Abstract
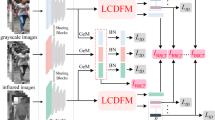
Person re-identification is an important part of the intelligent video analysis and processing system. A new type of surveillance camera can switch to the thermal infrared mode for 24-hour video surveillance. It is necessary to research the visible-thermal cross-modality person re-identification. However, there is a large modal discrepancy in the visible-thermal task. Therefore, the research focus on how to build a bridge to narrow the cross-modality gap and fully exploit the shared information. In this paper, we first employ grayscale transformation of the visible image to generate an intermediate modality, thereby reducing the distance between the original two domains. On this basis, a novel three-branch multiple center-constrained network (TMCC-Net) is built for the visible-thermal task. More specifically, TMCC-Net is a three-branch network that mines the shared information of pedestrians in three modalities through special feature learning and shared feature embedding. In order to obtain better performance, our work introduces two heterogeneous center-constrained losses to constrain the feature embedding. On the one hand, the proposed losses limit the distribution of features at the modality edge; on the other hand, they can strengthen the role of grayscale modality in the cross-modality task. Finally, an end-to-end model for visible-thermal person re-identification is built, which is effective for shared information mining. Extensive experiments are conducted on the two cross-modality datasets, including the SYSU-MM01 and RegDB datasets. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method compared to the state-of-the-art approaches.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen W, Chen X, Zhang J et al (2017) Beyond triplet loss: a deep quadruplet network for person re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Cheng Y, Xiao G, Tang X, Ma W, Gou X (2021) Two-phase feature fusion network for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp 1149–1153
Chhabra P, Garg N K, Kumar M (2020) Content-based image retrieval system using orb and sift features. Neural Comput Appl 32(7):1–9
Choi S, Lee S, Kim Y, Kim T, Kim C (2020) Hi-cmd: hierarchical cross-modality disentanglement for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 10254–10263
Dai J, Zhang P, Wang D, Lu H, Wang H (2019) Video person re-identification by temporal residual learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(3):1366–1377
Dai P, Ji R, Wang H, Wu Q, Huang Y (20187) Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training. In: Proceedings of the twenty-seventh international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 677–683
Dat N, Hyung H, Ki K, Kang P (2017) Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras. Sensors 17(3):605
Gong S, Cristani M, Yan S et al (2014) Person re-identification. Springer
Hao Y, Wang N, Li J, Gao X (2019) Hsme: hypersphere manifold embedding for visible thermal person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 8385–8392
Kaur A, Chauhan A S, Aggarwal A (2022) Prediction of enhancers in dna sequence data using a hybrid cnn-dlstm model. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinf, 1–1
Kumar, Munish, Chhabra, Payal, Garg, Naresh, Kumar (2018) An efficient content based image retrieval system using bayesnet and k-nn. Multimedia Tools and Applications
Kumar K (2019) Evs-dk: event video skimming using deep keyframe. J Vis Commun Image Represent 58:345–352
Kumar K, Kumar A, Bahuguna A (2017) D-cad: deep and crowded anomaly detection. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on computer and communication technology. ICCCT-2017. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, pp 100–105
Leng Q, Ye M, Tian Q (2020) A survey of open-world person re-identification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 30(4):1092–1108
Li D, Wei X, Hong X, Gong Y (2020) Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an x modality. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 4610–4617
Liao S, Hu Y, Zhu X et al (2015) Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Boston, pp 2197–2206
Liu H, Chai Y, Tan X, Li D, Zhou X (2021) Strong but simple baseline with dual-granularity triplet loss for visible-thermal person re-identification. IEEE Signal Process Lett 28:653–657
Liu H, Cheng J, Wang W, Su Y, Bai H (2020) Enhancing the discriminative feature learning for visible-thermal cross-modality person re-identification. Neurocomputing 398:11–19
Liu H, Tan X, Zhou X (2020) Parameter sharing exploration and hetero-center triplet loss for visible-thermal person re-identification. IEEE Trans Multimedia, 1–1
Liu J, Song W, Chen C, Liu F (2021) Cross-modality person re-identification via channel-based partition network. Appl Intell, 8
Liu J, Sun C, Xu X, Xu B, Yu S (2019) A spatial and temporal features mixture model with body parts for video-based person re-identification. Appl Intell 49(9):3436–3446
Lu Y, Wu Y, Liu B, Zhang T, Li B, Chu Q, Yu N (2020) Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 13376–13386
