Abstract
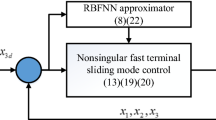
In this article, the issue of adaptive neural fixed-time tracking control for uncertain robotic manipulators subject to input saturation, external disturbance and prescribed constraints is studied. To handle the influence of input saturation, a novel auxiliary nonlinear dynamic system is constructed in which the system state is fixed-time stable. Radial basis function neural networks (RBF NNs) are used to approximate the system uncertainty. Instead of adjusting all weight vectors of RBF NNs, only one parameter is needed to be updated online. Then, based on performance function and auxiliary dynamic system, a fixed-time sliding mode controller with prescribed transient and steady-state performance is developed. Through theoretical analysis, it is concluded that the position tracking error can stabilize around the equilibrium point in fixed time and satisfy the prescribed requirements. Meanwhile, all signals in the closed-loop system are proved to be fixed-time stable by using the Lyapunov method. Finally, simulation results are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu YZ, Wang WX, Liu H, Liu LQ (2020) Reinforcement learning tracking control for robotic manipulator with kernel-based dynamic model. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(9):3570–3578
Ouyang YC, Dong L, Sun CY (2020) Critic learning-based control for robotic manipulators with prescribed constraints. IEEE T Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.3003550
Khan AH, Li S, Luo X (2020) Obstacle avoidance and tracking control of redundant robotic manipulator: an RNN-based metaheuristic approach. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 16(7):4670–4680
Panomruttanarug B (2020) Position control of robotic manipulator using repetitive control basedon inverse frequency response design. Int J Control Autom Syst 18(11):2830–2841
Rocco P (1996) Stability of PID control for industrial robot arms. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 12(4):606–614
Kreutz K (1989) On manipulator control by exact linearization. IEEE Trans Autom Control 34(7):763–767
Nikdel N, Nikdel P, Badamchizadeh MA, Hassanzadeh I (2014) Using neural network model predictive control for controlling shape memory alloy-based manipulator. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(3):1394–1401
Utkin VI (1977) Variable structure systems with sliding modes. IEEE Trans Autom Control 22(2):212–222
Jing CH, Xu HG, Niu XJ (2019) Adaptive sliding mode disturbance rejection control with prescribed performance for robotic manipulators. ISA Trans 91:41–51
Yi SC, Zhai JY (2019) Adaptive second-order fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control for robotic manipulators. ISA Trans 90:41–51
Oliveira J, Oliveira PM, Boaventura-Cunha J, Pinho T (2017) Chaos-based grey wolf optimizer for higher order sliding mode position control of a robotic manipulator. Nonlinear Dyn 90(2):1353–1362
Sun YX, Zheng CH, Mercorelli P (2020) Robust approximate fixed-time tracking control for uncertain robot manipulators. Mech Syst Signal Proc 135:106379
Zadeh SMH, Khorashadizadeh S, Fateh MM, Hadadzarif M (2016) Optimal sliding mode control of a robot manipulator under uncertainty using PSO. Nonlinear Dyn 84(4):2227–2239
Huang HH, Yang CG, Chen CLP (2020) Optimal robot-environment interaction under broad fuzzy neural adaptive control. IEEE T Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.2998984
Zhao D, Li S, Zhu Q, Gao F (2010) Robust finite-time control approach for robotic manipulators. IET Contr Theory Appl 4(1):1–15
Man ZH, Paplinski AP, Wu HR (1994) A robust MIMO terminal sliding mode control scheme for rigid robotic manipulators. IEEE Trans Autom Control 39(12):2464–2469
Feng Y, Yu XH, Man ZH (2002) Non-singular terminal sliding mode control of rigid manipulators. Automatica 38(12):2159–2167
Li J, Du HB, Chen YY, Wen GH, Chen XP, Jiang CH (2019) Position tracking control for permanent magnet linear motor via fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control. Nonlinear Dyn 97(4):2595–2605
Van M, Mavrovouniotis M, Ge SZS (2019) An adaptive backstepping nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control for robust fault tolerant control of robot manipulators. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern - Syst 49(7):1448–1458
Wang LA, Du HB, Zhao WJ, Wu D, Zhu WW (2020) Implementation of integral fixed-time sliding mode controller for speed regulation of PMSM servo system. Nonlinear Dyn 102(1):185–196
Zhang Y, Hua CC, Li K (2019) Disturbance observer-based fixed-time prescribed performance tracking control for robotic manipulator. Int J Syst Sci 50(13):2437–2448
Zhang JQ, Yu SH, Yan Y (2020) Fixed-time velocity-free sliding mode tracking control for marine surface vessels with uncertainties and unknown actuator faults. Ocean Eng 201:107107
