver. Meanwhile, no key management problem is caused. 2) Authenticity. The image, the sender and the receiver are all verified by using blockchain framework. 3) Traceability. All distributors’ fingerprints can be extracted correctly from the merged fingerprint based on the anti-collusion code, and the transmission of the image can be traced.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alawida M, Teh JS, Samsudin A, Alshoura WH (2019) An image encryption scheme based on hybridizing digital chaos and finite state machine. Signal Process 164:249–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.06.013
Anwar S, Meghana S (2019) A pixel permutation based image encryption technique using chaotic map. Multimed Tools Appl 78(19):27569–27590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-07852-2
Batool SI, Waseem HM (2019) A novel image encryption scheme based on Arnold scrambling and Lucas series. Multimed Tools Appl 78(19):27611–27637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-07881-x
Belazi A, Abd El-Latif AA, Belghith S (2016) A novel image encryption scheme based on substitution-permutation network and chaos. Signal Process 128:155–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.03.021
Blake-Wilson S (2000) Information security, mathematics, and public-key cryptography. Design Code Cryptogr 19(2-3):77–99. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008345904539
Borujeni SE, Eshghi M, Boroujeni MS (2012) Mehrab maps: one-dimensional piecewise nonlinear chaotic maps. Int J Bifurcat Chaos 22(5):Artn 1250127. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127412501271
Chai XL, Fu XL, Gan ZH, Lu Y, Chen YR (2019) A color image cryptosystem based on dynamic DNA encryption and chaos. Signal Process 155:44–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.09.029
Chai XL, Gan ZH, Yuan K, Chen YR, Liu XX (2019) A novel image encryption scheme based on DNA sequence operations and chaotic systems. Neural Comput Appl 31(1):219–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-2993-9
Chen L, Chen JX, Zhao G, Wang SH (2019) Cryptanalysis and improvement of a chaos-based watermarking scheme. IEEE Access 7:97549–97565. https://doi.org/10.1109/Access.2019.2926831
Chen YC, Hung TH, Hsieh SH, Shiu CW (2019) A new reversible data hiding in encrypted image based on multi-secret sharing and lightweight cryptographic algorithms. IEEE T Inf Foren Sec 14(12):3332–3343. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tifs.2019.2914557
Cheng MQ, Miao Y (2011) On anti-collusion codes and detection algorithms for multimedia fingerprinting. IEEE T Inform Theory 57(7):4843–4851. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tit.2011.2146130
Chuman T, Sirichotedumrong W, Kiya H (2019) Encryption-then-compression systems using Grayscale-based image encryption for JPEG images. IEEE T Inf Foren Sec 14(6):1515–1525. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tifs.2018.2881677
Conti M, Kumar ES, Lal C, Ruj S (2018) A survey on security and privacy issues of Bitcoin. IEEE Commun Surv Tut 20(4):3416–3452. https://doi.org/10.1109/Comst.2018.2842460
Fridrich J (1997) Image encryption based on chaotic maps. IEEE Sys Man Cybern:1105–1110
Gao ED, Pan ZB, Gao XY (2019) Reversible data hiding based on novel pairwise PVO and annular merging strategy. Inf Sci 505:549–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.07.101
Gul E, Ozturk S (2019) A novel hash function based fragile watermarking method for image integrity. Multimed Tools Appl 78(13):17701–17718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-7084-0
He XY, Zhang W, Zhang HF, Ma L, Li YB (2019) Reversible data hiding for high dynamic range images using edge information. Multimed Tools Appl 78(20):29137–29160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6589-x
Hoffmann L, Diffie W, Hellman M (2016) Finding new directions in cryptography. Commun ACM 59(6):112–111. https://doi.org/10.1145/2911977
Hua ZY, Zhou BH, Zhou YC (2019) Sine Chaotification model for enhancing Chaos and its hardware implementation. IEEE T Ind Electron 66(2):1273–1284. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tie.2018.2833049
Hussain I, Shah T, Gondal MA, Mahmood H (2013) An efficient approach for the construction of LFT S-boxes using chaotic logistic map. Nonlinear Dynam 71(1–2):133–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0646-1
Kang XJ, Tao R (2019) Color image encryption using pixel scrambling operator and reality-preserving MPFRHT. IEEE T Circ Syst Vid 29(7):1919–1932. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tcsvt.2018.2859253
Khalilov MCK, Levi A (2018) A survey on anonymity and privacy in Bitcoin-like digital cash systems. IEEE Commun Surv Tut 20(3):2543–2585. https://doi.org/10.1109/Comst.2018.2818623
Kim Y (2016) Secure code design against collusion attacks for protecting digital content rights. Multimed Tools Appl 75(22):14143–14159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3242-4
