Abstract
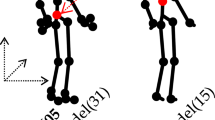
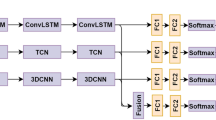
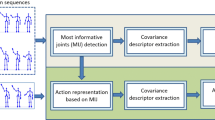
The 3D human body skeleton conveys rich information of human action and is regarded as an important data modality for action recognition. Due to the diversity of human action and the noise in skeleton data, skeleton-based action recognition methods face the challenges of overcoming the interference of irrelevant data and learning enough valid information of human action. Previous research has led us to a variety of effective skeleton features and many deep network models with strong learning abilities. However, a single model using a single feature cannot make full use of the valid information in the skeleton. To address this problem, this paper proposes the multi-level kinematic constraints to construct multiple skeleton features. By using different levels of constraints, a set of features containing information from local to global are extracted. The variability among these features leads to significant variability in classifiers trained on them, thus enhancing the ensemble performance of these classifiers. Extensive experiments on three representative datasets and four kinds of classification models demonstrate the generality of the proposed method. A substantial improvement can be achieved on multiple kinds of existing well-performing models and our method surpasses most state-of-the-art skeleton-based action recognition methods.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Notes
FLoating-number OPerations
References
Aggarwal JK, Xia L (2014) Human activity recognition from 3D data: a review. Pattern Recognit Lett 48:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/JPATREC201404011
Avola D, Cascio M, Cinque L, Foresti GL, Massaroni C, Rodola E (2020) 2-D skeleton-based action recognition via two-branch stacked LSTM-RNNs. IEEE Trans Multimed 22(10):2481–2496. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM20192960588
Bian C, Feng W, Wan L, Wang S (2021) Structural knowledge distillation for efficient skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:2963–2976. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3056895
Chen Y, Wang L, Li C, Hou Y, Li W (2020) ConvNets-based action recognition from skeleton motion maps. Multimed Tools Appl 79 (3–4):1707–1725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08261-1
Cheng K, Zhang Y, He X, Chen W, Cheng J, Lu H (2020) Skeleton-based action recognition with shift graph convolutional network. In: Proc conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 183–192. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600202000026
Ding W, Liu K, Belyaev E, Cheng F (2018) Tensor-based linear dynamical systems for action recognition from 3D skeletons. Pattern Recognit 77:75–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/JPATCOG201712004
Du Y, Fu Y, Wang L (2015) Skeleton based action recognition with convolutional neural network. In: 3rd IAPR Asian conference on pattern recognition, pp 579–583
Du Y, Wang W, Wang L (2015) Hierarchical recurrent neural network for skeleton based action recognition. In: Proc conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 1110–1118. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR20157298714
Evangelidis G, Singh G, Horaud R (2014) Skeletal quads: human action recognition using joint quadruples. In: 22nd International conference on pattern recognition, pp 4513–4518. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR2014772
Fan Z, Zhao X, Lin T, Su H (2019) Attention-based multiview re-observation fusion network for skeletal action recognition. IEEE Trans Multimed 21 (2):363–374. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM20182859620
Fernando B, Gavves E, Oramas JM, Ghodrati A, Tuytelaars T (2017) Rank pooling for action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(4):773–787. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI20162558148
Han J, Shao L, Xu D, Shotton J (2013) Enhanced computer vision with microsoft kinect sensor: a review. IEEE Trans Cybern 43(5, SI):1318–1334. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB20132265378
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In: Proc Int Conf Comput Vision, pp. 1026–1034. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV2015123
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proc Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit, pp. 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Hu G, Cui B, Yu S (2020) Joint learning in the spatio-temporal and frequency domains for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans Multimed 22 (9):2207–2220. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM20192953325
Hu J, Zheng W, Lai J, Zhang J (2017) Jointly learning heterogeneous features for RGB-D activity recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(11):2186–2200. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI20162640292
Ji X, Cheng J, Feng W, Tao D (2018) Skeleton embedded motion body partition for human action recognition using depth sequences. Singal Processing 143:56–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/JSIGPRO201708016
Johansson G (1973) Visual-perception of biological motion and a model for its analysis. Percep Psychophys 14(2):201–211. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03212378