Yuan WX, Sun W, Liu ZG, Zhang FX (2019) Adaptive fuzzy tracking control of stochastic mechanical system with input saturation. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(8):2600–2608
Chen ZT, Li ZJ, Chen CLP (2017) Disturbance observer-based fuzzy control of uncertain MIMO mechanical systems with input nonlinearities and its application to robotic exoskeleton. IEEE T Cybern 47(4):984–994
Chen TR, Hill DJ, Wang C (2020) Distributed fast fault diagnosis for multimachine power systems via deterministic learning. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 67(5):4152–4162
Hua CC, Chang YF (2014) Decentralized adaptive neural network control for mechanical systems with dead-zone input. Nonlinear Dyn 76(3):1845–1855
Wu YX, Huang R, Li X, Liu S (2019) Adaptive neural network control of uncertain robotic manipulators with external disturbance and time-varying output constraints. Neurocomputing 323:108–116
He W, Huang B, Dong YT, Li ZJ, Su CY (2018) Adaptive neural network control for robotic manipulators with unknown deadzone. IEEE T Cybern 48(9):2670–2682
Wu YX, Wang Y (2020) Asymptotic tracking control of uncertain nonholonomic wheeled mobile robot with actuator saturation and external disturbances. Neural Comput Appl 32(12):8735–8745
Li HY, Bai L, Zhou Q, Lu RQ, Wang LJ (2017) Adaptive fuzzy control of stochastic nonstrict-feedback nonlinear systems with input saturation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern - Syst 47(8):2185–2197
Si WJ, Dong XD (2019) Adaptive neural control for MIMO stochastic nonlinear pure-feedback systems with input saturation and full-state constraints. Neurocomputing 275:298–307
Liu ZJ, Liu JK, He W (2017) Partial differential equation boundary control of a flexible manipulator with input saturation. Int J Syst Sci 48(1):53–62
Bechlioulis CP, Rovithakis GA (2008) Robust adaptive control of feedback linearizable MIMO nonlinear systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans Autom Control 53(9):2090–2099
Xu G, Xia YQ, Zhai DH, Ma DL (2020) Adaptive prescribed performance terminal sliding mode attitude control for quadrotor under input saturation. IET Contr Theory Appl 14(17):2473–2480
Xu XC, Liu QS, Zhang CL, Zeng ZG (2020) Prescribed performance controller design for DC converter system with constant power loads in DC microgrid. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern - Syst 50(11):4339–4348
Zhou ZP, Zhu FL, Xu DZ, Gao ZF (2020) An interval-estimation-based anti-disturbance sliding mode control strategy for rigid satellite with prescribed performance. ISA Trans 105:63–76
Zhu YK, Qiao JZ, Guo L (2019) Adaptive sliding mode disturbance observer-based composite control with prescribed performance of space manipulators for target capturing. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66(3):1973–1983
Wang M, Yang AL (2017) Dynamic learning from adaptive neural control of robot manipulators with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern - Syst 47(8):2244–2255
He SD, Wang M, Dai SL, Luo F (2019) Leader-follower formation control of USVs with prescribed performance and collision avoidance IEEE Trans Ind. Inform 15(1):572–581
Liu YJ, Zeng Q, Tong SC, Chen CLP, Liu L (2020) Actuator failure compensation-based adaptive control of active suspension systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 67(8):7044–7053
Hu C, Wang ZF, Qin YC, Huang YJ, Wang JX, Wang RR (2020) Lane keeping control of autonomous vehicles with prescribed performance considering the rollover prevention and input saturation. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 21(7):3091–3103
Polyakov A (2012) Nonlinear feedback design for fixed-time stabilization of linear control systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 57(8):2106–2110
Zou ZY (2015) Nonsingular fixed-time consensus tracking for second-order multi-agent networks. Automatica 54:305–309
Ba DS, Li YX, Tong SC (2019) Fixed-time adaptive neural tracking control for a class of uncertain nonstrict nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing 363:273–280
Yang HJ, Ye D (2018) Adaptive fixed-time bipartite tracking consensus control for unknown nonlinear multi-agent systems: An information classification mechanism. Inf Sci 459:238–254
Park J, Sandberg IW (1991) Universal approximation using radial-basis-function networks. Neural Comput 3(2):246–257
Ge SS, Lee TH, Harris CJ (1998) Adaptive neural network control of robotic manipulators. World Scientific, Singapore
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2015B010133002 and 2017B090910011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Fang, H., Xu, T. et al. Adaptive Neural Fixed-time Sliding Mode Control of Uncertain Robotic Manipulators with Input Saturation and Prescribed Constraints. Neural Process Lett 54, 3829–3849 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10788-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10788-8