Abstract
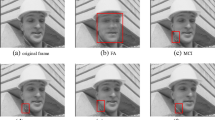
Motion Compensated Frame Interpolation (MCFI), a frame-based video operation to increase the motion continuity of low frame rate video, can be adopted by falsifiers for forging high bitrate video or splicing videos with different frame-rates. For existing MCFI detectors, their performance are degraded by stronger video compression, and noise. To deal with this problem, we propose a blind forensics method to detect the adopted MCFI operation. After investigating the synthetic process of interpolated frames, we discover that motion regions of interpolated frames exist some local slight artifacts, causing the optical flow based inter-frame discontinuity. To capture this irregularities introduced by various MCFI techniques, compact features are designed, which are calculated as Temporal Frame Difference-weighted histogram of Local Binary Pattern computed on Optical Flow field (TFD-OFLBP). Meanwhile, Local Inter-block and Edge-block difference Features (LIEF) are further proposed to detect interpolation frames with stable content. Besides, a set of forensics tools are adopted to eliminate the side effects of possible interferences of the scenes change, sudden lighting change, focus vibration, and some original frames with inherent local artifacts. Experimental results on four representative MCFI software and techniques show that the proposed approach outperforms existing MCFI detectors and also with robustness to compression, and noise.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adato Y., Zickler T., Ben-Shahar O. (2011) A polar representation of motion and implications for optical flow. In: Proceeding IEEE conference computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1145–1152
Bestagini P., Battaglia S., Milani S., Tagliasacchi M., Tubaro S. (2013) Detection of temporal interpolation in video sequences. In: Proceeding International Conference Acoustics, Speech Signal Process.(ICASSP),May, pp 3033–3037
Bian S., Luo W., Huang J. (2014) Detecting video frame-rate up conversion based on periodic properties of inter-frame similarity. Multimed. Tools Appl. 72 (1):437–451
Black M.J., Anandan P (1993) A framework for the robust estimation of optical flow. In: Proceeding fourth international conference computer vision (ICCV), pp 231–236
Chao J., Jiang X., Sun T. (2012) A novel video inter-frame forgery model detection scheme based on optical flow consistency. In: International workshop on digital watermarking, (IWDW), October, pp 267–281
Chaudhry R., Ravichandran A., Hager G., Vidal R. (2009) Histograms of oriented optical flow and binet-cauchy kernels on nonlinear dynamical systems for the recognition of human actions. In: Proceeding IEEE conference computer vision pattern recognition (CVPR), June, pp 1932–1939
Choi B.D., Han J.W., Kim C.S., Ko S.J. (2007) Motion-compensated frame interpolation using bilateral motion estimation and adaptive overlapped block motion compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 17(4):407–416
Dar Y., Bruckstein A.M. (2015) Motion-compensated coding and frame rate up-conversion: models and analysis. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24 (7):2051–2066
Dietterich T.G., Bakiri G. (1995) Solving multiclass learning problems via error correcting output codes. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2:263–286
Ding X., Gaobo Y., Li R., Zhang L., Li Y., Sun X. (2018) Identification of motion-compensated frame rate up-conversion based on residual signal. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 28(7):1497–1512
Ding X., Li Y., Xia M., He J., Gaobo Y. (2019) Detection of motion compensated frame interpolation via motion-aligned temporal difference. Multimed. Tools Appl. 78(6):7453–7477
Ding X., Zhu N., Li L., Li Y., Gaobo Y. (2019) Robust localization of interpolated frames by motion-compensated frame-interpolation based on artifact indicated map and tchebichef moments. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 29(7):1893–1906
Feng C., Xu Z., Jia S., Zhang W., Xu Y. (2017) Motion-adaptive frame deletion detection for digital video forensics. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 27(12):2543–2554
Fridrich J., Soukal D., Lukas J. (2003) Detection of copy-move forgery in digital images. In: Proceeding digital forens research workshop
H.264/AVC software[Online]. Available: http://iphome.hhi.de/suehring/tml/
H.265/HEVC software[Online]. Available: : https://hevc.hhi.fraunhofer.de/
Hastie T., Tibshirani R. (1998) Classification by pairwise coupling. Ann. Statist. 26(2):451–C471
Hsu C.C., Hung T.Y., Lin C.W., Hsu C.T (2008) Video forgery detection using correlation of noise residue. In: Proceeding IEEE International Workshop Multimedia Signal Process (MMSP), Oct. pp 170–174
Jia S., Feng C., Xu Z., Xu Y., Wang T. (2014) ACE algorithm in the application of video forensics. In: Proceeding international conference multimedia, communication computing application (MCCA), pp 177–184