Ke Q, An S, Bennamoun M, Sohel F, Boussaid F (2017) SkeletonNet: mining deep part features for 3-D action recognition. IEEE Signal Process Lett 24(6):731–735. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP20172690339
Ke Q, Bennamoun M, An S, Sohel F, Boussaid F (2017) A new representation of skeleton sequences for 3D action recognition. In: Proc conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 4570–4579. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR2017486
Ke Q, Bennamoun M, An S, Sohel F, Boussaid F (2018) Learning clip representations for skeleton-based 3D action recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(6):2842–2855. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP20182812099
Keselman L, Woodfill JI, Grunnet-Jepsen A, Bhowmik A (2017) Intel (R) realsense (TM) stereoscopic depth cameras. In: Proc conf comput vision pattern recognit workshops, pp 1267–1276. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW2017167
Kim TS, Reiter A (2017) Interpretable 3D human action analysis with temporal convolutional networks. In: Proc conf comput vision pattern recognit workshops, pp 1623–1631. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW2017207
Lea C, Flynn MD, Vidal R, Reiter A, Hager GD (2017) Temporal convolutional networks for action segmentation and detection. In: Proc conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 1003–1012. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR2017113
Lee I, Kim D, Kang S, Lee S (2017) Ensemble deep learning for skeleton-based action recognition using temporal sliding LSTM networks. In: Proc Int Conf Comput Vision, pp 1012–1020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV2017115
Li M, Chen S, Chen X, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Tian Q (2019) Actional-structural graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proc conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 3590–3598. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR201900371
Li Y, Xia R, Liu X (2020) Learning shape and motion representations for view invariant skeleton-based action recognition. Pattern Recognit, 103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107293
Liu J, Shahroudy A, Perez M, Wang G, Duan L, Kot AC (2020) NTU RGB+D 120: a large-scale benchmark for 3D human activity understanding. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(10):2684–2701. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI20192916873
Liu J, Shahroudy A, Wang G, Duan L, Kot AC (2020) Skeleton-based online action prediction using scale selection network. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(6):1453–1467. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI20192898954
Liu J, Shahroudy A, Xu D, Wang G (2016) Spatio-temporal LSTM with trust gates for 3D human action recognition. In: Proc Euro conf comput vision, pp 816–833. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46487-9_50
Liu J, Wang G, Duan L, Abdiyeva K, Kot AC (2018) Skeleton-based human action recognition with global context-aware attention LSTM networks. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(4):1586–1599. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP20172785279
Liu M, Liu H, Chen C (2017) Enhanced skeleton visualization for view invariant human action recognition. Pattern Recognit 68:346–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/JPATCOG201702030
Liu M, Yuan J (2018) Recognizing human actions as the evolution of pose estimation maps. In: Proc conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 1159–1168. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR201800127
Liu Z, Zhang H, Chen Z, Wang Z, Ouyang W (2020) Disentangling and unifying graph convolutions for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proc Conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 143–152. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600202000022
Nie Q, Wang J, Wang X, Liu Y (2019) View-invariant human action recognition based on a 3D bio-constrained skeleton model. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(8):3959–3972. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP20192907048
Pakrashi A, Mac Namee B (2019) Kalman filter-based heuristic ensemble (kfhe): a new perspective on multi-class ensemble classification using kalman filters. Inform Sci 485:456–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.02.017
Peddinti V, Wang Y, Povey D, Khudanpur S (2018) Low latency acoustic modeling using temporal convolution and LSTMs. IEEE Signal Process Lett 25(3):373–377. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP20172723507
Shahroudy A, Liu J, Ng TT, Wang G (2016) NTU RGB+D: a large scale dataset for 3D human activity analysis. In: Proc Conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 1010–1019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR2016115
Shahroudy A, Ng TT, Yang Q, Wang G (2016) Multimodal multipart learning for action recognition in depth videos. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(10):2123–2129. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI20152505295
Shi L, Zhang Y, Cheng J, Lu H (2019) Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proc Conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 12018–12027. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR201901230
Shi L, Zhang Y, Cheng J, Lu H (2020) Skeleton-based action recognition with multi-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:9532–9545. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3028207
