Abstract
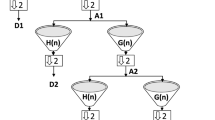
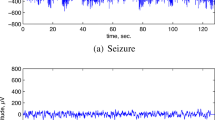
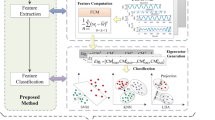
Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals can be used by a proficient neurologist to detect the presence of seizure activity inside the brain. Automated detection of seizures in EEG signals has clinical importance given that manual round-the-clock monitoring of EEG signals is impossible. A patient-independent algorithm for seizure detection is developed using features extracted from high-resolution time–frequency distributions (TFDs). In order to achieve good classification performance, a modified highly adaptive time–frequency distribution (HADTFD) is defined. The modified-HADTFD is used to obtain a clear and cross-term free time–frequency representation of EEG signals. This is followed by the extraction of features and training of a linear classifier. The proposed approach based on modified-HADTFD achieves the classification accuracy of \(98.56\%\) by using only three time–frequency features, which is \(37\%\) more than the accuracy achieved with other TFDs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarabi, A., Fazel-Rezai, R., & Aghakhani, Y. (2009). A fuzzy rule-based system for epileptic seizure detection in intracranial EEG. Clinical Neurophysiology, 120(9), 1648–1657. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2009.07.002.
Alam, S. M. S., & Bhuiyan, M. I. H. (2013). Detection of seizure and epilepsy using higher order statistics in the EMD domain. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 17(2), 312–318. doi:10.1109/JBHI.2012.2237409.
Ali Khan, N., & Ali, S. (2017). Sparsity-aware adaptive directional time-frequency distribution for source localization. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing,. doi:10.1007/s00034-017-0603-9.
Alotaiby, T. N., Alshebeili, S. A., El-Samie, F. E. A., Alabdulrazak, & A., Alkhnaian, E. (2016). Channel selection and seizure detection using a statistical approach. In: 2016 5th international conference on electronic devices, systems and applications (ICEDSA) (pp. 1–4). doi:10.1109/ICEDSA.2016.7818505.
Bhattacharyya, A., & Pachori, R. B. (2017). A multivariate approach for patient specific EEG seizure detection using empirical wavelet transform. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, PP(99), 1–1. doi:10.1109/TBME.2017.2650259.
Boashash, B. (2016). Chapter 1—Time–frequency and instantaneous frequency concepts0. In: B. Boashash (Ed.), Time–frequency signal analysis and processing (2nd ed) (pp. 31–63). Oxford: Academic Press. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-398499-9.00001-7.
Boashash, B., & Azemi, G. (2014). A review of time-frequency matched filter design with application to seizure detection in multichannel newborn EEG. Digital Signal Processing, 28, 28–38. doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2014.02.007.
Boashash, B., Azemi, G., & Khan, N. A. (2015). Principles of time-frequency feature extraction for change detection in non-stationary signals: Applications to newborn EEG abnormality detection. Pattern Recognition, 48(3), 616–627. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2014.08.016.
Boashash, B., Azemi, G., & O’Toole, J. M. (2013). Time-frequency processing of nonstationary signals: Advanced TFD design to aid diagnosis with highlights from medical applications. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 30(6), 108–119. doi:10.1109/MSP.2013.2265914.
Boashash, B., Khan, N. A., & Jabeur, T. B. (2015). Time-frequency features for pattern recognition using high-resolution TFDs: A tutorial review. Digital Signal Processing, 40, 1–30. doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2014.12.015.
Boashash, B., Ouelha, S. (2017). An improved design of high-resolution quadratic time-frequency distributions for the analysis of non-stationary multicomponent signals using directional compact kernels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, PP(99), 1–1. doi:10.1109/TSP.2017.2669899.
Cic, M., Soda, J., & Bonkovic, M. (2013). Automatic classification of infant sleep based on instantaneous frequencies in a single-channel EEG signal. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 43(12), 2110–2117. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2013.10.002.
Dalton, H. (1920). The measurement of the inequality incom. Economic, 30(119), 348–361.
De Vos, M., Deburchgraeve, W., Cherian, P. J., Matic, V., Swarte, R. M., Govaert, P., et al. (2011). Automated artifact removal as preprocessing refines neonatal seizure detection. Clinical Neurophysiology, 122(12), 2345–2354. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2011.04.026.
