Abstract
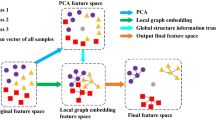
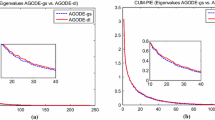
In the field of manifold learning, Marginal Fisher Analysis (MFA), Discriminant Neighborhood Embedding (DNE) and Double Adjacency Graph-based DNE (DAG-DNE) construct the graph embedding for homogeneous and heterogeneous k-nearest neighbors (i.e. double adjacency) before feature extraction. All of them have two shortcomings: (1) vulnerable to noise; (2) the number of feature dimensions is fixed and likely very large. Taking advantage of the sparsity effect and de-noising property of sparse dictionary, we add the \(l_{2,1}\) norm-based sparse dictionary coding regularization term to the graph embedding of double adjacency, to form an objective function, which seeks a small amount of significant dictionary atoms for feature extraction. Since our initial objective function cannot generate the closed-form solution, we construct an auxiliary function instead. Theoretically, the auxiliary function has closed-form solution w.r.t. dictionary atoms and sparse coding coefficients in each iterative step and its monotonously decreased value can pull down the initial objective function value. Extensive experiments on the synthetic dataset, the Yale face dataset, the UMIST face dataset and the terrain cover dataset demonstrate that our proposed algorithm has the ability of pushing the separability among heterogenous classes onto much fewer dimensions, and robust to noise.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nie F, Huang H, Cai X, Ding C (2010) Efficient and robust feature selection via joint \(L_{2,1}\) norm minimization. Proc Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 23:1813–1821
Hou C, Nie F, Li X, Yi D, Wu Y (2014) Joint embedding learning and sparse regression: a framework for unsupervised feature selection. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(6):793–804
Liu X, Wang L, Zhang J, Yin J, Liu H (2014) Global and local structure preservation for feature selection. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(6):1083–1095
Fang X, Xu Y, Li X, Fan Z, Liu H, Chen Y (2014) Locality and similarity preserving embedding for feature selection. Neurocomputing 128:304–315
Shi C, Ruan Q, An G (2014) Sparse feature selection based on graph Laplacian for web image annotation. Image Vis Comput 32:189–201
Aharon M, Elad M, Bruckstein A (2006) K-SVD: an algorithm for designing over-complete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 54(11):4311–4322
Zhang Q, Li B (2010) Discriminative K-SVD for dictionary learning in face recognition. In: Proceedings of IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Jiang Z, Lin Z, Davis L (2013) Label consistent K-SVD: learning a discriminative dictionary for recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(11):2651–2664
Lian Q, Shi B, Chen S (2015) Research advances on dictionary learning models, algorithms and applications. Acta Automatica Sinica 41(2):240–260
Xu J, Chang Z, Zhao X (2013) Dictionary training algorithm for image classification. Mod Electron Tech 51(2):211–221
Yan S, Xu D, Zhang B, Yang Q, Lin S (2007) Graph embedding and extension: a general framework for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Learn 29(1):40–51
Ding C, Zhang L (2015) Double adjacency graphs-based discriminant neighborhood embedding. Pattern Recognit 48:1734–1742
Wright J, Yang AY, Ganesh A, Sastry S, Ma Y (2009) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(2):210–227
Zou H, Hastie H (2005) Regression and variable selection via the elastic net. J R Stat Soc Ser B 67(2):301–320
Ye J (2005) Characterization of a family of algorithms for generalized discriminant analysis on undersampled problems. J Mach Learn Res 6:483–502
Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J (2001) The elements of statistical learning, data mining, inference and prediction, 2nd edn. Springer, Stanford
Yang M, Dai D, Shen L, Gool L (2014) Latent dictionary learning for sparse representation based classification. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4138–4145
Liu Z, Chen X (2016) Local subspace clustering. Acta Automatica Sinca 42(8):1238–1247
Mairal J, Bach F, Ponce J, Sapiro G, (2009) Online dictionary learning for sparse coding. In: Proceedings of the 26-th international conference on machine learning (ICML), pp 689–696
Zhang W, Xue X, Lu H, Guo Y (2006) Discriminant neighborhood embedding for classification. Pattern Recognit 39:2240–2243
Chen H, Chang H, Liu T (2005) Local discriminant embedding and its variants. In: CVPR’05: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Nie F, Xiang S, Song Y, Zhang C (2009) Orthogonal locality minimizing globality maximizing projections for feature extraction. Opt Eng 48(1):017202
Jia Y, Nie F, Zhang C (2009) Trace ratio problem revisited. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 20(4):729–735
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L (2004) Convex optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Shi X, Yang Y, Guo Z, Lai Z (2014) Face recognition by sparse discriminant analysis via joint \(L_{2,1}\) norm minimization. Pattern Recognit 47:2447–2453
Nie F, Xiang S, Zhang C (2007) Neighborhood minmax projections. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI), pp 993–998