Si C, Chen W, Wang W, Wang L, Tan T (2019) An attention enhanced graph convolutional LSTM network for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proc Conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 1227–1236. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR201900132
Song S, Lan C, Xing J, Zeng W, Liu J (2017) An end-to-end spatio-temporal attention model for human action recognition from skeleton data. In: Proc Conf AAAI artif intell. https://aaai.org/ocs/indexphp/AAAI/AAAI17/paper/view/14437, pp 4263–4270
Sun B, Kong D, Wang S, Wang L, Wang Y, Yin B (2019) Effective human action recognition using global and local offsets of skeleton joints. Multimed Tools Appl 78(5):6329–6353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6370-1
Vemulapalli R, Arrate F, Chellappa R (2014) Human action recognition by representing 3D skeletons as points in a lie group. In: Proc Conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 588–595. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR201482
Wang H, Wang L (2018) Learning content and style: joint action recognition and person identification from human skeletons. Pattern Recognit 81:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/JPATCOG201803030
Wang J, Liu Z, Wu Y, Yuan J (2014) Learning actionlet ensemble for 3D human action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36 (5):914–927. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI2013198
Wang J, Nie X, Xia Y, Wu Y, Zhu S (2014) Cross-view action modeling, learning and recognition. In: Proc Conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 2649–2656. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR2014339
Wang P, Li Z, Hou Y, Li W (2016) Action recognition based on joint trajectory maps using convolutional neural networks. In: ACM Int conf multimedia, pp 97–106. https://doi.org/10.1145/29642842967191
Wei P, Sun H, Zheng N (2019) Learning composite latent structures for 3D human action representation and recognition. IEEE Trans Multimed 21 (9):2195–2208. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM20192897902
Xia L, Chen CC, Aggarwal JK (2012) View invariant human action recognition using histograms of 3D joints. In: Proc Conf comput vision pattern recognit workshops, pp 20–27. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW20126239233
Xu Y, Cheng J, Wang L, Xia H, Liu F, Tao D (2018) Ensemble one-dimensional convolution neural networks for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Signal Process Lett 25(7):1044–1048. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP20182841649
Yan S, Xiong Y, Lin D (2018) Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proc Conf AAAI artif intell. https://aaai.org/ocs/indexphp/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/view/17135, pp 7444–7452
Yang J, Liu W, Yuan J, Mei T (2021) Hierarchical soft quantization for skeleton-based human action recognition. IEEE Trans Multimed 23:883–898. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2020.2990082
Yang X, Tian Y (2014) Effective 3D action recognition using EigenJoints. J Vis Commun Image Represent 25(1, SI):2–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/JJVCIR201303001
Yang Y, Deng C, Gao S, Liu W, Tao D, Gao X (2017) Discriminative multi-instance multitask learning for 3D action recognition. IEEE Trans Multimed 19(3):519–529. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM20162626959
Zhang P, Lan C, Xing J, Zeng W, Xue J, Zheng N (2019) View adaptive neural networks for high performance skeleton-based human action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(8):1963–1978. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI20192896631
Zhang P, Lan C, Zeng W, Xing J, Xue J, Zheng N (2020) Semantics-guided neural networks for efficient skeleton-based human action recognition. In: Proc Conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 1112–1121. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00119
Zhang S, Yang Y, Xiao J, Liu X, Yang Y, Xie D, Zhuang Y (2018) Fusing geometric features for skeleton-based action recognition using multilayer LSTM networks. IEEE Trans Multimed 20(9):2330–2343. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM20182802648
Zhang X, Xu C, Tao D (2020) Context aware graph convolution for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proc Conf comput vision pattern recognit, pp 14333–14342. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600202001434
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Nation Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant 2018YFB2003500.
Funding
This work was supported by the Nation Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant 2018YFB2003500.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors of this research paper have directly participated in the planning, execution, or analysis of the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors of this paper have read and approved the final version submitted.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, W., Wang, X., Zhang, W. et al. Generic enhanced ensemble learning with multi-level kinematic constraints for 3D action recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 9685–9711 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-11919-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-11919-y