Abstract
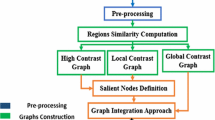
Salient object detection is getting more and more attention in computer vision field. In this paper, we propose a novel and effective framework for salient object detection. Firstly, we develop a robust background-based map by using spatial prior to remove the foreground noises of image boundary regions. The proposed background-based map and Objectness map are integrated to obtain a coarse saliency map. Then, an effective saliency propagation mechanism is utilized to further highlight salient object and suppress background region by defining a novel graph model, each node connects to its more similar neighbors and nodes with low saliency values in the proposed graph. As a result, the coarse saliency map is optimized to the refined saliency map by novel graph based saliency propagation. Finally, we construct a novel integration framework to further integrate two saliency maps for performance improvement. Experiments on three benchmark datasets are tested, experimental results show the superiority of the proposed algorithm than other state-of-the-art methods.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F, Susstrunk S (2009) Frequency-tuned salient region detection, CVPR 1597–1604
Achanta R, Shaji A, Smith K, Lucchi A, Fua P, Susstrunk S. Slic superpixels, Ecole Polytechnique Federal de Lausssanne, Technical Report
Alexe B, Deselaers T, Ferrari V (2012) Measuring the objectness of image windows, IEEE trans. Patt Anal Mach Intell 34(11):2189–2202
Chen S, Zheng L, Lu X, Zhou P (2016) Discriminative saliency propagation with sink points. Pattern Recogn 60:2–12
Chen X, He F, Yu P (2019) A matting method based on full feature coverage. Multimed Tools Appl 78(9):11173–11201
Fang S, Li J, Tian Y, Huang T, Chen X (2016) Learning discriminative subspaces on random contrasts for image saliency analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 1095–1108
Gong C, Tao D, Liu W, Maybank SJ, Fang M, Fu K, Yang J (2015) Saliency propagation from simple to difficult, CVPR
Huang F, Qi J, Lu H, Zhang L, Ruan X (2017) Salient object detection via multiple instance learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(4):1911–1922
Huo L, Jiao L, Wang S, Yang S (2016) Object-level saliency detection with color attributes. Pattern Recogn 49:162–173
Itti L (2004) Automatic foveation for video compression using a neurobiological model of visual attention. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(10):1304–1318
Jiang B, Zhang L, Lu H, Yang C, Yang M (2013) Saliency detection via absorbing markov chain, CVPR, 1665–1672
Lee G, Tai YW, Kim J (2016) Deep saliency with encoded low level distance map and high level features, CVPR 660–668
Li G, Yu Y (2016) Visual saliency detection based on multi-scale deep CNN features. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(11):5012–5024
Li Y, Hou X, Koch C, Rehg JM, Yuille AL (2014) The secrets of salient object segmentation. CVPR 280–287
Li H, Lu H, Lin Z, Shen X, Price B (2015) Inner and inter label propagation: salient object detection in the wild. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(10):3176–3186
Liu G, Yang J (2019) Exploiting color volume and color difference for salient region detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(1):6–16
Mahadevan V, Vasconcelos N (2009) Saliency-based discriminated tracking, CVPR 1007–1013
Movahedi V, Elder JH (2010) Design and perceptual validation of performance measures for salient object segmentation, POCV 49–56
Pang Y, Yu X, Wang Y, Wu C (2019) Salient object detection based on novel graph model. J Vis Commun Image Rrepresent 65:102676
Pang Y, Yu X, Wu Y, Wu C (2020) FSP: a feedback-based saliency propagation method for saliency detection. J Electron Imaging 29(1):013011
Qin Y, Lu H, Xu Y, Wang H (2015) Saliency detection via cellular automata, CVPR 110–119
Rutishauser U, Walther D, Koch C, Perona P (2004) Is bottom-up attention useful for object recognition? CVPR 37–44
Sun J, Lu H, Liu X (2015) Saliency region detection based on Markov absorption probabilities. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(5):1639–1649
Tong N, Lu H, Ruan X, Yang M (2015) Salient object detection via bootstrap learning, CVPR 1884–1892
Tong N, Lu H, Zhang Y, Ruan X (2015) Salient object detection via global and local cues. Pattern Recogn 48:3258–3267
Tu WC, He S, Yang Q, Chien SY (2016) Real-time salient object detection with a minimum spanning tree, CVPR 2334–2342
Von Neumann J. The general and logical theory of automata, Cerebral mechanisms in behavior 1–41
Wang J, Lu H, Li X, Tong N, Liu W (2015) Salliency detection via background and foreground seed selection. Neurocomputing 152:359–368
Wang L, Lu H, Xiang R, Yang M (2015) Deep networks for saliency detection via local estimation and global search, CVPR 3183–3192
Wei Y, Wen F, Zhu W, Sun J (2012) Geodesic saliency using background priors, ECCV 29–42
Xu L, Lu C, Xu Y, Jia J (2011) Image smoothing via L0 gradient minimization. ACM Trans Graph 30(6):174
Yan Q, Xu L, Shi J, Jia J (2013) Hierarchical saliency detection, CVPR 1155–1162
Yang J, Yang M (2012) Top-down visual saliency via joint CRF and dictionary learning, CVPR 2296–2303
Yang C, Zhang L, Lu H, Ruan X, Yang M (2013) Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking, CVPR 3166–3173
Yu H, He F, Pan Y (2019) A Novel Segmentation Model for Medical Images with Intensity Inhomogeneity Based on Adaptive Perturbation. Multimed Tools Appl 78(9):11779–11798
Zhang M, Pang Y, Wu Y, Du Y, Sun H, Zhang K (2018) Saliency detection via local structure propagation. J Vis Commun Image Rrepresent 52:131–142
Zhang M, Wu Y, Du Y, Fang L, Pang Y (2018) Saliency detection integrating global and local information. J Vis Commun Image Rrepresent 53:215–223
Zhang S, He F, Ren W (2020) Joint learning of image detail and transmission map for single image dehazing. Vis Comput 36(3):305–316
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant nos. 61701101, 61973093, U1713216, 61901098, 61971118, and the Fundamental Research Fund for the Central Universities of China N2026005, N181602014, N2026004, N2026006 and N2026001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, Y., Wu, Y., Wu, C. et al. Salient object detection via effective background prior and novel graph. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 25679–25695 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09226-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09226-5