Jia S., Xu Z., Wang H., Feng C., Wang T. (2018) Coarse-to-fine copy-move forgery detection for video forensics. IEEE Access 6:25323–25335
Jung D.J., Lee H.K. (2017) Frame-rate conversion detection based on periodicity of motion artifact. Multimed. Tools Appl., pp 1–22
Kodovsky J., Fridrich J., Holub V. (2012) Ensemble classifiers for steganalysis of digital media. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 7(2):432–444
Li R., Gan Z., Cui Z., Tang G., Zhu X. (2014) Multi-channel mixed-pattern based frame rate up-conversion using spatio-temporal motion vector refinement and dual weighted overlapped block motion compensation. J. Disp. Technol. 10 (12):1010–1023
Li Q., Lin W., Fang Y. (2016) No-reference quality assessment for multiply-distorted images in gradient domain. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(4):541–545
Li R., Liu Z., Zhang Y., Li Y., Fu Z. (2016) Noise-level estimation based detection of motion-compensated frame interpolation in video sequences. Multimed. Tools Appl., pp 1–26
Li Y., mei L., Li R., Wu C. (2018) Using noise level to detect frame repetition forgery in video frame rate up-conversion. Future Internet 10 (9):84(1–11)
Mahdian B., Saic S. (2008) Blind authentication using periodic properties of interpolation. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 3(3):529–538
Milani S., Fontani M., Bestagini P., Barni M., Piva A., Tagliasacchi M., Tubaro S. (2012) An overview on video forensics. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 1:1–18
Ojala T., Pietikainen M., Maenpaa T. (2002) Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(7):971–987
Portz T., Zhang L., Jiang H. (2012) Optical flow in the presence of spatially-varying motion blur. In: Proceeding IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR),June, pp 1752–1759
Rijsbergen C.J.V. (1979) Information Retrieval. Newton, MA, USA: Butterworth-Heinemann
Singh R.D., Aggarwal N. (2017) Optical flow and prediction residual based hybrid forensic system for inter-frame tampering detection. J. Circuit Syst. Comp. 26(7):1750107(1–37)
Stamm M.C., Lin W., Liu K.J. (2012) Temporal forensics and anti-forensics for motion compensated video. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Security. 7 (4):1315–1329
Stamm M.C., Wu M., Liu K.J.R. (2013) Information forensics: an overview of the first decade. IEEE Access. 1:167–200
Su L., Li C., Lai Y., Yang J. (2018) A fast forgery detection algorithm based on exponential-fourier moments for video region duplication. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 20(4):825–840
Sun D., Roth S., Black M.J. (2014) A quantitative analysis of current practices in optical flow estimation and the principles behind them. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 106(2):115–137
The online video databases[Online]. Available: http://media.xiph.org/video/derf/%23
The MCFI softwares[Online]. Available: http://www.wondershare.com/multimedia-tips/slow-motion-software.html
Wang W., Farid H (2007) Exposing digital forgeries in interlaced and deinterlaced video. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2(3):438–449
Wang W., Jiang X., Wang S., Wan M., Sun T. (2013) Identifying video forgery process using optical flow. In: International workshop on digital watermarking (IWDW), October, pp 244–257
Wu Y., Jiang X., Sun T., Wang W. (2014) Exposing video inter-frame forgery based on velocity field consistency. In: Proceeding international conference acoustics speech signal process. (ICASSP), May, pp 2674–2678
Xia M., Yang G., Li L., Li R., Sun X. (2017) Detecting video frame rate up-conversion based on frame-level analysis of average texture variation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 76(6):8399–8421
Yao H., Ni R., Zhao Y. (2019) An approach to detect video frame deletion under anti-forensics. J. Real-Time Image Proc. 1–14
Yao Y., Yang G., Sun X., Li L. (2016) Detecting video frame-rate up-conversion based on periodic properties of edge-intensity. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 26:39–50
Yoo D.G., Kang S.J., Kim Y.H. (2013) Direction-select motion estimation for motion-compensated frame rate up-conversion. J. Display Technol. 9 (10):840–850
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Doctoral research foundation of Hunan University of Science and Technology under E51974, the Scientific Research Foundation of Hunan Provincial Education Department of China under 19B199, and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China under Grant 2020JJ4029.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, X., Huang, Y., Li, Y. et al. Forgery detection of motion compensation interpolated frames based on discontinuity of optical flow. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 28729–28754 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09340-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09340-4