Mallika, Ubhi J S, Aggarwal A K (2022) Neural style transfer for image within images and conditional gans for destylization. J Vis Commun Image Represent 85:103483
Negi A, Kumar K (2022) Chapter 1 - ai-based implementation of decisive technology for prevention and fight with covid-19. In: Cyber-Physical Systems, pp 1–14
Qi WSHG (2021) Mask-guided dual attention-aware network for visible-infrared person re-identification. Multimed Tools Applic 80:17645–17666
Wang G A, Yang T, Cheng J, Chang J, Liang X, Hou Z (2020) Cross-modality paired-images generation for rgb-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Wang G, Zhang T, Cheng J, Liu S, Yang Y, Hou Z (2019) Rgb-infrared cross-modality person re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 3622–3631
Wang T, Gong S, Zhu X, et al. (2014) Person re-identification by video ranking. In: European conference on computer vision, Zurich, pp 688–703
Wang Z, Wang Z, Zheng Y, Chuang Y-Y, Satoh S (2019) Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person re-identification. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 618–626
Wei Z, Yang X, Wang N, Gao X (2021) Flexible body partition-based adversarial learning for visible infrared person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 1–12
Wen Y, Zhang K, Li Z, Qiao Y (2016) A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M (eds) Computer vision – ECCV 2016, Cham, pp 499–515
Wu A, Zheng W-S, Yu H-X, Gong S, Lai J (2017) Rgb-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 5390–5399
Yang Y, Yang J, Yan J, et al. (2014) Salient color names for person re-identification. In: European conference on computer vision, pp 536–551
Yao H, Zhang S, Hong R, Zhang Y, Xu C, Tian Q (2019) Deep representation learning with part loss for person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(6):2860–2871
Ye H, Liu H, Meng F, Li X (2021) Bi-directional exponential angular triplet loss for rgb-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1583–1595
Ye H, Liu H, Meng F, Li X (2021) Bi-directional exponential angular triplet loss for rgb-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1583–1595
Ye M, Lan X, Li J, Yuen P C (2018) Hierarchical discriminative learning for visible thermal person re-identification. In: AAAI
Ye M, Lan X, Wang Z, Yuen P C (2020) Bi-directional center-constrained top-ranking for visible thermal person re-identification. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 15:407–419
Ye M, Lan X, Wang Z, Yuen P C (2020) Bi-directional center-constrained top-ranking for visible thermal person re-identification. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 15:407–419
Ye M, Shen J, Lin G, Xiang T, Shao L, Hoi S CH (2021) Deep learning for person re-identification: a survey and outlook. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 1–1
Ye M, Shen J, Shao L (2021) Visible-infrared person re-identification via homogeneous augmented tri-modal learning. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 16:728–739
Ye M, Wang Z, Lan X, Yuen P C (2018) Visible thermal person re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking. In: Proceedings of the twenty-seventh international joint conference on artificial intelligence, IJCAI-18, pp 1092–1099
You J, Wu A, Li X, Zheng W S (2016) Top-push video-based person re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, pp 1345–1353
Zhao J, Wang H, Zhou Y, Yao R, Chen S, El Saddik A (2022) Spatial-channel enhanced transformer for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Multimedia, 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3163847https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3163847
Zheng L, Yang Y, Hauptmann AG (2016) Person re-identification: past, present and future. arXiv:1610.02984
Zheng W S, Gong S, Xiang T (2013) Reidentification by relative distance comparison. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(3):653–668
Zhong X, Lu T, Huang W, Ye M, Jia X, Lin C-W (2021) Grayscale enhancement colorization network for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol, 1–1
Zhu Y, Yang Z, Wang L, Zhao S, Hu X, Tao D (2020) Hetero-center loss for cross-modality person re-identification. Neurocomputing 386:97–109
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62177029 and 61807020, and in part by the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of Nanjing University of Posts and Communications under Grant NY221041 and NY222034, and in part by General Project of The Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Higher Education Institution of China 22KJB520025.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Availability of data and materials
Some generated or used during the study are available in a repository or online in accordance with funder data retention policies
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Wang, X., Chen, C. et al. Visible-thermal person re-identification via multiple center-based constraints. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 18459–18481 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14113-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14113-2