Lan RS, He JW, Wang SH, Gu TL, Luo XN (2018) Integrated chaotic systems for image encryption. Signal Process 147:133–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.01.026
Li M, Xiao D, Zhang YS, Nan H (2015) Reversible data hiding in encrypted images using cross division and additive homomorphism. Signal Process-Image 39:234–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2015.10.001
Li Z, Peng CG, Li LR, Zhu XY (2018) A novel plaintext-related image encryption scheme using hyper-chaotic system. Nonlinear Dynam 94(2):1319–1333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4426-4
Li M, Lu DD, Xiang Y, Zhang YS, Ren H (2019) Cryptanalysis and improvement in a chaotic image cipher using two-round permutation and diffusion. Nonlinear Dynam 96(1):31–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04771-7
Ma KD, Zhang WM, Zhao XF, Yu NH, Li FH (2013) Reversible data hiding in encrypted images by reserving room before encryption. IEEE T Inf Foren Sec 8(3):553–562. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tifs.2013.2248725
Natgunanathan I, Xiang Y, Hua G, Beliakov G, Yearwood J (2017) Patchwork-based multilayer audio watermarking. IEEE-Acm T Audio Spe 25(11):2176–2187. https://doi.org/10.1109/Taslp.2017.2749001
Nuida K, Fujitsu S, Hagiwara M, Kitagawa T, Watanabe H, Ogawa K, Imai H (2009) An improvement of discrete Tardos fingerprinting codes. Des Codes Cryptogr 52(3):339–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10623-009-9285-z
Salman T, Zolanvari M, Erbad A, Jain R, Samaka M (2019) Security services using Blockchains: a state of the art survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tut 21(1):858–880. https://doi.org/10.1109/Comst.2018.2863956
Solak E, Cokal C, Yildiz OT, Biyikoglu T (2010) Cryptanalysis of Fridrich's chaotic image encryption. Int J Bifurcat Chaos 20(5):1405–1413. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127410026563
Tardos G (2008) Optimal probabilistic fingerprint codes. J Acm 55(2):Artn 10. https://doi.org/10.1145/1346330.1346335
Wang ZJ, Wu M, Zhao HV, Trappe W, Liu KJR (2005) Anti-collusion forensics of multimedia fingerprinting using orthogonal modulation. IEEE T Image Process 14(6):804–821. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tip.2005.847284
Wang XY, Yang L, Liu R, Kadir A (2010) A chaotic image encryption algorithm based on perceptron model. Nonlinear Dynam 62(3):615–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-010-9749-8
Wang JX, Ni JQ, Zhang X, Shi YQ (2017) Rate and distortion optimization for reversible data hiding using multiple histogram shifting. IEEE T Cybernetics 47(2):315–326. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tcyb.2015.2514110
Wang D, Cheng HB, He DB, Wang P (2018) On the challenges in designing identity-based privacy-preserving authentication schemes for mobile devices. IEEE Syst J 12(1):916–925. https://doi.org/10.1109/Jsyst.2016.2585681
Wen WY (2016) Security analysis of a color image encryption scheme based on skew tent map and hyper chaotic system of 6th-order CNN against chosen-plaintext attack. Multimed Tools Appl 75(6):3553–3560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2464-1
Xie EY, Li CQ, Yu SM, Lu JH (2017) On the cryptanalysis of Fridrich’s chaotic image encryption scheme. Signal Process 132:150–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.10.002
Zhang Y, Li CQ, Li Q, Zhang D, Shu S (2012) Breaking a chaotic image encryption algorithm based on perceptron model. Nonlinear Dynam 69(3):1091–1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0329-y
Zhang YS, Xiao D, Wen WY, Li M (2014) Cryptanalyzing a novel image cipher based on mixed transformed logistic maps. Multimed Tools Appl 73(3):1885–1896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1684-5
Zhang LY, Liu YS, Pareschi F, Zhang YS, Wong KW, Rovatti R, Setti G (2018) On the security of a class of diffusion mechanisms for image encryption. IEEE T Cybernetics 48(4):1163–1175. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tcyb.2017.2682561
Zhang YS, Xiang Y, Zhang LY, Rong Y, Guo S (2019) Secure wireless communications based on compressive sensing: a survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tut 21(2):1093–1111. https://doi.org/10.1109/Comst.2018.2878943
Zhen P, Zhao G, Min LQ, Li XD (2014) A survey of chaos-based cryptography. 2014 ninth international conference on P2p, parallel, grid, cloud and internet computing (3pgcic):237-244. https://doi.org/10.1109/3pgcic.2014.69
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Educational Science Research Foundation of Henan Normal University (2018JK20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R. Fingerprint-related chaotic image encryption scheme based on blockchain framework. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 30583–30603 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08802-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08802-z