He X, Yan S, Hu Y, Niyogi P, Zhang H (2005) Face recognition using laplacianfaces. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(3):328–340
Roweis S, Saul L (2000) Nolinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 290(22):2323–2326
Zhang T, Yang J, Zhao D, Ge X (2007) Linear local tangent space alignment and application to face recognition. Neurocomputing 70(7–9):1547–1553
Liu W, Zha Z, Wang Y, Lu K, Tao D (2016) \(p\)-Laplacian regularized sparse coding for human activity recognition. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(8):5120–5129
Guan N, Tao D, Luo Z, Yuan B (2011) Non-negative patch alignment framework. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(8):1218–1229
Guan N, Tao D, Luo Z, Taylor J, MahNMF: Manhattan non-negative matrix factorization. J Mach Learn Res. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229156789_MahNMF_Manhattan_Non-negative_Matrix_Factorization
Guan N, Zhang X, Luo Z, Lan L (2012) Sparse representation based discriminative canonical correlation analysis for face recognition. In: The 11th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA) IEEE, vol 1, pp 51–56
Wang N, Gao X, Sun L, Li J (2017) Bayesian face sketch synthesis. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(3):1264–1274
Gao X, Wang N, Tao D, Li X (2012) Face sketch–photo synthesis and retrival using sparse representation. IEEE Trans Circuits System Video Technol 22(8):1213–1226
Wang N, Tao D, Gao X, Li X, Li J (2014) A comprehensive survey to face hallucination. Int J Comput Vis 106(1):9–30
Graham D, Allinson N (1998) Characterizing virtual eigensignatures for general purpose face recognition. Proc Face Recognit Theory Appl 163:446–456
Yu J, Rui Y, Tao D (2014) Click prediction for web image reranking using multimodal sparse coding. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(5):2019–2032
Yu J, Yang X, Gao F, Tao D (2016) Deep multimodal distance metric learning using click constraint for image ranking. IEEE Trans Cybern PP(99):1–11
Yu J, Rui Y, Tang Y, Tao D (2014) High-order distance-based multiview stochastic learning in image classification. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(12):2431–2442
Fan J, Kuang Z, Zhang B, Yu J, Lin D (2016) iPrivacy: image privacy protection by identifying sensitive objects via deep multi-task learning. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 12(5):1005–1016
Hong C, Yu J, Wan J, Tao D, Yang M (2015) Multimodal deep autoencoder for human pose recovery. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5659–5670
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their critical and constructive comments and suggestions. This work was partially supported by the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Jinling Institute of Technology (No. JIT-B-201617), the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars under Grant Nos. 61125305, 91420201 and 61472187, the Key Project of Chinese Ministry of Education under Grant No. 313030, the 973 Program No. 2014CB349303, Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities No. 30920140121005, and Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Theoretical Proofs of the SDCR-DAGE Algorithm
Appendix: Theoretical Proofs of the SDCR-DAGE Algorithm
Theorem 1
\(l(D,U,A)\ge f(D,U,A)\) always holds.
Proof
Based on \(M=I+\alpha L_{SD}\) and \(Y=XM^{-1}\), from Eq. (12) it gets that:
In light of triangle inequality,
Therefore, \(l(D,U,A)\ge f(D,U,A)\).\(\square \)
Theorem 2
The term \(I-M^{-1}\) in Eq. (14) is identical to \(\alpha L_{SD}^{\frac{1}{2}}M^{-1}L_{SD}^{\frac{1}{2}}\).
Proof
Let \(L_{SD}^{\frac{1}{2}}=U\Sigma V^{T}\), since \(L_{SD}\) is symmetric and positive definite, then \(U=V\), and \(VV^{T}=V^{T}V=I\), so \(V^{T}=V^{-1}\).
Besides, since \((I+BC)^{-1}=I-B(I+CB)^{-1}C\) and \((AB)^{-1}=B^{-1}A^{-1}\).
Therefore,
\(\square \)
Theorem 3
The monotonous decrease of l(D, U, A) can pull down the value of f(D, A) in Eq. (11).
Proof
In light of Eq. (15), let
Due to the monotonous decrease of l(D, U, A), if we fix U as \(U^{t}\) after the t-th iteration and update \(D^{t+1}\) and \(A^{t+1}\), since \(\parallel A\parallel _{2,1}=\sum _{k=1}^{s}\parallel a^{k}\parallel _{2}\), then: \(l(D^{t+1},U^{t},A^{t+1})\le l(D^{t},U^{t},A^{t} )\), i.e.
Based on
it gets:
Therefore for any iteration t, \(l(D^{t+1},A^{t+1})\le l(D^{t},A^{t})\). Using triangle inequality again, similar to Theorem 1, \(l(D,A)\ge f(D,A)\). Therefore, the monotonous decrease of l(D, U, A) can pull down the value of f(D, A). \(\square \)
Theorem 4
If the SVD decompositions \(X=U\Sigma V^{T}\) and \(MV=B\theta Q^{T}\), then \(YB=U\Sigma Q\theta ^{-1}\).
Proof
Since M is of full rank, therefore \(M^{-1}\) exists. In light of \(V^{T}M^{-1}MV=I\), we get \(V^{T}M^{-1}B\theta Q^{T}=I\), then \(XM^{-1}B=U\Sigma V^{T}M^{-1}B\theta Q^{T}Q\theta ^{-1}=U\Sigma Q\theta ^{-1}\). \(\square \)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, Y., Yang, J. & Gui, W. Robust \(l_{2,1}\) Norm-Based Sparse Dictionary Coding Regularization of Homogenous and Heterogenous Graph Embeddings for Image Classifications. Neural Process Lett 47, 1149–1175 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-017-9691-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-017-9691-6