Abstract
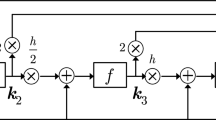
In this paper, we propose a new recurrent fuzzy neural network, which has the standard state space form, we call it state-space recurrent neural networks. Input-to-state stability is applied to access robust training algorithms for system identification. Stable learning algorithms for the premise part and the consequence part of fuzzy rules are proved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen D. S. and Jain R. C.: A robust back propagation learning algorithm for function approximation, IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 5(3) (1994).
M. Y. Chen D. A. Linkensm (2001) ArticleTitleA systematic neuro-fuzzy modeling framework with application to material property prediction IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B 31 781–790 Occurrence Handle10.1109/3477.956047
B. Egardt (1979) Stability of Adaptive Controllers, Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences Springer Berlin
S. Haykin (1994) Neural Networks – A Comprehensive Foundation Macmillan New York
Ioannou, P. A. and Sun, J.: Robust Adaptive Control, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice-Hall, 1996.
Z. P. Jiang Y. Wang (2001) ArticleTitleInput-to-State Stability for discrete-time nonlinear systems Automatica 37 IssueID2 857–869 Occurrence Handle2002j:93064
L. Jin M. M. Gupta (1999) ArticleTitleStable dynamic backpropagation learning in recurrent neural networks IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 10 IssueID6 1321–1334
C. F. Juang (2002) ArticleTitleA TSK-type recurrent fuzzy networks for dynamic systems processing by neural network and genetic algorithms IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 10 IssueID2 155–170 Occurrence Handle88d:93026
C. H. Lee C. C. Teng (2000) ArticleTitleIdentification and control of dynamic system using recurrent fuzzy neural networks IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 8 IssueID4 349–366
F. L. Lewis A. Yesildirek K. Liu (1996) ArticleTitleMultilayer neural-net robot controller with guaranteed tracking performance IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 7 IssueID2 388–399 Occurrence Handle10.1109/72.485674
Y. G. Leu T. T. Lee W. Y. Wang (1999) ArticleTitleObserver-based adaptive fuzzy-neural control for unknown nonlinear dynamical systems IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B 29 583–591
C. T. Lin G. Lee (1996) Neural fuzzy systems: A neural-fuzzy synergism to intelligent systems Prentice-Hall Inc. NJ
C. T. Lin (1995) ArticleTitleA neual fuzzy control system with structure and parameter learning Fuzzy Sets anc Syst. 70 183–212
E. H. Mamdani (1976) ArticleTitleApplication of fuzzy algorithms for control of simple dynamic plant IEE Proc. Control Theory Appl. 121 IssueID12 1585–1588
P. A. Mastorocostas J. B. Theocharis (2002) ArticleTitleA recurrent fuzzy-neural model for dynamic system identification IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B 32 IssueID2 176–190 Occurrence Handle10.1109/3477.990874
T. Takagi M. Sugeno (1985) ArticleTitleFuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 15 116–132
H. H. Tsai P. T. Yu (2000) ArticleTitleOn the optimal design of fuzzy neural networks with robust learning for function approximation IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B 30 217–223
S. Wu M. J. Er (2000) ArticleTitleDynamic fuzzy neural networks- a novel approach to function approximation IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B 30 358–364
C. H. Wang H. L. Liu C. T. Lin (2001) ArticleTitleDynamic optimal learning rates of a certain class of fuzzy neural networks and its applications with genetic algorithm IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B 31 467–475 Occurrence Handle10.1109/3477.915344 Occurrence Handle2002k:62046
L. X. Wang (1994) Adaptive Fuzzy Systems and Control Englewood Cliffs NJ, Prentice-Hall
W. Y. Wang Y. G. Leu C. C. Hsu (2001) ArticleTitleRobust adaptive fuzzy-neural control of nonlinear dynamical systems using generalized projection updated law and variable structure controller IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B 31 140–147 Occurrence Handle10.1109/3477.915344
W. Yu X. Li (2001) ArticleTitleSome stability properties of dynamic neural networks IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 48 IssueID1 256–259
W. Yu X. Li (2001) ArticleTitleSome new results on system identification with dynamic neural networks IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 12 IssueID2 412–417
J. Zhang A. J. Morris (1999) ArticleTitleRecurrent neuro-fuzzy networks for nonlinear process modeling IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 10 IssueID2 313–326
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, W. State-Space Recurrent Fuzzy Neural Networks for Nonlinear System Identification. Neural Process Lett 22, 391–404 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-005-1523-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-005-1523-4