Dong, S., Azemi, G., & Boashash, B. (2014). Improved characterization of HRV signals based on instantaneous frequency features estimated from quadratic time–frequency distributions with data-adapted kernels. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 10, 153–165. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2013.11.008.
Dong, S., Boashash, B., Azemi, G., Lingwood, B., & Colditz, P. B. (2014). Automated detection of perinatal hypoxia using time-frequency-based heart rate variability features. Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing, 52(2), 183–191. doi:10.1007/s11517-013-1129-3.
Fu, K., Qu, J., Chai, Y., & Zou, T. (2015). Hilbert marginal spectrum analysis for automatic seizure detection in EEG signals. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 18, 179–185. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2015.01.002.
Ghoraani, B., & Krishnan, S. (2011). Time-frequency matrix feature extraction and classification of environmental audio signals. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 19(7), 2197–2209. doi:10.1109/TASL.2011.2118753.
Hamid, H., Mostefa, M., & Boualem, B. (2004). Time-frequency feature extraction of newborn EEG seizure using svd-based techniques. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2004(16), 898124. doi:10.1155/S1110865704406167.
Honeine, P., Richard, C., & Flandrin, P. (2007). Time–frequency learning machines. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 55(7), 3930–3936. doi:10.1109/TSP.2007.894252.
Hosseini, M. P., Hajisami, A., & Pompili, D. (2016). Real-time epileptic seizure detection from EEG signals via random subspace ensemble learning. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on autonomic computing (ICAC) (pp. 209–218). doi:10.1109/ICAC.2016.57.
Hunyadi, B., Dupont, P., Van Paesschen, W., & Van Huffel, S. (2017). Tensor decompositions and data fusion in epileptic electroencephalography and functional magnetic resonance imaging data. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 7(1), e1197-n/a. doi:10.1002/widm.1197. E1197.
Ihle, M., Feldwisch-Drentrup, H., Teixeira, C. A., Witon, A., Schelter, B., Timmer, J., et al. (2012). Epilepsiae—A European epilepsy database. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 106(3), 127–138. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2010.08.011.
Jokanovic, B., & Amin, M. (2015). Sparsity and concentration measures for optimum quadratic time–frequency distributions of doppler signals. In: 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon) (pp. 1211–1215). doi:10.1109/RADAR.2015.7131179.
Kevric, J., & Subasi, A. (2014). The effect of multiscale PCA de-noising in epileptic seizure detection. Journal of Medical Systems, 38(10), 131. doi:10.1007/s10916-014-0131-0.
Khan, N. A., & Ali, S. (2016). Classification of EEG signals using adaptive time-frequency distributions. Metrology and Measurement Systems, 23(2), 251–260.
Khan, N. A., & Boashash, B. (2016). Multi-component instantaneous frequency estimation using locally adaptive directional time frequency distributions. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 30(3), 429–442.
Khan, N. A., & Sandsten, M. (2016). Time–frequency image enhancement based on interference suppression in Wigner–Ville distribution. Signal Processing, 127, 80–85.
Khlif, M., Colditz, P., & Boashash, B. (2013). Effective implementation of time frequency matched filter with adapted pre and postprocessing for data-dependent detection of newborn seizures. Medical Engineering Physics, 35(12), 1762–1769. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2013.07.005.
Li, J., Zhou, W., Yuan, S., Zhang, Y., Li, C., & Wu, Q. (2016). An improved sparse representation over learned dictionary method for seizure detection. International Journal of Neural Systems, 26(01), 1550035. doi:10.1142/S0129065715500355.
Liu, J., Wu, C., Wang, Z., & Wu, L. (2017). Reliable filter design for sensor networks in the type-2 fuzzy framework. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, PP(99), 1–1. doi:10.1109/TII.2017.2654323.
Mathieson, S. R., Stevenson, N. J., Low, E., Marnane, W. P., Rennie, J. M., Temko, A., et al. (2016). Validation of an automated seizure detection algorithm for term neonates. Clinical Neurophysiology, 127(1), 156–168. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2015.04.075.
