Abstract
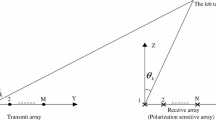
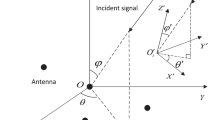
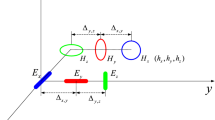
A novel blind direction-of-arrival (DOA) and polarization estimation algorithm for polarization-sensitive uniform linear array using dimension reduction multiple signal classification (MUSIC) is proposed in this paper. The proposed algorithm utilizes the signal subspace to obtain an initial estimation of DOA, then estimates more accurate DOA through a one-dimensional (1-D) local searching according to the initial estimation of DOA, and finally obtains polarization parameter estimation via the estimated polarization steering vectors. The proposed algorithm, which only requires a one-dimension local searching, can avoid the high computational cost within multi-dimensional MUSIC algorithm. The simulation results reveal that the proposed algorithm has better DOA and polarization estimation performance than both estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance technique algorithm and trilinear decomposition algorithm. Furthermore, the proposed algorithm can be suitable for irregular array geometry, obtain automatically paired multi-dimensional parameter estimation, and avoid multi-dimensional searching. Simulation results verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, M. I., Liu, Z., & Yougen X. (2008). Minimum variance beamforming using polarization sensitive array. 11th IEEE Singapore International Conference on Communication Systems, 2008. ICCS 2008. 19–21 Nov. 2008, (pp. 489–492).
Goossens R., Rogier H. (2008) Direction-of-arrival and polarization estimation with uniform circular arrays in the presence of mutual coupling. International Journal of Electronics and Communications 62(3): 199–206
Guo X., Wan Q., Chang C., Lam Edmund Y. (2010) . Source lcalization using a sparse representation framework to achieve superresolution. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing 21(4): 391–402
Li J., Compton R. T. (1991) Angle and polarization estimation using ESPRIT with a polarization sensitive array. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 39(9): 1376–1383
Li J., Compton R. T. (1992) Two-dimensional angle and polarization estimation using the ESPRIT algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 40(5): 550–555
Maiwald, D., Sidorovitch, D. V., & Bohme, J. F. (1993). Broadband maximum likelihood wave parameter estimation using polarization sensitive arrays. 1993 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, (Vol. 4, pp. 27–30) (pp. 356–359).
Shi, X., & Wang, Y. (2008). Parameter estimation of distributed sources with electromagnetic vector sensors, 2008. 9th International Conference on Signal Processing, 26–29 Oct. 2008, (pp. 203–206).
Shi, Y., & Zhang, X. (2008). Quadrilinear decomposition-based blind signal detection for polarization sensitive uniform square array. Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 87, (pp. 263–278).
Stoica P., Nehorai A. (1990) Performance study of conditional and unconditional direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 38: 1783–1795
Wong K. T., Zoltowski M. D. (1997) Uni-vector-sensor ESPRIT for multi-source azimuth-elevation angle estimation. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 45(10): 1467–1474
Wong K. T., Zoltowski M. D. (2000) Closed-form direction finding and polarization estimation with arbitrarily spaced electromagnetic vector sensors at unknown locations. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 48(5): 671–681
Xu Y., Liu Z. (2004) Cumulant-based two-dimensional DOA and polarization estimation with a polarization sensitive array comprising a spatially stretched tripole. Acta Electronica Sinica 32(12): 1962–1966
Xu Y., Liu Z. (2007) Closed-form multiple invariance ESPRIT. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing 18(1): 47–54
Yuan, Q., Chen, Q., & Sawaya, K. (2006). MUSIC based DOA finding and polarization estimation using USV with polarization sensitive array antenna. 2006 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium 17–19 Jan. 2006, (pp. 339–342).
Zhang, X., & Xu, D. (2008). Deterministic blind beamforming for electromagnetic vector sensor array. Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 84, (pp. 363–377).
Zhang, Q., Wang, L., Wang, Y., & Huang, J. (2006). Cyclostationarity-based DOA and polarization estimation for multipath signals with a uniform linear array of electromagnetic vector sensors, 2006 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics Aug. 2006, (pp. 2047–2052).
Zhang X., Shi Y., Xu D. (2008) Novel blind joint direction of arrival and polarization estimation for polarization-sensitive uniform circular array. Progress In Electromagnetics Research 86: 19–37
Zhang X., Xu L., Xu L. et al (2010) Direction of departure (DOD) and direction of arrival (DOA) estimation in MIMO radar with reduced-dimension MUSIC. IEEE Communications Letters 14(12): 1161–1163
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Chen, C., Li, J. et al. Blind DOA and polarization estimation for polarization-sensitive array using dimension reduction MUSIC. Multidim Syst Sign Process 25, 67–82 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-012-0186-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-012-0186-3