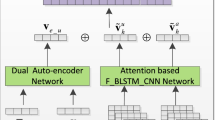
Abstract
Today, as social networks play an increasingly important role, people are more likely to use them to discuss hot topics. Thus, reposting behavior plays a crucial role in such networks for information diffusion. However, the existing models do not consider the impact of some important numerical features on the spread of tweets. In addition, the potential correlation of the user information in different groups and their tweets will also affect the effect of retweet prediction. Considering the above problems, in this article, we propose a novel deep multitask learning-based method, CH-Transformer, for retweet prediction. First, we extract numerical features to represent tweet information features and social features. Then, the numerical features are concatenated with textual features. After feature extraction, we obtain the feature embeddings and feed them into our model to achieve propagation prediction. Finally, we evaluate the proposed method using well-known evaluation measures. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albon C (2019). https://www.kaggle.com/kinguistics/election-day-tweets
Arora U, Paka WS, Chakraborty T (2019) Multitask learning for blackmarket tweet detection. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM international conference on advances in social networks analysis and mining, pp 127–130
Caruana R (1997) Multitask learning. Mach Learn 28(1):41–75
Chen X, Zhang K, Zhou F, Trajcevski G, Zhong T, Zhang F (2019) Information cascades modeling via deep multi-task learning. In: Proceedings of the 42nd international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, pp 885–888
Devlin J, Chang MW, Lee K, Toutanova K (2018) Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv:1810.04805
Fan W, Ma Y, Li Q, He Y, Zhao E, Tang J, Yin D (2019) Graph neural networks for social recommendation. In: The world wide web conference, pp 417–426
Hong C, Yu J, Tao D, Wang M (2014) Image-based 3d human pose recovery by multiview locality-sensitive sparse retrieval. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(6):3742–3751
Hong C, Yu J, Wan J, Tao D, Wang M (2015) Multimodal deep autoencoder for human pose recovery. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5659–5670
Hong C, Yu J, Zhang J, Jin X, Lee KH (2018) Multimodal face-pose estimation with multitask manifold deep learning. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 15(7):3952–3961
Liang D, Shu Y (2017) Deep automated multi-task learning. arXiv:1709.05554
Liu Y, Wu YFB (2020) Fned: a deep network for fake news early detection on social media. ACM Trans Inf Syst (TOIS) 38(3):1–33
Ma R, Hu X, Zhang Q, Huang X, Jiang YG (2019) Hot topic-aware retweet prediction with masked self-attentive model. In: Proceedings of the 42nd international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, pp 525–534
Mikolov T, Chen K, Corrado GS, Dean J (2013) Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv:1301.3781
Molaei S, Zare H, Veisi H (2020) Deep learning approach on information diffusion in heterogeneous networks. Knowl-Based Syst 189:105153
Sadr H, Pedram MM, Teshnehlab M (2019) A robust sentiment analysis method based on sequential combination of convolutional and recursive neural networks. Neural Process Lett 50(3):2745–2761
Sun X, Zhang H, Wang M, Yu M, Yin M, Zhang B (2020) Deep plot-aware generalized matrix factorization for collaborative filtering. Neural Process Lett 52(3):1983–1995
Tang X, Miao Q, Quan Y, Tang J, Deng K (2015) Predicting individual retweet behavior by user similarity: a multi-task learning approach. Knowl-Based Syst 89:681–688
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser L, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. arXiv:1706.03762
Wang X, Jin D, Liu M, He D, Musial K, Dang J (2019) Emotional contagion-based social sentiment mining in social networks by introducing network communities. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM international conference on information and knowledge management, pp 1763–1772
Wang Z, Chen C, Li W (2018) Attention network for information diffusion prediction. Companion Proc Web Conf 2018:65–66
Wang Z, Chen C, Li W (2018b) A sequential neural information diffusion model with structure attention. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM international conference on information and knowledge management, pp 1795–1798
Yu J, Tao D, Wang M, Rui Y (2014) Learning to rank using user clicks and visual features for image retrieval. IEEE Trans Cybern 45(4):767–779
Yu J, Tan M, Zhang H, Tao D, Rui Y (2019) Hierarchical deep click feature prediction for fine-grained image recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 99:1–1
Zhang Q, Gong Y, Wu J, Huang H, Huang X (2016) Retweet prediction with attention-based deep neural network. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM international on conference on information and knowledge management, pp 75–84
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi (2021GY-014) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JB210309, JB210312).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Yang, Y. Tweet Retweet Prediction Based on Deep Multitask Learning. Neural Process Lett 54, 523–536 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10642-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10642-3