Mohammadi, M., Pouyan, A. A., & Khan, N. A. (2016). A highly adaptive directional time-frequency distribution. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 10(7), 1369–1376. doi:10.1007/s11760-016-0901-x.
Nilufar, S., Ray, N., Molla, M.K.I., & Hirose, K. (2012). Spectrogram based features selection using multiple kernel learning for speech/music discrimination. In: 2012 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 501–504). doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2012.6287926.
Orosco, L., Correa, A. G., Diez, P., & Laciar, E. (2016). Patient non-specific algorithm for seizures detection in scalp EEG. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 71, 128–134. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.02.016.
Raghunathan, S., Jaitli, A., & Irazoqui, P. P. (2011). Multistage seizure detection techniques optimized for low-power hardware platforms. Epilepsy Behavior, 22, 61–68. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2011.09.008.
Riaz, F., Hassan, A., Rehman, S., Niazi, I. K., & Dremstrup, K. (2016). EMD-based temporal and spectral features for the classification of EEG signals using supervised learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 24(1), 28–35. doi:10.1109/TNSRE.2015.2441835.
Sejdi, E., Djurovi, I., & Jiang, J. (2009). Timefrequency feature representation using energy concentration: An overview of recent advances. Digital Signal Processing, 19(1), 153–183. doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2007.12.004.
Sharma, R., Pachori, R. B., & Acharya, U. R. (2015). Application of entropy measures on intrinsic mode functions for the automated identification of focal electroencephalogram signals. Entropy, 17(2), 669–691. doi:10.3390/e17020669.
Souli, S., & Lachiri, Z. (2013). Multiclass support vector machines for environmental sounds classification in visual domain based on log-gabor filters. International Journal of Speech Technology, 16(2), 203–213. doi:10.1007/s10772-012-9174-0.
Stankovi, L. (2001). A measure of some time frequency distributions concentration. Signal Processing, 81(3), 621–631. doi:10.1016/S0165-1684(00)00236-X. (Special section on Digital signal processing for multimedia).
Stankovic, L. (1994). A method for time–frequency analysis. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 42(1), 225–229. doi:10.1109/78.258146.
Temko, A., Thomas, E., Marnane, W., Lightbody, G., & Boylan, G. (2011). EEG-based neonatal seizure detection with support vector machines. Clinical Neurophysiology, 122(3), 464–473. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2010.06.034.
Wang, K. (2015). Time-frequency feature representation using multi-resolution texture analysis and acoustic activity detector for real-life speech emotion recognition. Sensors, 15(1), 1458–1478. doi:10.3390/s150101458.
Wu, L., Gao, Y., Liu, J., & Li, H. (2017). Event-triggered sliding mode control of stochastic systems via output feedback. Automatica, 82, 79–92. doi:10.1016/j.automatica.2017.04.032.
Yuan, Q., Zhou, W., Liu, Y., & Wang, J. (2012). Epileptic seizure detection with linear and nonlinear features. Epilepsy Behavior, 24(4), 415–421. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2012.05.009.
Zandi, A. S., Javidan, M., Dumont, G. A., & Tafreshi, R. (2010). Automated real-time epileptic seizure detection in scalp EEG recordings using an algorithm based on wavelet packet transform. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 57(7), 1639–1651. doi:10.1109/TBME.2010.2046417.
Zhang, Y., Zhou, W., & Yuan, S. (2015). Multifractal analysis and relevance vector machine-based automatic seizure detection in intracranial EEG. International Journal of Neural Systems, 25(06), 1550020. doi:10.1142/S0129065715500203.
Zhang, Z., & Parhi, K. K. (2016). Low-complexity seizure prediction from iEEG/sEEG using spectral power and ratios of spectral power. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 10(3), 693–706. doi:10.1109/TBCAS.2015.2477264.
Zhou, W., Liu, Y., Yuan, Q., & Li, X. (2013). Epileptic seizure detection using lacunarity and bayesian linear discriminant analysis in intracranial EEG. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 60(12), 3375–3381. doi:10.1109/TBME.2013.2254486.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi, M., Ali Khan, N. & Pouyan, A.A. Automatic seizure detection using a highly adaptive directional time–frequency distribution. Multidim Syst Sign Process 29, 1661–1678 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-017-0522-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-017-0522-8