Abstract
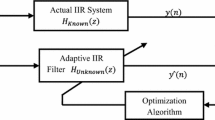
In this work we are optimizing an adaptive finite impulse response filter applied to the problem of system identification. We are proposing a breeder genetic algorithm (BGA) for performing the parametric search in highly multimoldal landscapes since in this kind of filters there exits epistiasis. The results of BGA were compared to the traditional genetic algorithm, and we found that the BGA was clearly superior (in accuracy) in most of the cases. We used the statistical least mean squared for validating the results. We suggest to hybridized both methods for real world applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belanche LA (1999) A Study in Function Optimization with the Breeder Genetic Algorithm. Research Report LSI-99-36-R, Universitad Politécnica de Catalunya. http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/belanche99study.html
O Castillo O Montiel R Sepúlveda P Melin (2001) Application of a Breeder Genetic Algorithm for System Identification in an Adaptive Finite Impulse Response Filter. The Third NASA/DoD Workshop on Evolvable Hardware Long Beach California, USA
EKP Chong SH Żak (1996) An Introduction to Optimization John Wiley Sons Inc., USA 67–68
O Cordón F Herrera F Hoffmann L Magdalena (2001) Genetic Fuzzy Systems. Evolutionary Tuning and Learning of Fuzzy Knowledge Bases World Scientific USA 69
DB Fogel (2000) Evolutionary Computation EditionNumber2 IEEE Press Editorial USA
DE Goldberg (1999) Genetic Algorithms in Search Optimization and Machine Learning. Addison Wesley USA 90–91
Harris SP and Ifeachor EC (1996) Nonlinear FIR Filter Design by Genetic Algorithm. In 1st Online Conference on Soft Computing, August 1996. http://www.lania.mx/ccoello/EMOO/EMOOconferences.html#H
SS Haykin (2002) Adaptive Filter Theory EditionNumber4 Prentice Hall USA 22–26
Herrera F and Lozano M (1998) Fuzzy Genetic Algorithms: Issues and Models. http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/16799.html.
Herrera F and Lozano M (2000) Gradual Distributed RealCoded Genetic Algorithms. IEEE-EC, 4(1) April 2000, p. 43. http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/herrera97gradual.html
EC Ifeachor BW Jervis (1996) Digital Signal Processing. A Practical Approach Addison-Wesley Publishing Company USA 254–255
Ingle VK and Proakis JG (2000) Digital Signal Processing using Matlab. Ed. Brooks/Cole, 2000, pp. 371–377
J-SR Jang C-T Sun E Mizutani (1997) ArticleTitleNeuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing, A Computational Approach to Learning and Machine Intelligence Matlab Curriculum Series. Prentice Hall 122 160–168
L Ljung (1999) System Identification EditionNumber2 Theory for the User Prentice Hall, USA 79–90
Madisetti VK and Williams DB (1997) The Digital Signal Processing Handbook. A CRC Handbook Published in Cooperation with IEEE Press, pp. 15--1, 18--1, 18--7, 20--1, 20--4
M Mitchell (1998) ArticleTitleAn Introduction to Genetic Algorithms MIT Press, USA, 1998, pp. 3 5–6
M Mokhtari M Marie (2000) Engineering Application of MATLAB 5.3 and SIMULINK 3 Springer-Verlag LondonGreat Britain 222
Montiel O, Castillo O and Sepúlveda R (2002) Error and Energy Measures in System Identification Using an Evolutionary Algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IC-AI’02) Volume III, pp. 1184–1189, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA
Mühlenbein H (1997) Evolutionary Algorithms: Theory and Applications. http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/110687.html.
Mühlenbein H (1997) 6 Genetic Algorithms. Borneo. http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/181734.html.
H Mühlenbein Schilierkamp-Voosen (1993) ArticleTitlePredictive Model for Breeder Genetic Algorithm. Evolutionary Computation 1 IssueID1 25–49
Proakis JG and Manolakis DG (1996) 3 ed. Digital Signal Processing. Principles, Algorithms, and Applications. Prentice Hall, pp. 47–50, 69, 70, 87–89, 931–936
Salomon R (1995) Genetic Algorithms and the O(n ln n) Complexity on Selected Test Functions. http://citesser.nj.nec.com/109962.html.
Slotine JE and W Li (1991) Applied Nonlinear Control. Prentice Hall, pp. 311–313
Tan KC (1997) Evolutionary System Identification in the Time-Domain. http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/236895.html.
Tan KC, Li Y, Murray-Smith DJ and Sharman KC (1995) System Identification and Linearisation Using Genetic Algorithms with Simulated Annealing. Proc. First IEE/IEEE Int. Conf. on GA in Eng. Syst.: Innovations and Appl., pp. 164–169. http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/tan95system.html
Voigt HM, Mühlenbein H and Cvetkovic D (1995) Fuzzy Recombination for the Breeder Genetic Algorithm. Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Genetic Algorithms, published by Morgan Kaufmann, pp. 1104–1111
Ziemer RE, Tranter WH and Ronald Fannin D (1998) Signal an Systems Continuous and Dicrete. 4 ed., Prentice Hall, USA, p. 77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montiel, O., Castillo, O., Melin, P. et al. Application of a breeder genetic algorithm for filter optimization. Nat Comput 4, 11–37 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11047-004-9097-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11047-004-9097-z